Condorcet (crater)
Condorcet is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, to the southeast of the Mare Crisium. It was named after French mathematician Marquis de Condorcet. To the northeast of Condorcet are the craters Hansen and Alhazen.

Condorcet crater and its satellite craters taken from Earth in 2012 at the University of Hertfordshire's Bayfordbury Observatory with the telescopes Meade LX200 14" and Lumenera Skynyx 2-1 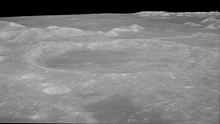
Oblique view from Apollo 11 facing northwest from about 40 km altitude, with Promontorium Agarum at left and Mare Crisium in background 
Apollo 11 view of five satellite craters of Condorcet. The large crater in the foreground is F, N is small and left of center, L is above center, Q is a large eroded crater in upper left, and R is a smaller crater above right of L. 
Satellite crater Condorcet D (photo by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter).
The outer rim of Condorcet is eroded, with a low saddle point along the northern wall and the satellite crater Condorcet Y lies across the northwestern rim. The interior floor has been resurfaced, leaving a level, nearly featureless surface that is marked only by a few tiny craterlets. The floor has a large dark patch in the western half, but the remainder is approximately the same albedo as the surrounding terrain.
Satellite craters

By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Condorcet.



| Condorcet | Coordinates | Diameter, km |
|---|---|---|
| A | 11°31′N 67°17′E / 11.51°N 67.29°E | 15.4 |
| D | 9°50′N 68°21′E / 9.84°N 68.35°E | 19.8 |
| E | 11°21′N 68°10′E / 11.35°N 68.16°E | 8.0 |
| F | 8°16′N 73°05′E / 8.27°N 73.09°E | 39.7 |
| G | 10°39′N 67°58′E / 10.65°N 67.97°E | 10.3 |
| H | 12°27′N 65°05′E / 12.45°N 65.08°E | 21.0 |
| J | 13°04′N 65°12′E / 13.07°N 65.2°E | 16.3 |
| L | 10°09′N 73°40′E / 10.15°N 73.67°E | 12.6 |
| M | 9°04′N 73°07′E / 9.07°N 73.12°E | 10.5 |
| N | 8°59′N 72°37′E / 8.98°N 72.61°E | 5.0 |
| P | 8°46′N 70°17′E / 8.76°N 70.29°E | 48.4 |
| Q | 11°14′N 73°22′E / 11.23°N 73.36°E | 35.8 |
| R | 11°45′N 74°45′E / 11.75°N 74.75°E | 19.9 |
| S | 10°40′N 75°38′E / 10.67°N 75.64°E | 10.2 |
| T | 11°48′N 65°50′E / 11.8°N 65.84°E | 14.7 |
| TA | 12°10′N 65°43′E / 12.16°N 65.72°E | 14.6 |
| U | 10°05′N 75°24′E / 10.08°N 75.4°E | 11.0 |
| W | 13°56′N 67°00′E / 13.94°N 67°E | 35.8 |
| X | 10°07′N 69°57′E / 10.12°N 69.95°E | 8.9 |
| Y | 12°52′N 68°55′E / 12.86°N 68.92°E | 14.2 |
The following craters have been renamed by the IAU.
- Condorcet K — See Wildt (crater).
References
- ^ "Condorcet (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Condorcet (crater).
