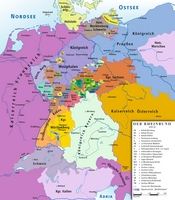
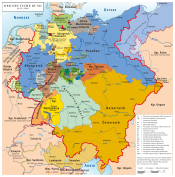
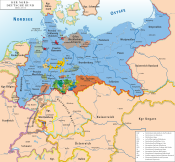
County Of Waldeck
History


The noble family of the Counts of Waldeck and the later Princes of Waldeck and Pyrmont were male line descendants of the Counts of Schwalenberg (based at Schwalenberg Castle), ultimately descendent from Widekind I of Schwalenberg (reigned 1127–1136/7). Waldeck Castle, overlooking the Eder river at Waldeck, was first attested in 1120. A branch of the family was named after the castle in 1180, when Volkwin II of Schwalenberg acquired the castle through his marriage with Luitgard, daughter of Count Poppo I of Reichenbach and Hollende, who was heiress of Waldeck. Over time, the family built up a small lordship in modern day North Hesse.
County of Waldeck
Initially, Waldeck was a fief of the Electorate of Mainz. In 1379, it became the County of Reichslehen. After the death of Count Henry VI in 1397, the family split into two lines: the senior Landau line founded by Adolph III and the junior Waldeck line founded by Henry VII, which sometimes feuded with one another. The two lines came under the sovereignty of the Landgraviate of Hesse in 1431 and 1438 respectively, due to financial difficulties and the final victory of the Landgraviate over Mainz in 1427, which led to the transfer of the County of Ziegenhain to Hesse. The Landgraves levied tribute on the Counts of Waldeck in exchange for forgiving their debts to them and taking on all their debts to others.
After the death of Henry VIII in 1486, the Waldeck line split once more, into the Waldeck-Wildungen and Waldeck-Eisenberg lines. The senior Landau line ended with the death of Otto IV in 1495 and its possessions passed to the Wildungen and Eisenberg lines. In 1526 and 1529, Philip IV of Waldeck-Wildungen and Philip III of Waldeck-Eisenberg converted their respective principalities to Lutheranism. Several partitions led to the creation of further lines, but these were reunited by the new Wildung line in 1692.
In 1626, the family also inherited the County of Pyrmont and thereafter called themselves "Counts of Waldeck and Pyrmont." The two counties of Waldeck and Pyrmont were physically separated and were not united into a single legal entity until the 19th century.
In 1639, Count Philip Dietrich of Waldeck from the new Eisenberg line, inherited the County of Culemborg in Gelderland along with the counties of Werth (Isselburg) in Münsterland, Pallandt, and Wittem. The Lordship of Tonna in Thüringen, a fief of the Dukes of Saxe-Altenburg was inherited by Waldeck-Pyrmont in 1640, but sold to Duke Frederick I of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg in 1677. Waldeck remained the main residence of the county until 1655, when the residence was shifted from Waldeck to Arolsen. Philip Dietrich was succeeded in 1664 by his brother Count George Frederick, whose full title was "Count and Lord of Waldeck, Pyrmont, and Cuylenburg, Lord of Tonna, Paland, Wittem, Werth." In 1682, he was promoted by Emperor Leopold I to the status of "Prince of Waldeck", with Imperial immediacy. His four sons all predeceased him, so on 12 June 1685, he made a contract with his cousin, Christian Louis of the new Wildung line, to transfer the whole Waldeck patrimony to him and for it to be inherited by primogeniture thereafter. This agreement was confirmed by Emperor Leopold in 1697. After George Frederick's death in 1692, Christian Louis became the sole ruler of the entire principality.
The County of Cuylenburg and the Lordship of Werth were lost in 1714, owing to the marriage of George Frederick's second daughter, Sophia Henriette (1662-1702) to Ernest of Saxe-Hildeburghausen.
Principality of Waldeck (1712–1848)
On 6 January 1712, Frederick Anthony Ulrich of Waldeck and Pyrmont was elevated to prince by Emperor Charles VI. During the American War of Independence from 1775 to 1783, Prince Frederick Carl Augustus provided a single battalion sized regiment to the British for the war in America in exchange for payment. A total of 1,225 Waldeck soldiers fought in America.
The principality was caught up in the Napoleonic Wars and in 1807 it joined the Confederation of the Rhine, but not the Napoleonic Kingdom of Westphalia. Waldeck was required to guarantee equal rights of worship to its Catholic citizens and supply 400 soldiers in case of a campaign. For a brief period, from 1806 until 1812, Pyrmont was a separate principality as a result of the partition of the territory between the brothers Frederick and George, but the territories were reunited after Frederick's death.
The independence of the principality was confirmed in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna, and Waldeck and Pyrmont became a member of the German Confederation. In 1832 it joined the Zollverein. In 1847, on Prussian initiative, the sovereignty of Hesse-Kassel over Waldeck (and Schaumburg-Lippe) was finally revoked by the Federal Convention of the Confederation. This had been the case de facto since Waldeck joined the Confederation of the Rhine in 1807, but the ruling meant that Hesse-Kassel lost the right to claim the territory in escheat.
Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont (1849–1918)
Since 1645, Waldeck had been in a personal union with the County (later Principality) of Pyrmont. Beginning in 1813, the prince strove to unite the two territories legally into the Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont. However, political opposition meant that this did not take place until 1849. Even after the unification, Pyrmont retained its own tiny Landtag for budgetary matters until 1863/64. In 1849–1850, Waldeck was divided into three districts: the District of the Eder, the of Eisenberg and the District of the Twiste.


On 1 August 1862, Waldeck-Pyrmont concluded a military convention with Prussia. As a result, Waldeck-Pyrmont fought on the Prussian side in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 and thus avoided annexation at the war's end – unlike the neighbouring Electorate of Hesse. However, the small, cash-strapped principality could not afford to pay its contributions to the new North German Confederation, so the principality's Landtag unanimously voted to reject the North German Constitution in order to pressure the prince into signing an accession treaty Prussia. Bismarck had previously ruled out unification with Prussia on grounds of prestige. Therefore, under the treaty that Waldeck-Pyrmont and Prussia signed in October 1867, the principality remained nominally independent and retained its legislative sovereignty, but from 1 January 1868 Prussian took control of the principality's state deficit, internal administration, judiciary, and schools. Thereafter, Prussia appointed a State Director formally with the agreement of the prince. Appellate jurisdiction for Waldeck was exercised by the Prussian state court (Landgericht) in Kassel and for Pyrmont by the state court in Hannover. The prince retained control over the administration of the church, the prerogative of mercy, and the right of veto over new laws. He also continued to receive the income from his domains. Prussian administration served to reduce administrative costs for the small state and was based on a ten-year contract that was repeatedly renewed for the duration of its existence. The situation continued in 1871, when the principality became a constituent state of the new German Empire. In 1905, Waldeck and Pyrmont had an area of 1121 km and a population of 59,000.
The princely house of Waldeck and Pyrmont is closely related to the royal family of the Netherlands. The last ruling prince, Frederick, was the brother of Queen Consort Emma of the Netherlands.
Free State of Waldeck-Pyrmont (1919–1929)
On 13 November 1918, at the end of World War I, during the German Revolution that resulted in the fall of all the German monarchies, a representative of the revolutionary workers' and soldiers' council of Kassel came to Waldeck and declared that the monarchy was abolished. The principality became the Free State of Waldeck-Pyrmont within the Weimar Republic. However, no new constitution was produced, so the monarchical constitution of 1849/1852 remained in force de jure until 1929. The terms of the treaty with Prussia also remained in force. Following a referendum, Pyrmont was separated from Waldeck on 30 November 1921 and joined Prussia, becoming part of the new Hameln-Pyrmont district of the Province of Hanover. After this, the territory was simply the Free State of Waldeck.
The remaining territory continued to be governed according to the 1867 treaty with Prussia until it was cancelled in 1926. On 9 April 1927, the federal Financial Equalisation act (Finanzausgleichsgesetz) was amended. For Waldeck, this meant that its allocation of federal tax income was reduced by almost 600,000 Reichsmarks. Without a massive rise in local taxes, the Free State was no longer financially viable. Therefore on 1 April 1929, the state was abolished and became part of the Prussian province of Hesse-Nassau. This marked the end of Waldeck's existence as a sovereign state.
Developments since 1929
When Waldeck joined Prussia in 1929, the three districts into which Waldeck had been divided in 1849–1850 (Eder, Eisenberg, and Twiste) were initially retained. Additionally, Höringhausen and Eimelrod, which had been exclaves of Prussia surrounded by Waldeck since 1866, were joined to Eisenberg district. In 1932, the federal government merged Eder and Eisenberg districts. The district of the Twiste was to be merged with the neighbouring district of Wolfhagen on 1 April 1934, but this was delayed after the Nazi seizure of power in 1933. A law of 28 February 1934 reversed the merger of Eder and Eisenberg and definitively cancelled the planned merger of Twiste and Wolfhagen.
On 1 February 1942, the three districts of Waldeck were merged into the new Waldeck district, which had its capital at Korbach. This new district had roughly the same borders as the old Free State. It was made part of Greater Hesse in 1945, which became the state of Hesse in the modern Federal Republic of Germany in 1946. On 1 August 1972, the city of Volkmarsen was separated from the district of Wolfhagen and reassigned to Waldeck. During the reform of the districts of Hesse in 1974, Waldeck was merged with the neighbouring district of Frankeberg to from the new district of Waldeck-Frankenberg, while the city of Züschen became a suburb of Fritzlar in Schwalm-Eder-Kreis.
Military
Waldeck had raised a battalion of infantry in 1681 but for much of the subsequent history leading up to the Napoleonic Wars, Waldeckers generally served as what is commonly described as 'mercenaries', but was actually 'auxiliaries' hired out by the rulers of Waldeck for foreign service. Such was the demand that the single battalion became two in 1740 (the 1st Regiment), three battalions in 1744, four in 1767 (forming a 2nd Regiment). Most notably the foreign service was with the Dutch (the 1st and 2nd Regiments) and British (after an agreement was signed with Great Britain in 1776 to supply troops for the American War of Independence, the 3rd Waldeck Regiment, of a single battalion, was raised). The 3rd Waldeck Regiment thus served in America, where they were known under the 'umbrella term' used during that conflict for all Germans—'Hessians'. The regiment, which was made up of 4 'Battalion companies', a 'Grenadier' company, staff and a detachment of artillery, was captured by French and Spanish troops supporting the Americans and only a small number returned to Germany, where some formed part of a newly raised 5th Battalion (1784).
By the time of Napoleon's conquest of Germany, the Waldeck regiments in Dutch service had been dissolved when, as the Batavian Republic, the country was made into a kingdom ruled by Napoleon's brother Louis. Reduced to battalion strength, they now formed the 3rd battalions of the 1st and 2nd Infantry Regiments of the Kingdom of Holland. The 5th Battalion was disbanded, and Waldeck was now also obliged to provide two companies to the II Battalion, 6th German Confederation (i.e., Confederation of the Rhine) Regiment (along with two companies from Reuß) in the service of the French Empire. As with all French infantry, they were referred to as 'Fusiliers'. They served mainly in the Peninsular War against the Duke of Wellington. In 1812, the 6th Confederation Regiment was re-formed, with three companies from Waldeck and one from Reuß again forming the II Battalion. By the time of the downfall of the French Empire in 1814 the battalions in Dutch service had disappeared, but Waldeck now supplied three Infantry and one Jäger Companies to the newly formed German Confederation.

By 1866, the Waldeck contingent was styled Fürstlisches Waldecksches Füselier-Bataillon, and in the Austro-Prussian War of that year Waldeck (already in a military convention with Prussia from 1862) allied with the Prussians; however the battalion saw no action. Joining the North German Confederation after 1867, under Prussian leadership, the Waldeck Fusilier Battalion became the III (Fusilier) Battalion of the Prussian Infantry Regiment von Wittich (3rd Electoral Hessian) No. 83, and as such it remained until 1918. The position of regimental 'Chef' (an honorary title) was held by the Prince of Waldeck and Pyrmont.
Unlike Hesse-Darmstadt, Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel) retained no distinctions to differentiate them from the Prussian. The Waldeckers however, were permitted the distinction of carrying the Cockade of Waldeck on the Pickelhaube. The Waldeck battalion was garrisoned, at various times, at Arolsen/Mengeringhausen/Helsen, Bad Wildungen, Bad Pyrmont and Warburg.
The regiment saw action in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870 (where it acquired the nickname Das Eiserne Regiment), and during the First World War—as part of the 22nd Division—fought mainly on the Eastern Front.
Gallery of castles
-
Castle Waldeck, Hesse
-
Friedrichstein Castle at Bad Wildungen
Rulers of Waldeck
Partitions of Waldeck under Waldeck rule
| County of Pyrmont (1189–1494) | ||||
| County of Waldeck (1107–1486) |
County of Schwalenberg (1220–1356) |
County of Sternberg (1255–1402) | ||
| County of Landau (1st creation) (1397–1495) |
||||
| Waldeck renamed County of Wildungen (1st creation, Waldeck line) (1486–1598) | ||||
| Inherited by Spiegelberg family (1494-1557); House of Lippe (1557-1583); Gleichen family (1583-1625) | ||||
| County of Landau (2nd creation) (1539–1579) |
||||
| County of Eisenberg (1475–1682) Raised to Principality of Eisenberg (1682–1692) |
County of Wildungen (2nd creation, Eisenberg line) (1607–1692) | |||
| County of Waldeck and Pyrmont (1692–1712) (Wildungen (Eisenberg) line) Raised to Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont (1712–1918) |
County of Bergheim (1706–1918) | |||
Table of rulers
| Ruler | Born | Reign | Ruling part | Consort | Death | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Widekind I | c.1090? Nephew of Bernard, Count of Hardenhausen |
1107 – 11 June 1137 | County of Waldeck (at Schwalenberg until 1127) |
Lutrud of Itter (d. bef. 2 March 1149) five children |
11 June 1137 aged 46-47? |
Brothers and first known ruling members of the family. | |
| Volkwin I | c.1090? Nephew of Bernard, Count of Hardenhausen |
1107–1111 | County of Waldeck (at Schwalenberg) |
Unknown | c.1111 aged c.20-21? | ||
| Regency of Lutrud of Itter (1137-1139) | Children of Widekind, divided their inheritance. | ||||||
| Volkwin II | 1125 First son of Widekind I and Lutrud of Itter |
11 June 1137 – 1178 | County of Waldeck | Luitgard of Reichenbach (d. aft. 1161) 1144 (annulled 1161) five children |
1178 aged 52-53 | ||
| Widekind II | 1148 Second son of Widekind I and Lutrud of Itter |
1178–1189 | County of Pyrmont | Unknown three children |
1189 aged 40-41 | ||
| Widekind III | 1162 First son of Volkwin II and Luitgard of Reichenbach |
1178–1190 | County of Waldeck (at Schwalenberg) |
Unknown three children |
c.1190 aged 27-28 |
Sons of Volkwin II, divided the inheritance, but most of it was quickly reunited with Waldeck. | |
| Herman I | 1163 Second son of Volkwin II and Luitgard of Reichenbach |
1178–1225 | County of Waldeck (at Schwalenberg) |
Unmarried | 1225 aged 61-62 | ||
| Henry I | c.1165 Third son of Volkwin II and Luitgard of Reichenbach |
1178–1214 | County of Waldeck | Heseke of Dassel (d. 25 July 1220) five children |
1214 aged 48-49 | ||
| Schwalenberg annexed to Waldeck | |||||||
| Gottschalk I | c.1170? Son of Widekind II |
1189–1247 | County of Pyrmont | Kunigunde of Limmer (d.1239) six children |
1247 aged 76-77? |
||
| Adolph I | c.1190 First son of Henry I and Heseke of Dassel |
1214 – 3 October 1270 | County of Waldeck | Sophie (d.1254) two children Ethelind of Lippe (1204-1273) 14 February 1254 no children |
3 October 1270 aged 79-80? |
Children of Henry I, divided the land. Adolph associated his eldest son to his rule, but he predeceased him. | |
| Henry III | 1225 Son of Adolph I and Sophie |
c.1250–1267 | Matilda of Cuyk-Arnsberg c.1240? four children |
1267 aged 41-42 | |||
| Volkwin III | c.1190 Second son of Henry I and Heseke of Dassel |
1214–1255 | County of Schwalenberg | Ermengard of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg (d.22 March 1274) 14 February 1254 twelve children |
c.1255 aged 64-65 | ||
| Gottschalk II | c.1220? First son of Gottschalk I and Kunigunde of Limmer |
1247–1262 | County of Pyrmont | Beatrice of Hallermund (d.1272) five children |
1262 aged 41-42 |
Children of Gottschalk I, ruled jointly. | |
| Herman I | c.1220? Second son of Gottschalk I and Kunigunde of Limmer |
1247 – May 1265 | Hedwig (d.20 June 1262) two children |
May 1265 aged 44-45 | |||
| Widekind I | c.1240 First son of Volkwin III and Ermengard of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
1255 – 28 September 1264 | County of Schwalenberg | Unknown c. 1246 Ermengard c. 1250 Unknown c. 1260 two children (in total) |
28 September 1264 aged 23-24 |
Elder children of Volkwin III, divided the land. Widekind didn't have children and his part was inherited by his younger brothers, while Henry I ruled independently at Sternberg and passed it to his own descendants. | |
| Henry I | c.1240 Second son of Volkwin III and Ermengard of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
1255–1279 | County of Sternberg | ? of Woldenberg two children |
1279 aged 38-39 | ||
| Adolph | c.1250? Third son of Volkwin III and Ermengard of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
28 September 1264 – 26 January 1305 | County of Schwalenberg | Adelaide (d.6 July 1274) Jutta (d.1 April 1305) |
26 January 1305 aged 54-55 |
Younger children of Volkwin III, ruled jointly in Schwalenberg. | |
| Albert | c.1250? Fourth son of Volkwin III and Ermengard of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
28 September 1264 – 1317 | Jutta of Rosdorf (d.aft.1 April 1305) 14 February 1254 twelve children |
1317 aged 66-67? | |||
| Herman II | c.1240? First son of Gottschalk II and Beatrice of Hallermund |
May 1265 – 25 November 1328 | County of Pyrmont | Luitgard of Waldeck-Schwalenberg (d.14 September 1317) five children |
25 November 1328 aged 87-88? |
Children of Gottschalk II and Herman I, ruled jointly. Herman III was a son of Herman I, and cousin of the other two rulers, sons of Gottschalk I. | |
| Gottschalk III | c.1240? Second son of Gottschalk II and Beatrice of Hallermund |
May 1265 – 1279 | Unmarried | 1279 aged 38-39? | |||
| Herman III | c.1240? Third son of Gottschalk II and Beatrice of Hallermund |
c.1265 | c.1265 aged 24-25? | ||||
| Adolph II | 1258 First son of Henry III and Matilda of Cuyk-Arnsberg |
3 October 1270 – 1276 | County of Waldeck | Unmarried | 13 December 1302 aged 43-44 |
Abdicated in 1276 to his brother Otto, after a dispute with him and his other brothers on who would marry Sophia of Hesse, daughter of Henry I, Landgrave of Hesse, which Otto won, resulting in Adolph's resignation. Entering in clergy, Adolph eventually became Bishop of Liège (1301-1302). | |
| Otto I | 1262 Third son of Henry III and Matilda of Cuyk-Arnsberg |
1276 – 11 November 1305 | County of Waldeck | Sophia of Hesse 1276 nine children |
11 November 1305 aged 42-43 |
Inherited the county as prize from his brothers after being chosen to marry Sophia of Hesse. | |
| Hoyer I | 1252 Son of Henry I and ? of Woldenberg |
1279 – 28 October 1299 | County of Sternberg | Agnes of Lippe c.1270? five children |
28 October 1299 aged 46-47 |
||
| Henry II | c.1270? Son of Hoyer I and Agnes of Lippe |
28 October 1299 – 8 January 1318 | County of Sternberg | Jutta of Tecklenburg (d.bef. 8 January 1318) five children |
8 January 1318 aged 47-48 |
||
| Henry IV | 1282 Son of Otto I and Sophia of Hesse |
11 November 1305 – 1 May 1348 | County of Waldeck | Adelaide of Cleves (d.1327) 1304 six children |
1 May 1348 aged 65-66 |
||
| Henry II | 1287 Son of Albert and Jutta of Rosdorf |
1317 – 11 April 1349 | County of Schwalenberg | Elisabeth of Wölpe (d. 2 February 1336) nine children Matilda of Rietberg (d.25 April 1400) 1342/45 one child |
11 April 1349 aged 61-62 |
||
| Henry III | c.1290 First son of Henry II and Jutta of Tecklenburg |
8 January 1318 – 1346 | County of Sternberg | Hedwig of Diepholz (d.aft.1335) bef.14 September 1330 four children |
1346 aged 55-56 |
Children of Hoyer II, ruled jointly. | |
| Hoyer II | c.1290 Second son of Henry II and Jutta of Tecklenburg |
8 January 1318 – 1320 | Unmarried | 1320 aged 29-30 | |||
| Gottschalk IV | 1289 First son of Herman II and Luitgard of Waldeck- Schwalenberg |
25 November 1328 – 24 February 1342 | County of Pyrmont | Adelaide of Homburg (d.11 October 1341) six children |
24 February 1342 | Children of Herman II, ruled jointly. | |
| Henry I | c.1290 Second son of Herman II and Luitgard of Waldeck- Schwalenberg |
25 November 1328 – c.1330 | Unmarried | c.1330 | |||
| Herman IV | 1310 Third son of Herman II and Luitgard of Waldeck- Schwalenberg |
25 November 1328 – 1334 | 1334 aged 23-24 | ||||
| Henry II | c.1320? First son of Gottschalk IV and Adelaide of Homburg |
24 February 1342 – 1390 | County of Pyrmont | Unknown three children |
1390 aged 69-70 |
Children of Gottschalk IV, ruled jointly. | |
| Gottschalk V | c.1320? Second son of Gottschalk IV and Adelaide of Homburg |
24 February 1342 – 1355 | Unmarried | 1355 aged 34-35? | |||
| Herman V | c.1320? Third son of Gottschalk IV and Adelaide of Homburg |
24 February 1342 – 1360 | Oda (d.1360) no children/ three children |
1360 aged 39-40? | |||
| Herman VI | c.1320? Fourth son of Gottschalk IV and Adelaide of Homburg |
24 February 1342 – 1377 | Unmarried | 1377 aged 56-57? | |||
| Henry IV | c.1330 Son of Henry III and Hedwig of Diepholz |
1346–1385 | County of Sternberg | Adelaide of Holstein-Pinneberg (c.1330–bef. 21 May 1376) 1348 two children |
1385 aged 54-55? |
||
| Otto II | c.1305 Son of Henry IV and Adelaide of Cleves |
1 May 1348 – 11 November 1369 | County of Waldeck | Matilda of Brunswick-Lüneburg (d.1355) 27 August 1339 two children Margaret of Löwenberg no children |
11 November 1369 aged 63-64 |
||
| Henry III | c.1330 Son of Henry II and Elisabeth of Wölpe |
11 April 1349 – 1356 | County of Schwalenberg | Unmarried | 1369 aged 38-39 |
Sold his estates to Waldeck in 1356, and pursued a religious life. | |
| Schwalenberg reabsorbed in Waldeck | |||||||
| Henry VI of Iron | c.1340 Son of Otto II and Matilda of Brunswick-Lüneburg |
11 November 1369 – 16 February 1397 | County of Waldeck | Elizabeth of Berg 16 December 1363 seven children |
16 February 1397 Waldeck aged 56-57 |
||
| John | c.1350 Son of Henry IV and Adelaide of Holstein-Pinneberg |
1385–1402 | County of Sternberg | Unmarried | 1402 aged 51-52 |
Left no heirs. The county was annexed to Waldeck. | |
| Sternberg annexed to Waldeck | |||||||
| Henry III | c.1360? Son of Henry II |
1390–1429 | County of Pyrmont | Pelek two children Haseke of Spiegelberg (d.22 March 1465) two children |
1429 aged 68-69? |
||
| Adolph III | c.1365 First son of Henry VI and Elizabeth of Berg |
16 February 1397 – 19 April 1431 | County of Landau | Agnes of Ziegenhain (d.aft.26 December 1438) 1387 one child |
19 April 1431 aged 65-66 |
Children of Henry VI, divided the land. | |
| Henry VII | c.1370 Second son of Henry VI and Elizabeth of Berg |
16 February 1397 – 1445 | County of Waldeck | Margaret of Nassau-Wiesbaden-Idstein (1380–aft.1435) 27 August 1398 three children |
c.1445 aged 74-75 | ||
| Henry IV | c.1410? Son of Henry III and Pelek |
1429–1478 | County of Pyrmont | Unmarried | 1478 aged 67-68? |
Children of Henry III, ruled jointly. | |
| Maurice | 1418 Son of Henry III and Haseke of Spiegelberg |
1429–1494 | Margaret of Nassau-Beilstein (d.27 December 1498) 1462 no children |
1494 aged 75-76? | |||
| Inherited by the Spiegelberg family (1494-1557), the House of Lippe (1557-1583) and the Gleichen family (1583-1625) Definitely annexed to Waldeck-Wildungen (from 1625) | |||||||
| Otto III | 1389 Son of Adolph III and Agnes of Ziegenhain |
19 April 1431 – 1459 | County of Landau | Anna of Oldenburg (d.aft.7 April 1438) 1424 three children |
1459 aged 69-70 |
||
| Wolrad I | 1399 Son of Henry VII and Margaret of Nassau-Wiesbaden-Idstein |
c. 1445–1475 | County of Waldeck | Barbara of Wertheim (1420–aft.1443) Bef.9 March 1440 three children |
1475 aged 75-76 |
||
| Otto IV | 1440 Son of Otto III and Anna of Oldenburg |
1459 – 14 October 1495 | County of Landau | Matilda of Neuenahr (d.26 May 1465) 16 January 1464 one child Elisabeth of Tecklenburg (d.aft.1499) 1465 no children |
14 October 1495 Bad Arolsen aged 54-55 |
||
| Landau annexed by Eisenberg | |||||||
| Philip I | 1445 First son of Wolrad I and Barbara of Wertheim |
1475 | County of Waldeck | Joanne of Nassau-Siegen 16 August 1452 or 14 October 1464 one child |
1475 aged 29-30 |
Children of Wolrad I. Philip I died months after his father, and Philip II ruled as regent of his nephew. | |
| Philip II | 
|
3 March 1453 Second son of Wolrad I and Barbara of Wertheim |
1475 – 16 October 1524 | County of Eisenberg | Catherine of Solms-Lich (1458–12 December 1492) 3 November 1478 six children Catherine of Querfurt (1450-22 February 1521) 1497 no children |
16 October 1524 Bielefeld aged 71 | |
| Regency of Philip II, Count of Waldeck-Eisenberg (1475-1486) | |||||||
| Henry VIII | 1465 Son of Philip I and Joanne of Nassau-Siegen |
1475 – 28 May 1513 | County of Waldeck (1475–86) County of Wildungen (1486-1513) |
Anastasia of Runkel (d.24 April 1503) Aft. 8 January 1492 three children |
28 May 1513 aged 47-48 | ||
| Philip IV | 
|
1493 Bad Wildungen Son of Henry VIII and Anastasia of Runkel |
28 May 1513 – 30 November 1574 | County of Wildungen | Margaret of East Frisia 17 February 1523 Emden nine children Catherine of Hatzfeld (d.1546) 1539 no children Jutta of Isenburg-Grenzau 6 October 1554 two children |
30 November 1574 Waldeck aged 80-81 |
Philip associated his eldest surviving son, Samuel, in a co-rulership after his marriage. However, Samuel didn't survive his father. |
| Samuel | 
|
2 May 1528 Waldeck Second son of Philip IV and Margaret of East Frisia |
8 October 1554 – 6 January 1570 | County of Wildungen (at Friedrichstein) |
Anna Maria of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg (7 December 1538 – 11 August 1583) 8 October 1554 Waldeck seven children |
6 January 1570 Friedrichstein aged 46 | |
| Philip III the Elder | 
|
9 December 1486 Waldeck Son of Philip II and Catherine of Solms-Lich |
16 October 1524 – 20 June 1539 | County of Eisenberg | Adelaide of Hoya 20 November 1503 Bad Wildungen four children Anna of Cleves 22 January 1519 Kleve four children |
20 June 1539 Bad Arolsen aged 52 |
|
| Otto V | 1504 First son of Philip III and Adelaide of Hoya |
20 June 1539 – 1539 | County of Eisenberg | Unmarried | 8 March 1541 aged 36-37 |
Children of Philip III, divided the land, by mediation of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse: the elder children kept Waldeck, while the younger ones inherited Landau. For the children who are usually said that did not reign (Otto, Philip and Francis), they are sometimes treated as Waldeck-Eisenberg (for Otto) and Waldeck-Landau (for Philip V and Francis), which are the parts the called reigning brothers actually ruled. This may imply a level of co-regency between each group of brothers. | |
| Wolrad II the Scholar | 
|
27 March 1509 Eilhausen Second son of Philip III and Adelaide of Hoya |
20 June 1539 – 15 April 1575 | Anastasia Günthera of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg (31 March 1526 – 1 April 1570) 6 June 1546 Waldeck thirteen children |
15 April 1575 Eilhausen aged 66 | ||
| Philip V the Dove | 
|
1519 First son of Philip III and Anna of Cleves |
20 June 1539 – c.1544? | County of Landau | Elisabeth von Elsen (d. 12 June 1584) 27 June 1576 Hückeswagen no children |
5 March 1584 Hückeswagen aged 64-65 | |
| John I the Pious | 
|
1521 Second son of Philip III and Anna of Cleves |
20 June 1539 – 9 April 1567 | Anna of Lippe 1 October 1550 Detmold eight children |
9 April 1567 Landau aged 45-46 | ||
| Francis II | 1526 Third son of Philip III and Anna of Cleves |
20 June 1539 – c.1540? | Maria Gogreve (d.1580) 1563 no children |
29 July 1574 aged 47-48 | |||
| Philip VI the Younger | 
|
4 October 1551 First son of John I and Anna of Lippe |
9 April 1567 – 9 November 1579 | County of Landau | Unmarried | 9 November 1579 Darmstadt aged 28 |
Children of John I, ruled jointly. As neither of them left descendants, Landau was reabsorbed in Eisenberg. |
| Francis III | 27 June 1553 Cloppenburg Second son of John I and Anna of Lippe |
9 April 1567 – 12 March 1597 | 12 March 1597 aged 43 | ||||
| Landau was reabsorbed into Eisenberg | |||||||
| Daniel | 1 August 1530 Third son of Philip IV and Margaret of East Frisia |
30 November 1574 – 7 June 1577 | County of Wildungen | Barbara of Hesse 11 November 1568 Kassel no children |
7 June 1577 Waldeck aged 46 |
Left no heirs, and was succeeded by his brother Henry. | |
| Josias I | 18 March 1554 Eisenberg First son of Wolrad II and Anastasia Günthera of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
15 April 1575 – 6 August 1588 | County of Eisenberg | Maria of Barby-Mühlingen 8 March 1582 four children |
6 August 1588 Eisenberg aged 34 |
Children of Wolrad II, ruled jointly. | |
| Wolrad III | 16 June 1563 Waldeck Second son of Wolrad II and Anastasia Günthera of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
15 April 1575 – 12 November 1587 | Unmarried | 12 November 1587 Anneau aged 24 | |||
| Henry IX | 10 December 1531 Fourth son of Philip IV and Margaret of East Frisia |
7 June – 3 October 1577 | County of Wildungen | Anna of Viermund-Nordenbeck 19 December 1563 Korbach no children |
3 October 1577 Werbe aged 45 |
Died shortly after his brother, and didn't have children as well. | |
| Günther | 19 June 1557 Friedrichstein Son of Samuel and Anna Maria of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg |
3 October 1577 – 23 May 1585 | County of Wildungen (at Friedrichstein since 1570) |
Margaret of Waldeck-Landau (1559-20 October 1580) 15 December 1578 Bad Wildungen no children Margaret of Gleichen (28 May 1556 – 14 January 1619) 20 May 1582 Gräfentonna one child |
23 May 1585 Friedrichstein aged 27 |
His second marriage brought the county of Bad Pyrmont back to Waldeck control. | |
| Regency of Margaret of Gleichen (1585-1598) | His death determined the extinction of the main branch of the House of Waldeck. | ||||||
| William Ernest | 
|
8 June 1584 Son of Günther and Margaret of Gleichen |
23 May 1585 – 16 September 1598 | County of Wildungen | Unmarried | 16 September 1598 Tübingen aged 14 | |
| Wildungen briefly annexed to Eisenberg | |||||||
| Christian | 25 December 1585 Eisenberg First son of Josias I and Maria of Barby-Mühlingen |
6 August 1588 – 31 December 1637 | County of Wildungen (in Eisenberg in co-rulership until 1607) |
Elisabeth of Nassau-Siegen 18 November 1604 Bad Wildungen fifteen children |
31 December 1637 Waldeck aged 52 |
Children of Josias I, divided their inheritance in 1607. | |
| Wolrad IV the Pious | 7 June 1588 Eisenberg Second son of Josias I and Maria of Barby-Mühlingen |
6 August 1588 – 6 October 1640 | County of Eisenberg | Anna of Baden-Durlach 8 September 1607 Durlach ten children |
6 October 1640 Bad Arolsen aged 52 | ||
| Philip VII | 
|
25 November 1613 Eisenberg Second son of Christian and Elisabeth of Nassau-Siegen |
31 December 1637 – 24 February 1645 | County of Wildungen | Anna Catharina of Sayn-Wittgenstein 26 October 1634 Frankfurt am Main six children |
24 February 1645 Jankov aged 31 |
Children of Christian, divided their inheritance |
| John II | 7 November 1623 Waldeck Fourth son of Christian and Elisabeth of Nassau-Siegen |
31 December 1637 – 10 October 1668 | County of Landau | Alexandrine Maria of Vehlen-Meggen (d.27 February 1662) 17 December 1644 no children Henriette Dorothea of Hesse-Darmstadt 10 November 1667 Merlau no children |
10 October 1668 Landau aged 44 | ||
| Landau reannexed to Wildungen | |||||||
| Philip Theodore | 
|
2 November 1614 Bad Arolsen Second son of Wolrad IV and Anna of Baden-Durlach |
6 October 1640 – 7 December 1645 | County of Eisenberg | Maria Magdalena of Nassau-Siegen 25 August 1639 Culemborg two children |
7 December 1645 Korbach aged 31 |
|
| Regency of George Frederick, Count of Waldeck-Eisenberg (1645-1659) | Left no heirs, and was succeeded by his uncle and previous regent. | ||||||
| Henry Wolrad | 28 March 1642 Culemborg Son of Wolrad IV and Anna of Baden-Durlach |
7 December 1645 – 15 July 1664 | County of Eisenberg | Juliane Elisabeth of Waldeck-Wildungen 27 January 1660 no children |
15 July 1664 Graz aged 22 | ||
| Regencies of Anna Catherine of Sayn-Wittgenstein (1645-1660) and Henry Wolrad, Count of Waldeck-Eisenberg (1659-1660) | Children of Philip VII, ruled jointly. | ||||||
| Christian Louis | 
|
29 July 1635 Waldeck First son of Philip VII and Anna Catharina of Sayn-Wittgenstein |
24 February 1645 – 12 December 1706 | County of Wildungen (1645–92) County of Waldeck and Pyrmont (1692–1706) |
Anna Elisabeth of Rappoltstein (7 March 1644 – 6 December 1676) 2 July 1658 fifteen children Johanna of Nassau-Idstein (14 September 1657 – 14 March 1733) 6 June 1680 Idstein ten children |
12 December 1706 Bad Arolsen aged 71 | |
| Josias II | 
|
2 July 1636 Bad Wildungen Second son of Philip VII and Anna Catharina of Sayn-Wittgenstein |
24 February 1645 – 8 August 1669 | Wilhelmine Christine of Nassau-Siegen 26 January 1660 Bad Arolsen seven children |
8 August 1669 Heraklion aged 33 | ||
| George Frederick | 
|
31 January 1620 Bad Arolsen Third son of Wolrad IV and Anna of Baden-Durlach |
15 July 1664 – 19 November 1692 | County of Eisenberg (1664–82) Principality of Eisenberg (1682–92) |
Elisabeth Charlotte of Nassau-Siegen 29 November 1643 Culemborg nine children |
19 November 1692 Bad Arolsen aged 72 |
In 1682, he received the title of Prince. Left no surviving male heirs. The principality was inherited by Wildungen, which was kept as a county until a few years later. |
| Eisenberg (except Culemborg) was definitely annexed to Wildungen | |||||||
| Louise Anna | 18 April 1653 Berlin Daughter of George Frederick and Elisabeth Charlotte of Nassau-Siegen |
19 November 1692 – 30 June 1714 | County of Eisenberg (at Culemborg) |
George IV, Count of Erbach-Fürstenau 22 August 1671 Arolsen four children |
30 June 1714 Bad Arolsen aged 61 |
Kept the lordship of Culemborg. As she survived all her children, the lordship was inherited, after her death, by her nephew, Ernest, Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen. | |
| Culemborg was inherited by Saxe-Hildburghausen | |||||||
| Frederick Anton Ulrich | 
|
26 November 1676 Waldeck Son of Christian Louis and Anna Elisabeth of Rappoltstein |
12 December 1706 – 1 January 1728 | County of Waldeck and Pyrmont (1706–12) Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont (1712–28) |
Louise of Palatinate-Birkenfeld 22 October 1700 Hanau eleven children |
1 January 1728 Bad Arolsen aged 51 |
Children of Christian Louis. Frederick Anton was elevated in 1712 to hereditary prince by Emperor Charles VI. On 30 September 1695, their father had changed the primogeniture house law of the Waldeck house, which he had enacted in 1685 and modified in 1687, insofar as he issued a paragium under the established suzerainty of the ruling line of the house, consisting of the three villages of Bergheim, Königshagen and Welle. This paragium, or vassal line, was inherited by Christian Louis' second son, Josias I. |
| Josias I | 
|
20 August 1696 Bad Arolsen Son of Christian Louis and Johanna of Nassau-Idstein |
12 December 1706 – 2 February 1763 | County of Bergheim | Dorothea Sophia of Solms-Rödelheim (27 January 1698 – 6 February 1774) 17 January 1825 seven children |
2 February 1763 Bergheim aged 66 | |
| Christian Philip | 
|
13 October 1701 Edertal First son of Frederick Anton Ulrich and Louise of Palatinate-Birkenfeld |
1 January – 17 May 1728 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Unmarried | 17 May 1728 Mannheim aged 26 |
Survived his father for a few months, and left no descendants. He was succeeded by his brother. |
| Charles August | 
|
24 September 1704 Hanau Second son of Frederick Anton Ulrich and Louise of Palatinate-Birkenfeld |
17 May 1728 – 29 August 1763 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Christiane Henriette of Palatinate-Birkenfeld 19 August 1741 Zweibrücken seven children |
29 August 1763 Bad Arolsen aged 58 |
|
| Frederick Charles August | 
|
25 October 1743 Zweibrücken Second son of Charles August and Christiane Henriette of Palatinate-Birkenfeld |
29 August 1763 – 24 September 1812 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Unmarried | 24 September 1812 Bad Arolsen aged 68 |
Left no heirs and was succeeded by his brother. |
| George | 
|
20 July 1732 Bergheim Second son of Josias I and Dorothea Sophia of Solms-Rödelheim |
2 February 1763 – 9 April 1771 | County of Bergheim | Christine of Isenburg-Meerholz (22 November 1742 – 20 March 1808) 31 August 1766 no children |
9 April 1771 Bergheim aged 38 |
Left no heirs and was succeeded by his brother. |
| Josias II | 
|
16 October 1733 Bergheim Third son of Josias I and Dorothea Sophia of Solms-Rödelheim |
9 April 1771 – 4 January 1788 | County of Bergheim | Christine Wilhelmine of Isenburg-Büdingen (24 June 1756 – 13 November 1826) 5 March 1772 no children |
4 January 1788 Bergheim aged 54 |
|
| Josias III | 
|
13 May 1774 Bergheim First son of Josias II and Christine Wilhelmine of Isenburg-Büdingen |
4 January 1788 – 9 June 1829 | County of Bergheim | Wilhelmine of Löwenstein-Wertheim-Freudenberg (23 April 1774 – 25 June 1817) 10 January 1802 no children |
9 June 1829 Bergheim aged 55 |
Left no heirs and was succeeded by his brother. |
| George I | 
|
6 May 1747 Bad Arolsen Third son of Charles August and Christiane Henriette of Palatinate-Birkenfeld |
24 September 1812 – 9 September 1813 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Augusta of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen 12 September 1784 Otterwisch three children |
9 September 1813 Rhoden aged 66 |
|
| George II | 
|
20 September 1789 Weil am Rhein Son of George I and Augusta of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen |
9 September 1813 – 15 May 1845 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Emma of Anhalt-Bernburg-Schaumburg-Hoym 26 June 1823 Schaumburg five children |
15 May 1845 Bad Arolsen aged 55 |
|
| Charles | 
|
17 November 1778 Bergheim Fourth son of Josias II and Christine Wilhelmine of Isenburg-Büdingen |
9 June 1829 – 21 January 1849 | County of Bergheim | Karoline Schilling von Canstatt (2 February 1798 – 7 October 1866) 25 April 1819 six children |
21 January 1849 Bergheim aged 70 |
|
| Regency of Emma of Anhalt-Bernburg-Schaumburg-Hoym (1845-1858) | |||||||
| George Victor | 
|
14 January 1831 Bad Arolsen Son of George II and Emma of Anhalt-Bernburg-Schaumburg-Hoym |
15 May 1845 – 12 May 1893 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Helena of Nassau 26 September 1853 Wiesbaden seven children Louise of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg 29 April 1891 Luisenlund one child |
12 May 1893 Mariánské Lázně aged 62 | |
| Adalbert I | 19 February 1833 Bergheim Son of Charles and Karoline Schilling von Canstatt |
21 January 1849 – 24 July 1893 | County of Bergheim | Agnes Caroline of Sayn-Hohenstein (18 April 1834 – 18 February 1886) 3 August 1858 seven children Ida Charlotte of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Hohenstein (25 February 1837 – 7 May 1922) 18 October 1887 no children |
24 July 1893 Bergheim aged 60 |
||
| Frederick | 
|
20 January 1865 Bad Arolsen Son of George Victor and Helena of Nassau |
12 May 1893 – 13 November 1918 | Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont | Bathildis of Schaumburg-Lippe 9 August 1895 Náchod four children |
26 May 1946 Bad Arolsen aged 81 |
Brother of Queen Emma of the Netherlands. Abolition of the monarchy in 1918. |
| Adalbert II | 6 January 1863 Bergheim Son of Adalbert I and Agnes Caroline of Sayn-Hohenstein |
24 July 1893 – 13 November 1918 | County of Bergheim | Unmarried | 23 February 1934 Bergheim aged 71 |
Abolition of the monarchy in 1918. | |
See also
References
- ^ A Pictorial Geography of the World: Comprising a System of Universal Geography, Popular and Scientific. Boston: C.D. Strong. 1848. p. 762.
- ^ Johann Adolph Theodor Ludwig Varnhagen: Grundlagen der Waldeckischen Regentengeschichte, vol. 1. Göttingen 1824, No. 88.
- ^ Thomas Brückner, Lehnsauftragung. Inaugural-Dissertation. Juristische Fakultät der Bayerischen Julius-Maximilians-Universität, Würzburg 2002, p. 68.
- ^ Akzessionsvertrag Waldecks zum Rheinbund, 18. April 1807
- ^ Stenographische Berichte über die Verhandlungen des Preußischen Hauses der Abgeordneten: 1877/78, Vol. 2, Part 123, p. 1025
- ^ Frank-Lothar Kroll, Geschichte Hessens. C. H. Beck, München 2006, ISBN 3-406-53606-9, p. 77.
- ^ Staatsvertrag zwischen Preußen und Waldeck-Pyrmont über die Vereinigung des Gebietsteils Pyrmont mit Preußen of 29 November 1921 (Preuß. GS 1922, p. 37, Waldeckisches Regierungsblatt. 1922, p. 55, Sammlung des bereinigten niedersächsischen Rechts, Vol. II, p. 7).
- ^ Numbered III because, despite being the second ruler named Henry, traditional genealogies numbered another Henry, son of Count Henry I, and a canon at Paderborn (1211-1288) as Henry II. This Henry II never ruled.
- ^ Actually the third ruler named Henry.
- ^ This numbering takes in account Henry I, Count of Sternberg as Henry I of Schwalenberg
- ^ Numbered VI because, despite being the fourth ruler named Henry, traditional genealogies numbered another Henry, son of Count Henry IV, and a dean at Minden (d.1349) as Henry V. This Henry V never ruled.
- ^ Despite never missing any number from this point on, the numbering of the Henrys is irredeemably compromised (because of Henry II and Henry V, who never ruled). So, despite the total counting of 9 Henrys, only 7 actually ruled. Henry VII was the fifth ruler named Henry.
- ^ Henry VIII was the sixth ruler named Henry.
- ^ Despite succeeding first, he was numbered IV, probably because he was born after the then-still-heir Philip III of Eisenberg
- ^ Otto joined the Order of St. John in 1539, and abdicated in the same year of his father's death, which seems to imply that he reigned in that year. See Haarmann (2014), p. 21.
- ^ Philip V, like Otto, may have reigned, even if for only a few months, in Landau, together with his brother John I. Also, at the time of the division, Philip was not exercising any clerical position (was canon at Mainz in 1530, and then reappears as canon in Cologne in 1544), which would possibly extend a co-rulership that ended with Philip resuming his religious life at Cologne. See Haarmann (2014), p. 21; and Blankertz, Wilhelm, Schloß Hückeswagen Sonderdruck einer Artikelserie des „Bergischer Volksbote" (Burscheider Zeitung) July 1940, PDF, retrieved 14 December 2014.
- ^ Counted II because Francis I was a son of Count Philip II, and counted as I, despite never ruling, and that was bishop of Münster and Osnabrück (r.1532-1553).
- ^ He was taken by Anne of Cleves to England in 1540. Given that he is documented starting his religious career only in 1549, nothing seems to oppose a brief co-rulership of Francis in 1539–40, before his trip to England.
- ^ In fact he was the second Francis ruling.
- ^ Henry IX was the seventh and final ruler named Henry.
External links
 Media related to Waldeck (state) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Waldeck (state) at Wikimedia Commons- Principality of Waldeck (in German)
- Canon law of the regnancy Waldeck, 1556
- Decorations of the Principality of Waldeck
- National anthem and flags