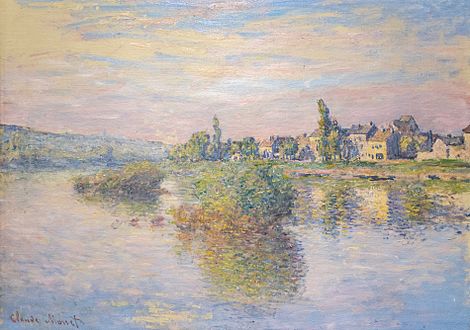Frick Art And Historical Center
The complex, located on 5.5 acres (22,000 m) of lawn and gardens in the city's Point Breeze neighborhood, includes Clayton, the restored Frick mansion; The Frick Art Museum; The Car and Carriage Museum; the Greenhouse; the Frick children's playhouse; and The Café. The site welcomes over 100,000 visitors a year. Admission is free.
Helen Clay Frick (1888–1984) was the driving force to preserve the Frick estate and allow it to open to the public after her death.
History

Today's museum began as an eleven-room, Italianate-style house purchased by the Fricks shortly after their marriage in 1881. The house was built in the 1860s, original architect unknown. After modifications by Pittsburgh architect Andrew Peebles, it was renamed "Clayton". Further remodeling of the house was done in 1892 by Pittsburgh architect Frederick J. Osterling. The Playhouse was constructed in 1897 to designs by architects Alden & Harlow. The house served as the Fricks' primary residence from 1883 to 1905. The Fricks moved to New York City in 1905, where they eventually established the Frick Collection, but in 1981 daughter Helen Clay Frick returned to Clayton, where she had previously spent part of each year, and remained there permanently until her death in 1984. Clayton opened to the public in 1990, and in 1997 the 1950s carriage house was enlarged to create the Car and Carriage Museum.
In May 2013 the center announced a $15 million renovation to break ground on June 6, 2013. The renovation was completed in 2015; the Car and Carriage Museum was expanded to twice its original size, and a community center and education center were built.
Collections

The Frick Art Museum's collection includes a large group of works on paper by Jean-François Millet, Renaissance and Baroque bronzes, and nineteenth-century European paintings. There are also Late Medieval and Renaissance paintings of a devotional nature by: Bernardo Daddi, Lippo Memmi, Giovanni di Paolo, Francesco di Vannuccio ("Saint Catherine"), Rainaldo di Rainuccio da Spoleto, Sassetta, Matteo Di Giovanni, Francesco Melzi, and Jean Bellegambe. In the Frick Art Museum, there are Renaissance and Baroque paintings with secular themes by: Apollonio Di Giovanni ("Scenes from Homer's Odyssey"), Jean-Louis de Marne ("Seine at Saint Cloud"), Carle Van Loo, Maurice Quentin de la Tour, Peter Paul Rubens, Jan Steen, Jan van Os, and Arthur Devis. In Clayton, in the mansion Frick lived in are 19th Century paintings by Jules Cazin, Jean-François Raffaëlli, and Anton Mauve.
Automobiles on display include an 1881 Brougham, 1898 Panhard et Levassor Tonneau, 1903 Baker Electric, 1906 Outing Wagon, 1909 Bailey Electric Phaeton, 1909 Keystone Sixty-Six Roadster, 1911 Penn 30 Touring Car, 1912 Daimler Landaulet, 1914 Ford Model T Touring Car, 1914 Rolls-Royce Silver Ghost Touring Car, 1917 Standard Model E Touring Car, 1924 Auto Red Bug Flyer, 1931 Lincoln Model K Sport Phaeton, and 1940 American Bantam Convertible Coupe.
The museum hosts numerous exhibitions. For example, from June 11, 2016 to September 4, 2016, it hosted the visiting exhibition "Killer Heels: The Art of the High-Heeled Shoe."
Selection of works
-
1806, Jena, Jean-Louis-Ernest Meissonier, 1890
-
Rest in the Park, (Le Repos dans le Parc), Jean-Baptiste Pater
-
Portrait of Charlotte Marguerite de Montmorency, Princess of Conde, Peter Paul Rubens, circa 1610
-
View on the Grand Canal at San Geremia, Venice, Francesco Guardi, 1760–65
-
Still Life with Fruit, Jan van Os, 1769
-
Chagrin d'Enfant, Emile Friant, 1898
-
Sir Joshua and Family at Roehampton House, Putney, Arthur Devis, 1752
-
Banks of the Seine at Lavacourt, Claude Monet, 1879
-
The Arts in Supplication, Carle van Loo, 1764
-
Madonna and Child with Saints, Scenes from Life of Christ and Life of the Virgin, painter unknown, from Master of the Scrovegni Chapel Presbytery, circa 1308
-
Madonna and Child Enthroned with Four Scenes of Christ's Passion, Rainaldo di Rainuccio da Spoleto, 1265
See also

References
- ^ "Frick Art & Historical Center to get makeover – Pittsburgh Post-Gazette". Archived from the original on June 19, 2013.
- ^ "Big Changes Coming To Frick Art & Historical Center". CBS Pittsburgh. May 28, 2013. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Lyons, Kim (November 17, 2015). "Frick Art & Historical Center sparkles with $15 million update". NEXTpittsburgh. Retrieved February 3, 2024.
- ^ Harrop, JoAnne Klimovich (September 21, 2015). "Frick Art & Historical Center to host 'Killer Heels' exhibit". Tribune. Retrieved October 14, 2015.
- ^ "Killer Heels: The Art of the High-Heeled Shoe". The Frick Pittsburgh. Retrieved September 25, 2023.
Further reading
- Kidney, Walter C. (1997). Pittsburgh's Landmark Architecture: The Historic Buildings of Pittsburgh and Allegheny County. Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh History & Landmarks Foundation. ISBN 0-916670-18-X.
- Sanger, Martha Frick Symington (2007). Helen Clay Frick: Bittersweet Heiress. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press. ISBN 978-0-8229-4341-9.