Guerande
The Guérande Peninsula overlooks two contrasting landscapes: the "Pays Blanc" (White Land), because of its salt marshes, and the "Pays Noir", with the Brière peat bog. The town's salt marshes have made it a renowned producer of salt, and it is the traditional source of fleur de sel, a type of garnishing salt.
Since 2004, the medieval town of Guérande has been a member of a national network of 120 towns, the Villes et Pays d'Art et d'Histoire (Towns and Regions of Art and History). The fortified wall of Guérande is one of the best preserved and complete in France. Its circumference stretches 1434 meters.
Geography
Location
The main towns around Guérande are Saint-Nazaire and Nantes to the East (19 km (11.81 mi) and 80 km (49.71 mi) away), and Vannes (70 km (43.50 mi) to the North).
The Guérande Peninsula is surrounded by water. It stretches out from the Atlantic Ocean (west) to the Brière Regional Nature Reserve (east), and from the river Vilaine (north) to the Loire estuary (south).
Guérande is in the heart of the peninsula called "Presqu'île guérandaise", along with other towns, such as La Baule, Le Croisic, Pornichet, Batz-sur-Mer, Le Pouliguen, or Piriac.
According to the classification established by the INSEE in 1999, Guérande is now classified as an urban district, 1 out of 9 forming the urban area of Saint-Nazaire.
Guérande in figures : -32 towns and villages, the biggest ones are Saillé, Clis, Careil and La Madeleine -2000 hectares of salt marshes
History
Neolithic period
About half of the remaining megalithic monuments of the Département Loire-Atlantique, is located on the Peninsula, which makes it an important area for Prehistory. It is now known that these structures date from around 5200–2200 BC.
Antiquity
Celtic period
At the end of the Iron Age, the Peninsula was occupied by 2 tribes:
- the Veneti, in the North, with the river Vilaine as a frontier. In 56 BC, the Veneti double-crossed Caesar and he '...put the whole of their senate to the sword, and sold the rest of the men as slaves....' (Source: Caesar, cited by Nora Chadwick, The Celts.) and
- the Namnetes, further South, whose frontier was the Loire river. As a seaboard people, their fortunes increased as they sided with Rome.
The Peninsula represented an important crossroads for these and other tribes, as it was surrounded by waterways. One waterway was the river Vilaine, used by the tribes Redones and Veneti. The Loire river was used by the tribes Namnetes and Pictones, and the Atlantic Ocean was used by the tribes Veneti and by Greek traders.
Gallo-Roman period
The many artifacts from the Gallo-Roman age demonstrates that Guérande had been home to many groups.
3rd century
The area was evangelized in the 3rd century by St. Clair, the first Bishop of Nantes.
6th century
The Bretons of the prince of "Vannes" (Waroch II (577–594)) may have built the first parish. Waroch is supposed to have created a baptistery in place of the actual choir of the collegiate church "Saint-Aubin".
9th century
Around 848, under the reign of Nominoe, 1st King of Brittany, the city became the head of a temporary bishopric. Salomon ("Selyfan", "Salaun", "Tudwal Mwyn Fawr", "3rd King of Brittany", "857–874",) built a canon college that was a benefit to the city's development. At the turn of the second millennium, a fortified town was built and a political and administrative organization could be established thanks to the existing castle.
10th century
According to local legends, a Viking band arrived in Guerande in 919 determined to pillage the city. The Guerandais apparently took refuge in the collegiate church praying to St Aubin who apparently sent a sign giving courage to the locals who took up arms and drove out the invaders.

Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, the town had a very rich history, with many important events. It was also the capital of the Pays Guérandais, an ancient region of the Duchy of Brittany.
14th century
Sacking of Guerande
In 1343 during the Breton War of Succession, Guerande was captured by Breton-French troops led by Luis de la Cerda, a commander of Charles of Blois. The former admiral used his Spanish and Genoese auxiliaries to attack the town from all sides. Without giving a quarter to the inhabitants, they engaged in frenzied plunder and did not respect even the churches, five of which were desecrated and burned, while approximately 8000 inhabitants were massacred in the streets, burned in their homes or in the Church of Saint Aubin. Charles was not impressed as Luis had exceeded the measure of his command and was made to hang on the spot twenty-four of the principal culprits.
Jean of Montfort, (John IV) Duke of Brittany, demanded that the town be properly protected, by improving its fortifications. Work started soon after and continued for more than a century, with the town's architecture adapted to reflect the latest developments in siege and artillery.
First Treaty of Guérande
At the end of the Breton War of Succession, peace was finally concluded before the high altar of Saint Aubin, (Albinus of Angers) on Holy Saturday in 1365. In this the first Treaty of Guérande, Joanna of Penthièvre abdicated her disputed claims to the Dukedom in favour of John V of the House of Montfort. A modified form of Salic law was introduced in Brittany as a result.
Second Treaty of Guérande
The second Treaty of Guérande (1381) established Brittany's neutrality in the Anglo-French conflict, and was accorded between Duke John V of Brittany and King Charles VI of France.
15th century
It was not until 1488, or 145 years later, that the ramparts, by then complete, were inaugurated during the reign of Francis II, Duke of Brittany (father of Anne of Brittany), only a few months before his death. The old walled town (known in French as vieille ville) is surrounded by nearly intact ramparts and has four fortified gates (the largest of which is a 15th-century châtelet known as Porte Saint-Michel) as well as ten towers.
16th century
Guérande was visited regularly by Breton rulers such as Duchess Anne of Brittany. In 1532, upon the marriage of Anne of Brittany to Charles VIII of France, Brittany (and with it the pays of Guerande) became unified with the French Kingdom.
In the late Middle Ages, the city was regularly visited by merchants from Rouen who came to buy salt.
Modern times
During the 17th and 18th centuries, the city was transformed, with bourgeois houses in granite replacing the houses of the 15th and 16th centuries. In 1686, at the Saint-Aubin public place, a new building was built called Les Halles; which was notable for its large auditorium. These mansions and houses represent about 50% of the buildings still visible today in the sector called the intra muros.
Chouannerie of 1815
The Chouannerie was a royalist uprising or counter-revolution in twelve of the western départements of France, particularly in the provinces of Brittany and Maine, against the First Republic during the French Revolution. Fighting took place around Guerande on June and July 1815 between the Chouans who attacked the town and the Governments 65th Infantry Regiment that defended it. The 150 men from the 65th line infantry regiment, were entrenched behind the city walls and pushed back the Chouans without much difficulty.
World War 2
Guerande was part of the Saint-Nazaire pocket during 1944 and 1945.
Breton language
In 2008, 2.02% of the children attended bilingual schools (in French and Breton) in primary education.
Twin towns – sister cities
Guérande is twinned with:
 Almagro, Spain
Almagro, Spain Castro Marim, Portugal
Castro Marim, Portugal Dinkelsbühl, Germany
Dinkelsbühl, Germany Dolgellau, Wales, United Kingdom
Dolgellau, Wales, United Kingdom
Heritage
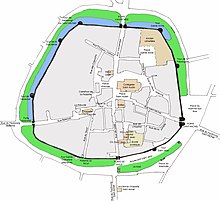
Medieval town
Ramparts (15th–16th century)
Listed building in 1877.
- The surrounding wall: This surrounding wall strengthened Guérande; it is a rare example of a medieval city which has preserved its rampart in its entirety. It is also one of the best preserved in France. Very little has been re-engineered since its main construction phase (in the 15th century), while little has been "restored" in the 19th century. The wall includes at present 10 towers, four doors and a poterne (opened to the 19th century), connected by a curtain, on a 1.434-kilometre-long (0.891 mi) (for comparison: quoted from Carcassonne, 1.250 km (0.78 mi) for the internal surrounding wall). After the sack of Guérande by the troops of Louis of Spain in 1342 during the War of Succession of Brittany, the city began to build a rampart in the following year of 1343. These works would last for more than a century and a half.

The names of the four gates are:
- La porte Saint-Michel – the main gate: Originally, the gate was occupied by the Captain of the city, who was the representative of the authority of the Duke of Brittany in Guerande. After Brittany's unification with the Kingdom of France in 1532, the Captain of the City ceded his authority to a French Governor. During the French Revolution, however, the populace of Guérande would remove its last Governor, eventually placing a prison in the Gate of Saint Michel. The building was not suited to this function, so the municipality eventually settled the functions of city hall here. Even then, the building would become too small too fast. The city hall eventually was resited elsewhere and this building became a museum to the Friends de Guérande, established in 1928. The museum contains a collection of helmets and traditional costumes, an archaeological collection and the Treasury of the Collegiate Church.
- La porte Vannetaise (13th century)
- La porte de Saillé (16th century)
- La porte Bizienne – it is the most recent part of the walls.
The ramparts are not the only element of defense of the old city. Also found are:
- A ditch along a large portion of the walls.
- Boulevard in front of the Gate of Saint-Michel.
Saint Aubin's Church (15th–16th century)
Listed building in 1853.
One of the main sites of interest in the medieval town.
Very little is known about the succession of religious buildings on the site of the original baptistery built by Prince Waroch. Dedicated to Saint Aubin, Bishop of Angers in the 6th century and a native of the peninsula, the church became a collegiate church in the 9th century following the foundation of a chapter of canons attributed to King Salomon. It was rebuilt in about 1200, and the Romanesque pillars in the nave are evidence of that work.
Very badly damaged during the Breton Wars of Succession, the Collegiate Church was restored in time for the signing of the first peace treaty in 1365. Various building projects succeeded one another until the 18th century, improving and adding new features: choir and chevet (15th–16th centuries), Baroque altarpieces and stalls (17th century). But hardly had this work been completed, than the church found itself in the midst of the French Revolution. It suffered little damage, other than to the windows. However, the Revolution led to major structural changes, since, in 1792, the status of Collegiate Church was abolished and the canons exiled to Spain.
In 1840, following the creation of the National Historical Monuments commission, the church's true value was realised and it was listed. The works undertaken by the architect Bourgerel were overly ambitious and caused the collapse of the west front in 1876. It was Eugène Boismen who was charged with reconstructing it in the original style.
Others sights
- Notre-Dame la Blanche Church. Listed building in 1910. Built in Gothic style in the 14th century under Jean de Montfort, is the oldest building in the medieval city.
- Saint-Jean Church
Sights of the outer suburbs
- Ursuline's convent
- The mill of the devil
Local tradition tells the story of a peasant named Yves Herbic, who was very poor. At daytime, he would work for his lord. At night, he would cultivate his own small piece of land. He sowed wheat but this didn't bring in enough money to pay the rent that the lord demanded. Therefore, he decided he had to build his own mill, but he couldn't do it alone. The Devil offered him a deal. Yves agreed to give his soul to the Devil in exchange for the mill. His wife was not pleased about that deal but she didn't know Yves had a cunning plan. Yves watched the Devil closely while he was building the mill. At the last moment the Devil finished building the mill, Yves placed a statue of the Virgin Mary on top of it. The Devil vanished instantly into thin air and never returned. Yves got his mill and kept his soul.
Natural sites
Salt marshes
| Designations | |
|---|---|
| Official name | Marais salants de Guérande et du Mès |
| Designated | 1 September 1995 |
| Reference no. | 746 |
The salterns of Guérande are a swamp of salt water about 1 700 hectares in size. The current saltmarshes began before the 9th century and lasted for several centuries. Around the year 1500, the marshes reached 80% of the current surface. The latest were built around 1800. In the middle of the 19th century, a gradual decline started for different reasons : competition from a salt mine, lower consumption of salt as a product of conservation and improvement of transport by land. The salt of Guérande used to be traded throughout Brittany, tax free until Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte decided to tax it resulting in the beginning of a decline of salt activity.
Certain parts of the swamps and "Traict" are classified as a Nature Reserve (major stage for migratory birds) and is managed by the Conservatoire du littoral. The "Traict" and swamps have also been classified as "site Natura" since 2000. These swamps have also been registered since 1971 on the list of protected wet-lands under the Ramsar Convention.
The salterns of Guérande include two salicoles ponds:
- The pond of Guérande: the biggest and the best known can be found between Guérande and the peninsula of Croisic, on Traict
- The pond of Mès, a smaller area, to Mesquer. It is the pond salicole most well known in northern Europe.
They are a part of the salterns of the Atlantic Ocean, more than three-quarters of them, found in the Gironde and the peninsula of Quiberon.
Salterns are sites where the salt workers collect approximately 15,000 tons of cooking salt a year, and approximately 300 tons of Fleur de sel or flower of salt. A cooperative promote quality with a label (the French Label rouge). Today around 250 workers live on the salt marshes. These salterns are also classified as "remarkable Sites of taste". The principle is simple. Channels that feed the water reservoirs with sea water, use the tides. Salty water then evaporates in different dams till there are only a few centimeters of sea water left. The last step is where the salt crystallizes and produces the fleur de sel and coarse salt.
-
Salt marshes
-
Mulon de sel
-
Salt marshes
-
Salt marshes from above
la Brière Natural Park
Brière is a territory of 490 km (189.19 sq mi) of which 170 km (65.64 sq mi) is wet-lands. This swamp of brackish water is called The Swamp of Grande Brière and covers 70 km (27.03 sq mi). There are 21 municipalities which are a part of this territory and of which Guérande is a member.
The regional nature reserve of Brière was created on 16 October 1970 (revised on 6 June 2001).
This is one of the first natural parks to be listed as a "Parc Naturel Régional" in 1970.
Villages of Guerande
Clis
This small village between Guerande and La Turballe has many typical houses of salt workers. There are many monuments of interest such as the Sainte-Catherine church (built during the 15th century), Requer's Cross (listed building in 1944) as well as parts of an old Roman wall.
Saillé
This village is situated in the heart of the salt marshes. Like Clis, there are many typical houses of salt workers.
Careil
This village is famous for its castle.
La Madeleine
A typical village in the swamps of La Brière.
Population
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: EHESS and INSEE (1968-2017) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cultural references
Literature
- The Balzac novel Béatrix is set in Guérande, concerning Calyste, son of the Baron de Guenic, and his relations with characters based on George Sand, Franz Liszt, and Marie d'Agoult.
- The ramparts of anger:Guerande by Bernard Glotin is a murder mystery set in Guerande.
Festivals
Celtic Guerande
Occurs in early August each year. This festival crosses multiple origins and styles of dance music, traditional singing tales, from the most authentic blend of culture forms.
Medieval Guerande
Occurs in May each year. This fete takes Guerande back in time to the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, with an intramural market and medieval fair, with medieval encampments, taverns, equestrian events, live music, theater, juggling and children's entertainment. More than 500 guerandais volunteers dress to the theme. There is a grand costume parade on the Sunday morning.
See also
- La Baule - Guérande Peninsula
- Communes of the Loire-Atlantique department
- Brière
- Parc naturel régional de Brière
- The works of Jean Fréour. Breton sculptor
References
- ^ "Répertoire national des élus: les maires" (in French). data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises. 13 September 2022.
- ^ "Populations de référence 2022" (in French). The National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies. 19 December 2024.
- ^ INSEE commune file
- ^ PC-NET Services Informatique. "Ξ Collégiale Saint-Aubin de Guérande Sites & monuments - Côte d'Amour". Macotedamour.com. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ^ Ref 5th volume: Y Historia genealógica y heráldica de la monarquía española1 de D. Francisco Fernandez de Béthencourt, 1904 dedicated to the title of Medina Celi
- ^ Tanneguy Lehideux, Combats d'un Chouan: Terrien coeur de lion, colonel de Chouans, Chevalier de Saint-Louis or La Chouannerie in Upper Brittany and Anjou, La Crèche, Geste éditions, 2009, 443 p. (ISBN 978-2-84561-509-0, notice BnF no FRBNF41454424).
- ^ Louis d'Andigné, Memoirs of General d'Andigné, t. II, Plon, 1901, 434 p. (BnF notice no FRBNF34146667, read online) Aurélien Lignereux, Chouans and Vendéens against the Empire: 1815, the other Hundred-Day War, Paris, Vendémiaire, coll. “Revolution”, 2015, 379 p. (ISBN 978-2-36358-187-7, notice BnF no FRBNF44432607).
- ^ (in French) Ofis ar Brezhoneg: Enseignement bilingue
- ^ "Présentation de la ville" (in French). Guérande. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
- ^ "Marais salants de Guérande et du Més". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- ^ Des villages de Cassini aux communes d'aujourd'hui: Commune data sheet Guérande, EHESS (in French).
- ^ Population en historique depuis 1968, INSEE
External links
 Guerande travel guide from Wikivoyage
Guerande travel guide from Wikivoyage- Tourist office of La Baule Guérande
- Official website (in French)



