Battle Of Courtrai (1302)
8,400–10,400
8,000–10,000 militia infantry
400 men-at-arms
8,000–8,500
1,000 pikemen
1,000 crossbowmen
3,500 assorted infantry
2,500–3,000 men-at-arms
and knights
The Battle of the Golden Spurs (Dutch: Guldensporenslag; French: Bataille des éperons d'or) or 1302 Battle of Courtrai was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the 1297–1305 Franco-Flemish War. It took place near the town of Kortrijk in modern-day Belgium and resulted in an unexpected victory for the Flemish.
On 18 May 1302, after two years of French military occupation and several years of unrest, many cities in Flanders revolted against French rule, and the local militia massacred many Frenchmen in the city of Bruges. King Philip IV of France immediately organized an expedition of 8,000 troops, including 2,500 men-at-arms, under Count Robert II of Artois to put down the rebellion. Meanwhile, 9,400 men from the civic militias of several Flemish cities were assembled to counter the expected French attack.
When the two armies met outside the city of Kortrijk on 11 July, the cavalry charges of the mounted French men-at-arms were unable to defeat the mail-armoured and well-trained Flemish militia infantry's pike formation. The result was a rout of the French nobles, who suffered heavy losses at the hands of the Flemish. The 500 pairs of spurs that were captured from the French horsemen gave the battle its popular name. The battle was a famous early example of an all-infantry army defeating an enemy force reliant on heavy cavalry by means of superior numbers, the environment, and by taking advantage of their foes' overconfidence.
While France was victorious in the overall Franco-Flemish War, the Battle of the Golden Spurs became an important cultural reference point for the Flemish Movement during the 19th and 20th centuries. In 1973, the date of the battle was chosen for the official holiday of the Flemish Community in Belgium. A 1985 film called De leeuw van Vlaanderen (The Lion of Flanders) depicts a vision of the battle, and the politics that led up to it.
Background
The origins of the Franco-Flemish War (1297–1305) can be traced back to the accession of Philip IV "the Fair" to the French throne in 1285. Philip hoped to reassert control over the County of Flanders, a semi-independent polity notionally part of the Kingdom of France, and possibly even to annex it into the crown lands of France. In the 1290s, Philip attempted to gain support from the Flemish aristocracy and succeeded in winning the allegiance of some local nobles, including John of Avesnes (Count of Hainaut, Holland and Zeeland). He was opposed by a faction led by the Flemish knight Guy of Dampierre, who attempted to form a marriage alliance with the English against Philip. In Flanders, however, many of the cities were split into factions known as the "Lilies" (Leliaerts), who were pro-French, and the "Lions" (Liebaards), who would later be referred to as the "Claws" (Klauwaerts), led by Pieter de Coninck in Bruges and seeking independence.

In June 1297, the French invaded Flanders and gained some rapid successes. King Edward I of England had been at war against Philip for three years but was obliged to withdraw most of his attention from France to face the First War of Scottish Independence. He entered negotiations with France leading to the 1299 Treaty of Montreuil, while the Flemish and French signed the 1297 Truce of Sint-Baafs-Vijve, a temporary armistice which halted their conflict. When the truce expired in January 1300, Edward had just married Philip's sister Margaret and the French invaded Flanders again. By May, were in total control of the county. Guy of Dampierre was imprisoned and Philip himself toured Flanders while setting up a French-controlled administrative apparatus.
After Philip left Flanders, unrest broke out again in the Flemish city of Bruges in the form of a rebellion against the new French governor, Jacques de Châtillon. On 18 May 1302, rebellious citizens who had fled Bruges returned to the city and murdered every Frenchman they could find, an act known as the "Bruges Matins". With Guy of Dampierre still imprisoned, command of the rebellion fell to his allies John and Guy of Namur. Most of the towns of the County of Flanders agreed to join the Bruges rebellion, except for the city of Ghent which refused to take part. Most of the Flemish nobility also took the French side, fearful of what they perceived as an attempt by the lower classes to seize power.
Forces
To quell the revolt, Philip sent a powerful force led by Count Robert II of Artois to march on Bruges. Against the French, the Flemish under William of Jülich fielded an army of mostly infantry, drawn mainly from Bruges, West Flanders, and the east of the county. The city of Ypres sent a contingent of five hundred men under Jan van Renesse, and despite their city's refusal to join the revolt, Jan Borluut arrived with seven hundred volunteers from Ghent.

The Flemish forces were primarily town militia who were well equipped and trained. The militia fought primarily as infantry, were organized by guild, and were equipped with steel helmets, mail haubergeons, spears, pikes, bows, crossbows and the goedendag, a specifically Flemish weapon made from a thick, five-foot-long (1.5 m) wooden shaft and topped with a steel spike. All Flemish troops at the battle had helmets, neck protection, iron or steel gloves and effective weapons, though not all could afford mail armor. They were a well-organized force of 8,000–10,000 infantry, as well as four hundred noblemen acting as officers, and the urban militias of the time prided themselves on their regular training and preparation. About 900 of the Flemish were trained crossbowmen. The Flemish militia formed a line formation against the French cavalry with goedendags and pikes pointed outward. Because of the high rate of defections among the Flemish nobility, there were few mounted knights on the Flemish side; the Annals of Ghent claimed that there were just ten cavalrymen in the Flemish force.
The French, by contrast, fielded an army built around a core of 2,500 noble cavalry, including knights and squires, arrayed into ten formations of 250 armored horsemen. During the deployment for the battle, they were arranged into three battles, of which the first two were to attack and the third to function as a rearguard and reserve. They were supported by about 5,500 infantry, a mix of crossbowmen, spearmen, and light infantry. The French had about 1,000 crossbowmen, most of whom were from the Kingdom of France and perhaps a few hundred recruited from northern Italy and Spain. Contemporary military theory valued each knight as equal to roughly ten footmen.
Battle
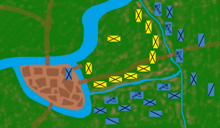



The combined Flemish forces met at Kortrijk on 26 June and laid siege to the local castle, which housed a French garrison. Anticipating a French attempt to break the siege, they prepared to face their enemies in a field battle. The size of the French response was impressive, with 3,000 knights and 4,000–5,000 infantry being an accepted estimate. The Flemish ultimately chose to break off the siege and the two forces clashed on 11 July in an open field next to the Groeninge stream.
The field near Kortrijk was crossed by numerous ditches and streams dug by the Flemish as Philip's army assembled. Some drained from the river Leie (or Lys), while others were concealed with dirt and tree branches, resulting in an uneven terrain that made cavalry charges, the main French battle tactic, less effective by limiting the momentum and maneuverability of horsemen and their mounts. The French assigned scouting parties to cover the marsh with wood planks, but they were driven off before the task was finished. The Flemish placed themselves in a strong defensive position, in deeply stacked lines forming a square. The rear of the square was covered by a curve of the river. The front presented a wedge to the French army and was placed behind larger rivulets.
The 1,000 French crossbowmen began the battle by attacking their 900 Flemish counterparts and succeeded in forcing them back. Eventually, the French crossbow bolts and arrows began to hit the main Flemish infantry formations' front ranks, but inflicted little damage due to the strong defensive lines.
Robert II of Artois expressed concern that his outnumbered infantry would be overwhelmed by the Flemish soldiers positioned on the other side of the brooks. Furthermore, the Flemish would then have their formations blocking the brooks physically and a successful French cavalry crossing would be extremely difficult. He therefore recalled his foot soldiers to clear the way for 2,300 heavy cavalry arranged into two attack formations. The French cavalry unfurled their banners and advanced on the command "Forward!"

Some of the French footmen were trampled to death by the advancing cavalry, but most managed to get around them or through the gaps in their lines. The cavalry advanced rapidly, hoping to give the Flemish no time to react. The brooks presented difficulties for the French horsemen and a few fell from their steeds. Despite this, the crossing was successful in the end. The French then hastily reorganized themselves for a direct assault.
Ready for combat, the French knights and men-at-arms charged at a quick trot and with their lances ready against the main Flemish line. The Flemish crossbowmen and archers fell back behind the pikemen. A great noise rose throughout the dramatic battle scene. The disciplined Flemish foot-soldiers kept their pikes ready on the ground and their goedendags raised to meet the French charge. The Flemish infantry wall did not flinch as expected and a part of the French cavalry hesitated. The bulk of the French formations continued their attack and fell on the Flemish in an ear-splitting crash of horses against men. Unable at most points to break the Flemish line of pikemen, many French knights were quickly knocked from their horses and killed with the goedendag, the spike of which was designed to penetrate the spaces between armour segments. The few that managed to break through ran right into the Flemish reserves; they were swiftly routed and cut down.

Realizing that the attack had failed, Artois ordered his rearguard of 700 men-at-arms to advance. As trumpets blared, he then rode forward with his own knights to lead them. The rearguard failed to obey Artois' orders in full; after the initial advance, they soon turned back to protect their vulnerable baggage train. Without support, the count and his men were unable to break through the Flemish line. As they were surrounded and cut off from their forces, the men-at-arms showed great courage as they fought for their lives. Artois in particular was said to have defended himself skillfully. His horse was struck down by a lay brother, Willem van Saeftinghe, and the count himself was soon felled by multiple wounds. According to some tales, he begged for his life, but the Flemish mocked him by claiming they did not understand French.
The death of Artois, coupled with the collapse of their advance, shattered the resolve of the surviving knights and they were soon driven back into the marshes. There, disorganized, unhorsed, and encumbered by the mud, they were easy targets. A last-ditch effort by the garrison to reinforce their countrymen failed when they were ambushed by Flemish troops waiting to prevent such an attempt. By this point, the only remaining French soldiers were the recalled infantry. Overcome with fear, they abandoned their lines and tried to retreat. The Flemish charged forth and killed many while pursuing the rest over 10 km (6 mi). Unusually for the period, the Flemish infantry took few if any of the French knights prisoner for ransom, in revenge for the French "cruelty".
The Annals of Ghent concludes its description of the battle:
And so, by the disposition of God who orders all things, the art of war, the flower of knighthood, with horses and chargers of the finest, fell before weavers, fullers and the common folk and foot soldiers of Flanders, albeit strong, manly, well armed, courageous and under expert leaders. The beauty and strength of that great [French] army was turned into a dung-pit, and the [glory] of the French made dung and worms.
Aftermath


With the French army defeated, the Flemish consolidated their control over the area. Kortrijk castle surrendered on 13 July and John of Namur entered Ghent on 14 July. The patrician regime in the city and in Ypres, who had supported the French, were overthrown and replaced. Guilds, which had contributed heavily to the Flemish cause, were also officially recognised.
The battle soon became known as the Battle of the Golden Spurs, after the 500 pairs of spurs taken from the bodies of the French dead and presented as a gift to the nearby Church of Our Lady. After the Battle of Roosebeke in 1382, the spurs were taken back by the French and Kortrijk was sacked by Charles VI in retaliation.
According to the Annals, the French lost more than 1,000 men during the battle, including 75 important nobles. These included:
- Robert II, Count of Artois and his half-brother James
- Raoul of Clermont-Nesle, Lord of Nesle, Constable of France
- Guy I of Clermont, Lord of Breteuil, Marshal of France
- Simon de Melun, Lord of La Loupe and Marcheville, Marshal of France
- John I of Ponthieu, Count of Aumale
- John II of Trie, Count of Dammartin
- John II of Brienne, Count of Eu
- John of Avesnes, Count of Ostrevent, son of John II, Count of Holland
- Godfrey of Brabant, Lord of Aarschot and Vierzon, and his son John of Vierzon
- Jacques de Châtillon, Lord of Leuze and former royal governor
- Pierre de Flotte, chief advisor to Philip IV the Fair
- Raoul de Nesle, son of John III, Count of Soissons.
The Flemish victory at Kortrijk in 1302 was quickly reversed by the French. In 1304, the French destroyed the Flemish fleet at the Battle of Zierikzee and won a major victory at the Battle at Mons-en-Pévèle. In June 1305, negotiations between the two sides led to the Peace of Athis-sur-Orge in which the Flemish were forced to pay the French substantial tribute. Robert of Béthune subsequently led a war of resistance to French occupation between 1314 and 1320, but was eventually defeated.
The town of Kortrijk hosts many monuments and a museum dedicated to the battle.
Historical significance
Effect on warfare
The Battle of the Golden Spurs had been seen as the first example of the gradual "Infantry Revolution" in medieval warfare across Europe during the 14th century. Conventional military theory placed emphasis on mounted and heavily armoured knights which were considered essential to military success. Infantry remained, however, an essential arm in parts of Europe, such as the British Isles, throughout the Middle Ages. This meant that warfare was the preserve of a wealthy elite of bellatores (nobles specialized in warfare) serving as men-at-arms. The fact that this form of army, which was expensive to maintain, could be defeated by militia drawn from the "lower orders" led to a gradual change in the nature of warfare during the subsequent century. The tactics and composition of the Flemish army at Courtrai were later copied or adapted at the battles of Bannockburn (1314), Crécy (1346), Aljubarrota (1385), Sempach (1386), Agincourt (1415), Grandson (1476) and in the battles of the Hussite Wars (1419–34). As a result, cavalry became less important and nobles more commonly fought dismounted. The comparatively low costs of militia armies allowed even small states (such as the Swiss) to raise militarily significant armies and meant that local rebellions were more likely to achieve military success.
In Flemish culture and politics
Interest in medieval history in Belgium emerged during the 19th century alongside the rise of Romanticism in art and literature. According to the historian Jo Tollebeek, it soon became connected to nationalist ideals because the Middle Ages were "a period that could be linked with the most important contemporary aspirations" of romantic nationalism.

Amid that resurgence, the Battle of the Golden Spurs became the subject of an "extensive cult" in 19th- and 20th-century Flanders. After Belgian independence in 1830, the Flemish victory was interpreted as a symbol of local pride. The battle was painted in 1836 by a leading Romanticist painter Nicaise de Keyser. Probably inspired by the painting, the Flemish writer Hendrik Conscience used it as the centerpiece of his classic 1838 novel, The Lion of Flanders (De Leeuw van Vlaenderen) which brought the events to a mass audience for the first time. It inspired an engraving by the artist James Ensor in 1895. A large monument and triumphal arch were also subsequently erected on the site of the battle between 1906 and 1908. The battle was evoked by King Albert I at the start of World War I to inspire bravery among Flemish soldiers as an equivalent of the Walloon six hundred Franchimontois of 1468. In 1914, the Belgian victory against German cavalry at the Battle of Halen was dubbed the "Battle of the Silver Helmets" in analogy to the Golden Spurs. Its anniversary, 11 July, became an important annual Flemish observance. In 1973, the date was formalised as the official holiday of the Flemish Community.
As the Battle of the Golden Spurs became an important part of Flemish identity, it became increasingly important within the Flemish Movement. Emerging in the 1860s, it sought autonomy or even independence for Flemish (Dutch)-speaking Flanders and became increasingly radical after World War I. The battle was seen as a "milestone" in a historic struggle for Flemish national liberation and a symbol of resistance to foreign rule. Flemish nationalists wrote poems and songs about the battle and celebrated its leaders. As a result of that linguistic-based nationalism, the contribution of French-speaking soldiers and command of the battle by the Walloon noble Guy of Namur was neglected.
References
- ^ Rogers 1999, p. 137.
- ^ Tucker 2010, p. 294.
- ^ Verbruggen 1997, p. 190.
- ^ Verbruggen 1997, p. 194.
- ^ Rogers 1999, p. 141.
- ^ Verbruggen 2002, p. 193.
- ^ "IMDb entry". IMDb. Archived from the original on 22 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, pp. 186–87.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, pp. 187–89.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, p. 190.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, pp. 190–91.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, pp. 191–92.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, p. 192.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, p. 193.
- ^ Verbruggen 2002, p. 209.
- ^ Verbruggen 2002, p. 194.
- ^ Verbruggen 2002, p. 192.
- ^ Verbruggen 1997, p. 192.
- ^ Verbruggen 1997, p. 193.
- ^ Annals of Ghent, p. 31.
- ^ Annals of Ghent, pp. 30–31.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, p. 194.
- ^ DeVries 2006, p. 26.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, p. 195.
- ^ Nicholas 1992, pp. 196–97.
- ^ "Official site of the museum of the battle". Kortrijk 1302 (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 29 September 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ^ Rogers 1999, pp. 141–43.
- ^ Rogers 1999, pp. 139–42.
- ^ Rogers 1999, pp. 142–44.
- ^ Rogers 1999, p. 142.
- ^ Del Negro 2007, p. 7.
- ^ Rogers 1999, p. 144.
- ^ Tollebeek 2011, p. 117.
- ^ Tollebeek 2011, p. 118.
Sources
- Del Negro, Piero (2007). Guerra ed eserciti da Machiavelli a Napoleone [Warfare and Armies from Machiavelli to Napoleon] (in Italian). Roma-Bari: Laterza. ISBN 978-88-420-6295-0.
- DeVries, Kelly (2006). Infantry Warfare in the Early Fourteenth Century: Discipline, Tactics, and Technology. The Boydell Press.
- Johnstone, Hilda, ed. (1985). Annales Gandenses: Annals of Ghent (Repr. ed.). Oxford: Clarendon. ISBN 978-0-19-822211-8.
- Nicholas, David (1992). Medieval Flanders. London: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-01679-8.
- Rogers, Clifford J. (1999). "The Age of the Hundred Years' War". In Keen, Maurice (ed.). Medieval Warfare: A History (Repr. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 136–60. ISBN 978-0-19-820639-2.
- Tollebeek, Jo (2011). "An Era of Grandeur: The Middle Ages in Belgian National Historiography, 1830–1914". In Evans, R.J.W.; Marchal, Guy P. (eds.). The Uses of the Middle Ages in Modern European States: History, Nationhood and the Search for Origins. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 9781349366026.
- Tucker, Spencer C., ed. (2010). A Global Chronology of Conflict. Vol. 1. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-85-109667-1.
- Verbruggen, J. F. (1997) [1954]. De Krijgskunst in West-Europa in de Middeleeuwen, IXe tot begin XIVe eeuw [The Art of Warfare in Western Europe During the Middle Ages: From the Eighth Century to 1340]. Translated by Willard, S. (2nd ed.). Suffolk: Boydell Press. ISBN 0-85115-630-4.
- Verbruggen, J. F. (2002) [1952]. The Battle of the Golden Spurs: Courtrai, 11 July 1302 (Rev. ed.). Woodbridge: Boydell Press. ISBN 978-0-85115-888-4.
Further reading
- TeBrake, William H. (1993). A Plague of Insurrection: Popular Politics and Peasant Revolt in Flanders, 1323–1328. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-3241-7.
- Nörtemann, Gevert H. (2016). "Memories and identities in conflict: The myth concerning the battle of Courtrai (1302) in nineteenth-century Belgium". In Fenoulhet, Jane; Gilbert, Lesley (eds.). Narratives of Low Countries History and Culture: Reframing the Past. London: UCL Press. pp. 63–72. doi:10.2307/j.ctt1hd18bd.11. ISBN 9781910634981. JSTOR j.ctt1hd18bd.11.
External links
- Liebaart.org Archived 14 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine