Euler's Number
The number e is of great importance in mathematics, alongside 0, 1, π, and i. All five appear in one formulation of Euler's identity and play important and recurring roles across mathematics. Like the constant π, e is irrational, meaning that it cannot be represented as a ratio of integers, and moreover it is transcendental, meaning that it is not a root of any non-zero polynomial with rational coefficients. To 30 decimal places, the value of e is:
Definitions
The number e is the limit an expression that arises in the computation of compound interest.
It is the sum of the infinite series
It is the unique positive number a such that the graph of the function y = a has a slope of 1 at x = 0.
One has where is the (natural) exponential function, the unique function that equals its own derivative and satisfies the equation Since the exponential function is commonly denoted as one has also
The logarithm of base b can be defined as the inverse function of the function Since one has The equation implies therefore that e is the base of the natural logarithm.
The number e can also be characterized in terms of an integral:
For other characterizations, see § Representations.
History
The first references to the constant were published in 1618 in the table of an appendix of a work on logarithms by John Napier. However, this did not contain the constant itself, but simply a list of logarithms to the base . It is assumed that the table was written by William Oughtred. In 1661, Christiaan Huygens studied how to compute logarithms by geometrical methods and calculated a quantity that, in retrospect, is the base-10 logarithm of e, but he did not recognize e itself as a quantity of interest.
The constant itself was introduced by Jacob Bernoulli in 1683, for solving the problem of continuous compounding of interest. In his solution, the constant e occurs as the limit where n represents the number of intervals in a year on which the compound interest is evaluated (for example, for monthly compounding).
The first symbol used for this constant was the letter b by Gottfried Leibniz in letters to Christiaan Huygens in 1690 and 1691.
Leonhard Euler started to use the letter e for the constant in 1727 or 1728, in an unpublished paper on explosive forces in cannons, and in a letter to Christian Goldbach on 25 November 1731. The first appearance of e in a printed publication was in Euler's Mechanica (1736). It is unknown why Euler chose the letter e. Although some researchers used the letter c in the subsequent years, the letter e was more common and eventually became standard.
Euler proved that e is the sum of the infinite series where n! is the factorial of n. The equivalence of the two characterizations using the limit and the infinite series can be proved via the binomial theorem.
Applications
Compound interest

Jacob Bernoulli discovered this constant in 1683, while studying a question about compound interest:
An account starts with $1.00 and pays 100 percent interest per year. If the interest is credited once, at the end of the year, the value of the account at year-end will be $2.00. What happens if the interest is computed and credited more frequently during the year?
If the interest is credited twice in the year, the interest rate for each 6 months will be 50%, so the initial $1 is multiplied by 1.5 twice, yielding $1.00 × 1.5 = $2.25 at the end of the year. Compounding quarterly yields $1.00 × 1.25 = $2.44140625, and compounding monthly yields $1.00 × (1 + 1/12) = $2.613035.... If there are n compounding intervals, the interest for each interval will be 100%/n and the value at the end of the year will be $1.00 × (1 + 1/n).
Bernoulli noticed that this sequence approaches a limit (the force of interest) with larger n and, thus, smaller compounding intervals. Compounding weekly (n = 52) yields $2.692596..., while compounding daily (n = 365) yields $2.714567... (approximately two cents more). The limit as n grows large is the number that came to be known as e. That is, with continuous compounding, the account value will reach $2.718281828... More generally, an account that starts at $1 and offers an annual interest rate of R will, after t years, yield e dollars with continuous compounding. Here, R is the decimal equivalent of the rate of interest expressed as a percentage, so for 5% interest, R = 5/100 = 0.05.
Bernoulli trials

The number e itself also has applications in probability theory, in a way that is not obviously related to exponential growth. Suppose that a gambler plays a slot machine that pays out with a probability of one in n and plays it n times. As n increases, the probability that gambler will lose all n bets approaches 1/e. For n = 20, this is already approximately 1/2.789509....
This is an example of a Bernoulli trial process. Each time the gambler plays the slots, there is a one in n chance of winning. Playing n times is modeled by the binomial distribution, which is closely related to the binomial theorem and Pascal's triangle. The probability of winning k times out of n trials is:
In particular, the probability of winning zero times (k = 0) is
The limit of the above expression, as n tends to infinity, is precisely 1/e.
Exponential growth and decay
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time at an ever-increasing rate. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast to other types of growth, such as quadratic growth). If the constant of proportionality is negative, then the quantity decreases over time, and is said to be undergoing exponential decay instead. The law of exponential growth can be written in different but mathematically equivalent forms, by using a different base, for which the number e is a common and convenient choice: Here, denotes the initial value of the quantity x, k is the growth constant, and is the time it takes the quantity to grow by a factor of e.
Standard normal distribution
The normal distribution with zero mean and unit standard deviation is known as the standard normal distribution, given by the probability density function
The constraint of unit standard deviation (and thus also unit variance) results in the 1/2 in the exponent, and the constraint of unit total area under the curve results in the factor . This function is symmetric around x = 0, where it attains its maximum value , and has inflection points at x = ±1.
Derangements
Another application of e, also discovered in part by Jacob Bernoulli along with Pierre Remond de Montmort, is in the problem of derangements, also known as the hat check problem: n guests are invited to a party and, at the door, the guests all check their hats with the butler, who in turn places the hats into n boxes, each labelled with the name of one guest. But the butler has not asked the identities of the guests, and so puts the hats into boxes selected at random. The problem of de Montmort is to find the probability that none of the hats gets put into the right box. This probability, denoted by , is:
As n tends to infinity, pn approaches 1/e. Furthermore, the number of ways the hats can be placed into the boxes so that none of the hats are in the right box is n!/e, rounded to the nearest integer, for every positive n.
Optimal planning problems
The maximum value of occurs at . Equivalently, for any value of the base b > 1, it is the case that the maximum value of occurs at (Steiner's problem, discussed below).
This is useful in the problem of a stick of length L that is broken into n equal parts. The value of n that maximizes the product of the lengths is then either
- or
The quantity is also a measure of information gleaned from an event occurring with probability (approximately when ), so that essentially the same optimal division appears in optimal planning problems like the secretary problem.
Asymptotics
The number e occurs naturally in connection with many problems involving asymptotics. An example is Stirling's formula for the asymptotics of the factorial function, in which both the numbers e and π appear:
As a consequence,
Properties
Calculus
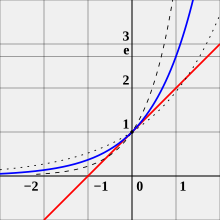

The principal motivation for introducing the number e, particularly in calculus, is to perform differential and integral calculus with exponential functions and logarithms. A general exponential function y = a has a derivative, given by a limit:
The parenthesized limit on the right is independent of the variable x. Its value turns out to be the logarithm of a to base e. Thus, when the value of a is set to e, this limit is equal to 1, and so one arrives at the following simple identity:
Consequently, the exponential function with base e is particularly suited to doing calculus. Choosing e (as opposed to some other number) as the base of the exponential function makes calculations involving the derivatives much simpler.
Another motivation comes from considering the derivative of the base-a logarithm (i.e., loga x), for x > 0:
where the substitution u = h/x was made. The base-a logarithm of e is 1, if a equals e. So symbolically,
The logarithm with this special base is called the natural logarithm, and is usually denoted as ln; it behaves well under differentiation since there is no undetermined limit to carry through the calculations.
Thus, there are two ways of selecting such special numbers a. One way is to set the derivative of the exponential function a equal to a, and solve for a. The other way is to set the derivative of the base a logarithm to 1/x and solve for a. In each case, one arrives at a convenient choice of base for doing calculus. It turns out that these two solutions for a are actually the same: the number e.

The Taylor series for the exponential function can be deduced from the facts that the exponential function is its own derivative and that it equals 1 when evaluated at 0: Setting recovers the definition of e as the sum of an infinite series.
The natural logarithm function can be defined as the integral from 1 to of , and the exponential function can then be defined as the inverse function of the natural logarithm. The number e is the value of the exponential function evaluated at , or equivalently, the number whose natural logarithm is 1. It follows that e is the unique positive real number such that
Because e is the unique function (up to multiplication by a constant K) that is equal to its own derivative,
it is therefore its own antiderivative as well:
Equivalently, the family of functions
where K is any real or complex number, is the full solution to the differential equation
Inequalities

The number e is the unique real number such that for all positive x.
Also, we have the inequality for all real x, with equality if and only if x = 0. Furthermore, e is the unique base of the exponential for which the inequality a ≥ x + 1 holds for all x. This is a limiting case of Bernoulli's inequality.
Exponential-like functions

Steiner's problem asks to find the global maximum for the function
This maximum occurs precisely at x = e. (One can check that the derivative of ln f(x) is zero only for this value of x.)
Similarly, x = 1/e is where the global minimum occurs for the function
The infinite tetration
- or
converges if and only if x ∈ [(1/e), e] ≈ [0.06599, 1.4447] , shown by a theorem of Leonhard Euler.
Number theory
The real number e is irrational. Euler proved this by showing that its simple continued fraction expansion does not terminate. (See also Fourier's proof that e is irrational.)
Furthermore, by the Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem, e is transcendental, meaning that it is not a solution of any non-zero polynomial equation with rational coefficients. It was the first number to be proved transcendental without having been specifically constructed for this purpose (compare with Liouville number); the proof was given by Charles Hermite in 1873. The number e is one of only a few transcendental numbers for which the exact irrationality exponent is known (given by ).
An unsolved problem thus far is the question of whether or not the numbers e and π are algebraically independent. This would be resolved by Schanuel's conjecture – a currently unproven generalization of the Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem.
It is conjectured that e is normal, meaning that when e is expressed in any base the possible digits in that base are uniformly distributed (occur with equal probability in any sequence of given length).
In algebraic geometry, a period is a number that can be expressed as an integral of an algebraic function over an algebraic domain. The constant π is a period, but it is conjectured that e is not.
Complex numbers
The exponential function e may be written as a Taylor series
Because this series is convergent for every complex value of x, it is commonly used to extend the definition of e to the complex numbers. This, with the Taylor series for sin and cos x, allows one to derive Euler's formula:
which holds for every complex x. The special case with x = π is Euler's identity:
which is considered to be an exemplar of mathematical beauty as it shows a profound connection between the most fundamental numbers in mathematics. In addition, it is directly used in a proof that π is transcendental, which implies the impossibility of squaring the circle. Moreover, the identity implies that, in the principal branch of the logarithm,
Furthermore, using the laws for exponentiation,
for any integer n, which is de Moivre's formula.
The expressions of cos x and sin x in terms of the exponential function can be deduced from the Taylor series:
The expression is sometimes abbreviated as cis(x).
Representations
The number e can be represented in a variety of ways: as an infinite series, an infinite product, a continued fraction, or a limit of a sequence. In addition to the limit and the series given above, there is also the simple continued fraction
which written out looks like
The following infinite product evaluates to e:
Many other series, sequence, continued fraction, and infinite product representations of e have been proved.
Stochastic representations
In addition to exact analytical expressions for representation of e, there are stochastic techniques for estimating e. One such approach begins with an infinite sequence of independent random variables X1, X2..., drawn from the uniform distribution on [0, 1]. Let V be the least number n such that the sum of the first n observations exceeds 1:
Then the expected value of V is e: E(V) = e.
Known digits
The number of known digits of e has increased substantially since the introduction of the computer, due both to increasing performance of computers and to algorithmic improvements.
| Date | Decimal digits | Computation performed by |
|---|---|---|
| 1690 | 1 | Jacob Bernoulli |
| 1714 | 13 | Roger Cotes |
| 1748 | 23 | Leonhard Euler |
| 1853 | 137 | William Shanks |
| 1871 | 205 | William Shanks |
| 1884 | 346 | J. Marcus Boorman |
| 1949 | 2,010 | John von Neumann (on the ENIAC) |
| 1961 | 100,265 | Daniel Shanks and John Wrench |
| 1978 | 116,000 | Steve Wozniak on the Apple II |
Since around 2010, the proliferation of modern high-speed desktop computers has made it feasible for amateurs to compute trillions of digits of e within acceptable amounts of time. On Dec 5, 2020, a record-setting calculation was made, giving e to 31,415,926,535,897 (approximately π×10) digits.
Computing the digits
One way to compute the digits of e is with the series
A faster method involves two recursive functions and . The functions are defined as
The expression produces the nth partial sum of the series above. This method uses binary splitting to compute e with fewer single-digit arithmetic operations and thus reduced bit complexity. Combining this with fast Fourier transform-based methods of multiplying integers makes computing the digits very fast.
In computer culture
During the emergence of internet culture, individuals and organizations sometimes paid homage to the number e.
In an early example, the computer scientist Donald Knuth let the version numbers of his program Metafont approach e. The versions are 2, 2.7, 2.71, 2.718, and so forth.
In another instance, the IPO filing for Google in 2004, rather than a typical round-number amount of money, the company announced its intention to raise 2,718,281,828 USD, which is e billion dollars rounded to the nearest dollar.
Google was also responsible for a billboard that appeared in the heart of Silicon Valley, and later in Cambridge, Massachusetts; Seattle, Washington; and Austin, Texas. It read "{first 10-digit prime found in consecutive digits of e}.com". The first 10-digit prime in e is 7427466391, which starts at the 99th digit. Solving this problem and visiting the advertised (now defunct) website led to an even more difficult problem to solve, which consisted in finding the fifth term in the sequence 7182818284, 8182845904, 8747135266, 7427466391. It turned out that the sequence consisted of 10-digit numbers found in consecutive digits of e whose digits summed to 49. The fifth term in the sequence is 5966290435, which starts at the 127th digit. Solving this second problem finally led to a Google Labs webpage where the visitor was invited to submit a résumé.
The last release of the official Python 2 interpreter has version number 2.7.18, a reference to e.
References
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A001113 (Decimal expansion of e)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Miller, Jeff. "Earliest Uses of Symbols for Constants". MacTutor. University of St. Andrews, Scotland. Retrieved 31 October 2023.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "e". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-08-10.
- ^ Pickover, Clifford A. (2009). The Math Book: From Pythagoras to the 57th Dimension, 250 Milestones in the History of Mathematics (illustrated ed.). Sterling Publishing Company. p. 166. ISBN 978-1-4027-5796-9. Extract of page 166
- ^ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (September 2001). "The number e". MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. University of St Andrews.
- ^ Sawyer, W. W. (1961). Mathematician's Delight. Penguin. p. 155.
- ^ Wilson, Robinn (2018). Euler's Pioneering Equation: The most beautiful theorem in mathematics (illustrated ed.). Oxford University Press. p. (preface). ISBN 978-0-19-251405-9.
- ^ Posamentier, Alfred S.; Lehmann, Ingmar (2004). Pi: A Biography of the World's Most Mysterious Number (illustrated ed.). Prometheus Books. p. 68. ISBN 978-1-59102-200-8.
- ^ Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W., eds. (2010), "E (mathematical constant)", NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5, MR 2723248.
- ^ Bruins, E. M. (1983). "The Computation of Logarithms by Huygens" (PDF). Constructive Function Theory: 254–257.
- ^ Jacob Bernoulli considered the problem of continuous compounding of interest, which led to a series expression for e. See: Jacob Bernoulli (1690) "Quæstiones nonnullæ de usuris, cum solutione problematis de sorte alearum, propositi in Ephem. Gall. A. 1685" (Some questions about interest, with a solution of a problem about games of chance, proposed in the Journal des Savants (Ephemerides Eruditorum Gallicanæ), in the year (anno) 1685.**), Acta eruditorum, pp. 219–23. On page 222, Bernoulli poses the question: "Alterius naturæ hoc Problema est: Quæritur, si creditor aliquis pecuniæ summam fænori exponat, ea lege, ut singulis momentis pars proportionalis usuræ annuæ sorti annumeretur; quantum ipsi finito anno debeatur?" (This is a problem of another kind: The question is, if some lender were to invest [a] sum of money [at] interest, let it accumulate, so that [at] every moment [it] were to receive [a] proportional part of [its] annual interest; how much would be owing [at the] end of [the] year?) Bernoulli constructs a power series to calculate the answer, and then writes: " … quæ nostra serie [mathematical expression for a geometric series] &c. major est. … si a = b, debebitur plu quam 2½a & minus quam 3a." ( … which our series [a geometric series] is larger [than]. … if a=b, [the lender] will be owed more than 2½a and less than 3a.) If a = b, the geometric series reduces to the series for a × e, so 2.5 < e < 3. (** The reference is to a problem which Jacob Bernoulli posed and which appears in the Journal des Sçavans of 1685 at the bottom of page 314.)
- ^ Carl Boyer; Uta Merzbach (1991). A History of Mathematics (2nd ed.). Wiley. p. 419. ISBN 978-0-471-54397-8.
- ^ Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm (2003). "Sämliche Schriften Und Briefe" (PDF) (in German).
look for example letter nr. 6
- ^ Euler, Meditatio in experimenta explosione tormentorum nuper instituta. Scribatur pro numero cujus logarithmus est unitas, e, qui est 2,7182817… (English: Written for the number of which the logarithm has the unit, e, that is 2,7182817...")
- ^ Lettre XV. Euler à Goldbach, dated November 25, 1731 in: P.H. Fuss, ed., Correspondance Mathématique et Physique de Quelques Célèbres Géomètres du XVIIIeme Siècle … (Mathematical and physical correspondence of some famous geometers of the 18th century), vol. 1, (St. Petersburg, Russia: 1843), pp. 56–60, see especially p. 58. From p. 58: " … ( e denotat hic numerum, cujus logarithmus hyperbolicus est = 1), … " ( … (e denotes that number whose hyperbolic [i.e., natural] logarithm is equal to 1) … )
- ^ Remmert, Reinhold (1991). Theory of Complex Functions. Springer-Verlag. p. 136. ISBN 978-0-387-97195-7.
- ^ Leonhard Euler, Mechanica, sive Motus scientia analytice exposita (St. Petersburg (Petropoli), Russia: Academy of Sciences, 1736), vol. 1, Chapter 2, Corollary 11, paragraph 171, p. 68. From page 68: Erit enim seu ubi e denotat numerum, cuius logarithmus hyperbolicus est 1. (So it [i.e., c, the speed] will be or , where e denotes the number whose hyperbolic [i.e., natural] logarithm is 1.)
- ^ Calinger, Ronald (2016). Leonhard Euler: Mathematical Genius in the Enlightenment. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-11927-4. p. 124.
- ^ Rudin, Walter (1976). Principles of Mathematical Analysis (3rd ed.). McGraw–Hill. pp. 63–65. ISBN 0-07-054235-X.
- ^ Gonick, Larry (2012). The Cartoon Guide to Calculus. William Morrow. pp. 29–32. ISBN 978-0-06-168909-3.
- ^ Abramson, Jay; et al. (2023). "6.1 Exponential Functions". College Algebra 2e. OpenStax. ISBN 978-1-951693-41-1.
- ^ Kardar, Mehran (2007). Statistical Physics of Particles. Cambridge University Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-521-87342-0. OCLC 860391091.
- ^ Illowsky, Barbara; Dean, Susan; et al. (2023). "6.1 The Standard Normal Distribution". Statistics. OpenStax. ISBN 978-1-951693-22-0.
- ^ Grinstead, Charles M.; Snell, James Laurie (1997). Introduction to Probability (published online under the GFDL). American Mathematical Society. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-8218-9414-9. Archived from the original on 2011-07-27.
- ^ Knuth, Donald (1997). The Art of Computer Programming. Vol. I. Addison-Wesley. p. 183. ISBN 0-201-03801-3.
- ^ Steven Finch (2003). Mathematical constants. Cambridge University Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-521-81805-6.
- ^ Gbur, Greg (2011). Mathematical Methods for Optical Physics and Engineering. Cambridge University Press. p. 779. ISBN 978-0-521516-10-5.
- ^ Kline, M. (1998). Calculus: An intuitive and physical approach. Dover Publications. p. 337 ff. ISBN 0-486-40453-6.
- ^ Strang, Gilbert; Herman, Edwin; et al. (2023). "6.3 Taylor and Maclaurin Series". Calculus, volume 2. OpenStax. ISBN 978-1-947172-14-2.
- ^ Strang, Gilbert; Herman, Edwin; et al. (2023). "4.10 Antiderivatives". Calculus, volume 2. OpenStax. ISBN 978-1-947172-14-2.
- ^ Dorrie, Heinrich (1965). 100 Great Problems of Elementary Mathematics. Dover. pp. 44–48.
- ^ A standard calculus exercise using the mean value theorem; see for example Apostol (1967) Calculus, § 6.17.41.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A073230 (Decimal expansion of (1/e)^e)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A073229 (Decimal expansion of e^(1/e))". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Euler, L. "De serie Lambertina Plurimisque eius insignibus proprietatibus." Acta Acad. Scient. Petropol. 2, 29–51, 1783. Reprinted in Euler, L. Opera Omnia, Series Prima, Vol. 6: Commentationes Algebraicae. Leipzig, Germany: Teubner, pp. 350–369, 1921. (facsimile)
- ^ Knoebel, R. Arthur (1981). "Exponentials Reiterated". The American Mathematical Monthly. 88 (4): 235–252. doi:10.2307/2320546. ISSN 0002-9890. JSTOR 2320546.
- ^ Anderson, Joel (2004). "Iterated Exponentials". The American Mathematical Monthly. 111 (8): 668–679. doi:10.2307/4145040. ISSN 0002-9890. JSTOR 4145040.
- ^ Sandifer, Ed (Feb 2006). "How Euler Did It: Who proved e is Irrational?" (PDF). MAA Online. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-02-23. Retrieved 2010-06-18.
- ^ Gelfond, A. O. (2015) [1960]. Transcendental and Algebraic Numbers. Dover Books on Mathematics. Translated by Boron, Leo F. New York: Dover Publications. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-486-49526-2. MR 0057921.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Irrationality Measure". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2024-09-14.
- ^ Murty, M. Ram; Rath, Purusottam (2014). Transcendental Numbers. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-0832-5. ISBN 978-1-4939-0831-8.
- ^ Waldschmidt, Michel (2021). "Schanuel's Conjecture: algebraic independence of transcendental numbers" (PDF).
- ^ Khoshnevisan, Davar (2006). "Normal numbers are normal" (PDF). Clay Mathematics Institute Annual Report 2006. Clay Mathematics Institute. pp. 15, 27–31.
- ^ Kontsevich, Maxim; Zagier, Don (2001). "Periods" (PDF).
- ^ Whittaker, Edmund Taylor; Watson, George Neville (1927-01-02). A Course Of Modern Analysis: An Introduction to the General Theory of Infinite Processes and of Analytic Functions; with an Account of the Principal Transcendental Functions (4th ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 581. ISBN 978-0-521-06794-2.
- ^ Dennery, P.; Krzywicki, A. (1995) [1967]. Mathematics for Physicists. Dover. pp. 23–25. ISBN 0-486-69193-4.
- ^ Milla, Lorenz (2020). "The Transcendence of π and the Squaring of the Circle". arXiv:2003.14035 [math.HO].
- ^ Hines, Robert. "e is transcendental" (PDF). University of Colorado. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-06-23.
- ^ Sultan, Alan; Artzt, Alice F. (2010). The Mathematics That Every Secondary School Math Teacher Needs to Know. Routledge. pp. 326–328. ISBN 978-0-203-85753-3.
- ^ Hofstadter, D.R. (1995). Fluid Concepts and Creative Analogies: Computer Models of the Fundamental Mechanisms of Thought. Basic Books. ISBN 0-7139-9155-0.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A003417 (Continued fraction for e)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Russell, K.G. (February 1991). "Estimating the Value of e by Simulation". The American Statistician. 45 (1): 66–68. doi:10.1080/00031305.1991.10475769. JSTOR 2685243.
- ^ Dinov, ID (2007) Estimating e using SOCR simulation, SOCR Hands-on Activities (retrieved December 26, 2007).
- ^ Sebah, P. and Gourdon, X.; The constant e and its computation
- ^ Gourdon, X.; Reported large computations with PiFast
- ^ Roger Cotes (1714) "Logometria," Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 29 (338) : 5–45; see especially the bottom of page 10. From page 10: "Porro eadem ratio est inter 2,718281828459 &c et 1, … " (Furthermore, by the same means, the ratio is between 2.718281828459… and 1, … )
- ^ Leonhard Euler, Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum (Lausanne, Switzerland: Marc Michel Bousquet & Co., 1748), volume 1, page 90.
- ^ William Shanks, Contributions to Mathematics, ... (London, England: G. Bell, 1853), page 89.
- ^ William Shanks (1871) "On the numerical values of e, loge 2, loge 3, loge 5, and loge 10, also on the numerical value of M the modulus of the common system of logarithms, all to 205 decimals," Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 20 : 27–29.
- ^ J. Marcus Boorman (October 1884) "Computation of the Naperian base," Mathematical Magazine, 1 (12) : 204–205.
- ^ Daniel Shanks; John W Wrench (1962). "Calculation of Pi to 100,000 Decimals" (PDF). Mathematics of Computation. 16 (77): 76–99. doi:10.2307/2003813. JSTOR 2003813. p. 78:
We have computed e on a 7090 to 100,265D by the obvious program
- ^ Wozniak, Steve (June 1981). "The Impossible Dream: Computing e to 116,000 Places with a Personal Computer". BYTE. Vol. 6, no. 6. McGraw-Hill. p. 392. Retrieved 18 October 2013.
- ^ Alexander Yee, ed. (5 December 2020). "e". Numberworld.
- ^ Finch, Steven R. (2005). Mathematical constants. Cambridge Univ. Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81805-6. OCLC 180072364.
- ^ Knuth, Donald (1990-10-03). "The Future of TeX and Metafont" (PDF). TeX Mag. 5 (1): 145. Retrieved 2017-02-17.
- ^ Roberge, Jonathan; Melançon, Louis (June 2017). "Being the King Kong of algorithmic culture is a tough job after all: Google's regimes of justification and the meanings of Glass". Convergence: The International Journal of Research into New Media Technologies. 23 (3): 306–324. doi:10.1177/1354856515592506. ISSN 1354-8565.
- ^ "First 10-digit prime found in consecutive digits of e". Brain Tags. Archived from the original on 2013-12-03. Retrieved 2012-02-24.
- ^ Kazmierczak, Marcus (2004-07-29). "Google Billboard". mkaz.com. Archived from the original on 2010-09-23. Retrieved 2007-06-09.
- ^ The first 10-digit prime in e Archived 2021-04-11 at the Wayback Machine. Explore Portland Community. Retrieved on 2020-12-09.
- ^ Shea, Andrea. "Google Entices Job-Searchers with Math Puzzle". NPR. Retrieved 2007-06-09.
- ^ Peterson, Benjamin (20 April 2020). "Python 2.7.18, the end of an era". LWN.net.
Further reading
- Maor, Eli, ed. (2009). e: The Story of a Number. Princeton science library. Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05854-2.
- Commentary on Endnote 10 of the book Prime Obsession for another stochastic representation
- McCartin, Brian J. (March 2006). "e: The Master of All" (PDF). The Mathematical Intelligencer. 28 (2): 10–21. doi:10.1007/BF02987150. ISSN 0343-6993. S2CID 123033482.
External links
- The number e to 1 million places and NASA.gov 2 and 5 million places
- e Approximations – Wolfram MathWorld
- Earliest Uses of Symbols for Constants Jan. 13, 2008
- "The story of e", by Robin Wilson at Gresham College, 28 February 2007 (available for audio and video download)
- e Search Engine 2 billion searchable digits of e, π and √2


















![{\displaystyle \Pr[k~\mathrm {wins~of} ~n]={\binom {n}{k}}\left({\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{k}\left(1-{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n-k}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/11467bf6b08712fd2081a929d154c3e1c17f07dd)
![{\displaystyle \Pr[0~\mathrm {wins~of} ~n]=\left(1-{\frac {1}{n}}\right)^{n}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/534de6d23bfaf39e681e5d8cf2724fa19fc687e8)








![{\displaystyle {\sqrt[{x}]{x}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/61b4a0a76158849854a302fc639dfc882ec16008)







![{\displaystyle e=\lim _{n\to \infty }{\frac {n}{\sqrt[{n}]{n!}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ce0cd8eb0003d22f6e68f69c95cf434c43bebc58)




























![{\displaystyle e=[2;1,2,1,1,4,1,1,6,1,...,1,2n,1,...],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/eda10aefcc9d9e0268fb3b0734147f652800e6ac)










