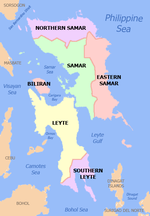
Biliran Province
Biliran lies less than a kilometer north of the island of Leyte. A bridge-causeway fixed link over Poro Island in the gateway town of Biliran connects the province to Leyte. Its capital is the municipality of Naval on the western coast of the island which is the most populous in the province.
Etymology
During the early Spanish era, what is now called Biliran was known as Isla de Panamao. The present name, believed to be adopted sometime between the late 17th century and the early 18th century, was, according to many publications, derived from a native grass called borobiliran which once grew abundantly on the island's plains. A contending theory states that the name came from the word bilir, which was defined in an old Visayan dictionary to be the "corner or edge of a boat, vase or anything protruding, like veins, or the furrow made by the plow." The dictionary also gives biliran as an alternate spelling for bilir. This theory is supported by the fact that Biliran was site of the first large-scale shipyard, built in the 17th century. Galleons were built to support the Galleon trade between Manila and Acapulco in Mexico.
History
Spanish colonial period
The first town, named Biliran, was founded in 1712 after petitioning for a municipality and parish status. During this time, the island was a part of Cebu Province. Biliran, together with the islands of Samar and Leyte, were constituted into a separate province in 1735. Later when Samar and Leyte were split into two provinces in 1768, Biliran became part of Leyte Province as its sub-province. The first parish priest, Gaspar Ignacio de Guevara, was assigned in 1765, but its parish status was apparently withdrawn because of Padre Gaspar's apostasy. The parish was re-established on February 22, 1782.
Moro raids
In May 1735, representative inhabitants of Leyte petitioned Governor-General Fernando Valdes y Tamon to allow them to resettle Biliran Island. They claimed it had been abandoned for the past 50 years and was presently inhabited by bagamundos (vagabonds) due to the frequent Moro raids.
On May 26, 1754, Moros destroyed Biliran and the town of Catbalogan in Samar. Panamao was reportedly razed to the ground and only the gobernadorcillo (mayor) of Biliran town escaped capture by the raiders. The old settlements of Caybiran, Mapuyo and Maripipi were also destroyed by the Moros.
The Moros staged their attack by marching inland along the Anas River for a distance of 1.5-2 leguas (leagues). Having covered part of the interior around a mountain, they managed to capture the inhabitants, with the exception of the gobernadorcillo who escaped. The houses and property of the natives were burned or destroyed. The church building suffered the same fate and its valuables were taken away by the raiders.
Post-Muslim raids
When the Muslim raiders were diminished in the early 19th century, Leytenians organized new towns in the present geography of Biliran Province.
In 1828, Caibiran on the east became an independent municipality and parish, the second to be created on Biliran Island.
Naval became the third town, carved out of the territory of Biliran town. It first became a separate parish in 1860. The Spanish colonial government officially recognized its municipality status on September 23, 1869, following the petition submitted around 1861.
Almeria became a separate town in 1886 and was named after the city of Almería in Spain.
Maripipi used to be a barrio of Naval. It was officially inaugurated as a town in 1867, two years ahead of its mother town, then folded up and was reduced into a barrio of Almeria, and then became a town again in 1899. Maripipi and the new towns of San Clemente (later Kawayan), Culaba and Esperanza (later Cabucgayan) were created around 1899 by the revolutionary government under President Emilio Aguinaldo.
Japanese occupation era
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2016) |
During the World War II, Biliran had its own guerrilla forces under the Leyte command of Colonel Ruperto Kangleon. The guerrilla operation was of invaluable assistance to the successful landing of the American liberation forces at Palo, Leyte, on October 20, 1944, just before the Battle of Leyte Gulf.
In 1945, Biliran was liberated by the Philippine Commonwealth forces of the 9th Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army who landed in Biliran. Aided by the local guerrilla forces, they attacked the Japanese troops on the island during the Battle of Biliran during World War II.
Philippine independence
Provincehood
On April 8, 1959, Republic Act No. 2141 was signed into law effectively making Biliran a sub-province of Leyte. The island became an independent province on May 11, 1992, through Republic Act No. 7160, making it one of the newest provinces in the country.
Geography
 NASA Landsat image of Biliran | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Samar Sea |
| Coordinates | 11°31′23″N 124°32′06″E / 11.523°N 124.535°E |
| Archipelago | Visayas |
| Area | 535 km (207 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,340 m (4400 ft) |
| Administration | |
Philippines | |
Biliran has a total land area of 536.01 square kilometres (206.95 sq mi), making it the fourth smallest province in the Philippines. The island lies off the northern coast of Leyte island across Biliran Strait. To the southeast is Carigara Bay, to the northeast is the Samar Sea, and across this sea is Samar. To the west is the Visayan Sea and Masbate lies 30 kilometres (19 mi) to the northwest. The province is composed of two major volcanic islands: the main island also named Biliran and Maripipi, a smaller island to the northwest. Other smaller islands include Higatangan and Dalutan.
Topography
The main volcanic island of Biliran features mountainous interiors with very narrow coastal areas. Only the municipalities of Naval and Caibiran have wide plains extending about 7 km (4.3 mi) from the coast suitable for agriculture. Mount Suiro, an inactive volcano, is the highest point on Biliran with an elevation of 1,301 m (4,268 ft).
The only known historical volcanic activity at Biliran was a phreatic eruption and possible debris avalanche at a thermal area on September 26, 1939. Ashfalls were reported at Caibiran and adjoining areas with maximum deposits at 6.35 centimetres (2.50 in) thick. There are five active solfatara fields on the island. The solfatara on the west side of Mt. Giron contained more than 400 tones of sulfur in 1880.
Maripipi is a 924-metre (3,031 ft) volcanic island with the Maripipi Volcano located in the center and the Municipality of Maripipi surrounding its shores and lower slopes. The volcano is classified as potentially active but has had no historical eruptions.
Climate
Biliran has a combination of warm and cool climatic zones, thus the prevailing climate is ideal for the cultivation of a wide range of agricultural crops. There is no distinct dry season but the heavy wet season generally occurs in December.
| Climate data for Biliran | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.2 (84.6) |
30.3 (86.5) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.3 (90.1) |
32 (90) |
32.1 (89.8) |
32 (90) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
31.4 (88.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.9 (75.0) |
24 (75) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.1 (77.2) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.9 (76.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 290.5 (11.44) |
241 (9.5) |
192.2 (7.57) |
118.2 (4.65) |
139.2 (5.48) |
189.5 (7.46) |
178.5 (7.03) |
184.4 (7.26) |
155 (6.1) |
215.2 (8.47) |
265.4 (10.45) |
385.5 (15.18) |
2,554.6 (100.59) |
| Average rainy days | 21 | 17 | 16 | 14 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 21 | 202 |
| Source 1: Storm247 (for average temperature and rainy days) | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: WorldWeatherOnline (for average precipitation) | |||||||||||||
Administrative divisions
Biliran is subdivided into 8 municipalities, with a total of 132 barangays. All municipalities are located on Biliran Island, with the exception of Maripipi, which is an island municipality located to the northwest. The largest among the towns in terms of land area is the provincial capital Naval, while the smallest is Maripipi.

| Municipality | Population | ±% p.a. | Area | Density | Barangay | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2020) | (2015) | km | sq mi | /km | /sq mi | |||||||
| 11°37′13″N 124°22′54″E / 11.6202°N 124.3816°E | Almeria | 10.0% | 17,954 | 16,951 | +1.10% | 57.46 | 22.19 | 310 | 800 | 13 | ||
| 11°28′00″N 124°28′31″E / 11.4666°N 124.4752°E | Biliran | 9.8% | 17,662 | 16,882 | +0.86% | 70.30 | 27.14 | 250 | 650 | 11 | ||
| 11°28′22″N 124°34′30″E / 11.4729°N 124.5749°E | Cabucgayan | 12.0% | 21,542 | 20,788 | +0.68% | 54.19 | 20.92 | 400 | 1,000 | 13 | ||
| 11°34′20″N 124°34′53″E / 11.5723°N 124.5813°E | Caibiran | 13.5% | 24,167 | 22,524 | +1.35% | 83.55 | 32.26 | 290 | 750 | 17 | ||
| 11°39′20″N 124°32′26″E / 11.6555°N 124.5406°E | Culaba | 7.2% | 12,972 | 12,325 | +0.98% | 73.42 | 28.35 | 180 | 470 | 17 | ||
| 11°40′48″N 124°21′25″E / 11.6799°N 124.3570°E | Kawayan | 11.4% | 20,455 | 20,291 | +0.15% | 61.02 | 23.56 | 340 | 880 | 20 | ||
| 11°46′43″N 124°20′58″E / 11.7787°N 124.3494°E | Maripipi | 3.6% | 6,373 | 7,159 | −2.19% | 27.83 | 10.75 | 230 | 600 | 15 | ||
| 11°33′46″N 124°23′50″E / 11.5629°N 124.3972°E | Naval | † | 32.5% | 58,187 | 54,692 | +1.19% | 108.24 | 41.79 | 540 | 1,400 | 26 | |
| Total | 179,312 | 171,612 | +0.84% | 536.01 | 206.95 | 330 | 850 | 132 | ||||
| † Provincial capital | Municipality | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 21,661 | — |
| 1918 | 35,751 | +3.40% |
| 1939 | 54,367 | +2.02% |
| 1948 | 67,661 | +2.46% |
| 1960 | 87,285 | +2.14% |
| 1970 | 90,498 | +0.36% |
| 1975 | 103,270 | +2.68% |
| 1980 | 111,421 | +1.53% |
| 1990 | 118,012 | +0.58% |
| 1995 | 132,209 | +2.15% |
| 2000 | 140,274 | +1.28% |
| 2007 | 150,031 | +0.93% |
| 2010 | 161,760 | +2.78% |
| 2015 | 171,612 | +1.13% |
| 2020 | 179,312 | +0.87% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority | ||
The population of Biliran in the 2020 census was 179,312 people, with a density of 330 inhabitants per square kilometre or 850 inhabitants per square mile.
Based on the May 2000 census, the province had a total population of 140,274, which made it the fifth least populous province in the country, and the smallest in the region. There were 27,907 households in the province with an average size of 5.02 persons, slightly higher than the national average of 4.99. 87.05% of the population was Roman Catholic.
Languages
Waray-Waray and Cebuano are the languages spoken by the majority of the people in Biliran Province. The latter is primarily spoken in Naval, Almeria and Kawayan. Whereas Waray-waray is spoken in the towns of Caibiran, Culaba, Cabucgayan, Biliran and Maripipi. Both are Visayan languages.
The majority of the residents also speak and understand English and Filipino.
Economy
Poverty incidence of Biliran
10
20
30
40
2006
29.81 2009
39.18 2012
27.45 2015
21.34 2018
19.62 2021
19.90 Source: Philippine Statistics Authority |
The economy of Biliran is largely based on fishing. Most of its towns, especially Naval and Biliran, have excellent seaports. There are 95 hectares (230 acres) of brackish water fish ponds which produce prawns, shrimps and milkfish. Another 30 hectares (74 acres) of seawater are suitable for seaweed farming and 10 more hectares for fishcage culture.
Being mountainous, Biliran can support various agricultural crops. The warm lowlands are conducive to rice (palay) production and other tropical crops. The cool highlands are favorable to high-value crops such as cut flowers and varieties of upland vegetables.
The inhabitants also engage in hunting, lumber, and manufacturing. The principal raw material produced is copra and coconut oil. Processed goods include white clay ceramics, dried fish, raw gulaman, and citronella oil.
The untapped natural resources of the island include geothermal power and the abundant sulfur and gypsum deposits.
Major industries includes fashion bags, Romblon bags, baskets, shellcrafts, placemats, hot pads, beverage coasters and trays.
Biliran has been eyed as an emerging destination for mountaineers, bikers, canyoneers, hikers, and other adventure seekers. For example, Sampao River in the municipality of Almeria has been developed into a canyoning venue.
Points of interest
- Bagongbong Falls
- It is also called Bagumbong falls, crystal-clear and ice-cold rapids of water coming from the cathedral-like falls nestled in a forested area of Almeria town.
- Ulan-ulan Falls
- Derived from the Visayan dialect which means "rain," the falls' cascading waters form a catch basin with water sufficient for swimming.
- Recoletos Falls
- The waterfall which is approximately 15 meters high, has a wide pool with deep water that is perfect for swimming and cliff jumping. The wide and flat stones surrounding the basin of water is perfect for picnic.
- Kasabangan Falls
- The nice ambience of the waterfall adds to its attraction, and its cold water is refreshing and relaxing. There are 13 layers of this waterfall from its highest level up in the mountain.
- Tingkasan Bat Cave
- The bat cave is a favorite stop for tourists going to Sambawan island. The place is ideal for spelunking, diving and spearfishing.
- Iyusan Rice Terraces
- A manmade agricultural landform and tourist attraction found in Barangay Iyusan, Almeria, Biliran.
See also
References
- ^ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Archived from the original on 19 April 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ "Biliran". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ "Poro Island, Biliran, Eastern Visayas, Philippines". Google Maps. Retrieved on 2013-11-15.
- ^ Borrinaga, Rolando O. "History of Biliran". Biliran Island Undiscovered Paradise. Retrieved on 2013-11-06.
- ^ "History of Biliran". biliranisland.com. 2014-09-04. Retrieved December 21, 2018.
- ^ "Biliran". Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. Retrieved on 2013-11-13.
- ^ "Biliran, Philippines" Archived 2017-04-30 at the Wayback Machine. Volcano World. Retrieved on 2013-11-06.
- ^ "Maripipi". Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. Retrieved on 2013-11-06.
- ^ Local Government Unit: Province of Biliran Archived 2007-11-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Weather forecast for Biliran, Philippines". Storm247. Archived from the original on 11 November 2017. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "Biliran Monthly Climate Average, Philippines". World Weather Online. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "Province: Biliran". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Biliran psa.gov.ph
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- ^ "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 29 November 2005.
- ^ "2009 Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 8 February 2011.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Updated Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population with Measures of Precision, by Region and Province: 2015 and 2018". Philippine Statistics Authority. 4 June 2020.
- ^ "2021 Full Year Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 August 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ "Canyoning in Biliran: Daring to Take the Challenge of the Mighty Sampao River (Part 1)". 2016-03-10.
- ^ "Canyoning in Biliran: Daring to Take the Challenge of the Mighty Sampao River (Part 2)". 2016-03-17.
External links
 Biliran travel guide from Wikivoyage
Biliran travel guide from Wikivoyage Media related to Biliran at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Biliran at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Biliran at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Biliran at OpenStreetMap- Biliran Island
- Provincial Government of Biliran Archived 2009-04-13 at the Wayback Machine