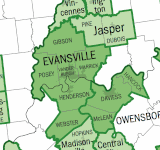
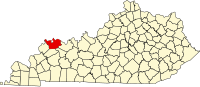
Henderson County, KY
The county was formed in 1798 and named for Richard Henderson who purchased 17,000,000 acres (69,000 km) of land from the Cherokee, part of which would later make up the county.
Henderson County lies within the West Kentucky Coal Field area. It is also part of the Evansville, IN-KY Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
The Transylvania Co., also known as Richard Henderson & Co., in 1775 purchased from the Cherokees a large swath of wilderness between the Kentucky River and Cumberland River, encompassing approximately half of what would become Kentucky as well as a portion of northern Tennessee. Their intention was to establish a 14th colony to be called Transylvania Colony. To help attract people to purchase land and populate the region, Henderson & Co. hired pioneer, explorer, woodsman, and frontiersman Daniel Boone to lead settlers through Cumberland Gap and direct woodsmen to cut the Wilderness Road through the Kentucky forest. However, the Continental Congress declined to act on Transylvania Co.'s petition without the consent of Virginia and North Carolina, which laid claim to the disputed lands.
In December 1778, Virginia's Assembly declared the Transylvania claim void. In compensation, Henderson and his partners received a grant of 200,000 acres on the Ohio River below the mouth of Green River. In 1797, the surviving Transylvania Company investors and heirs sent Samuel Hopkins and Thomas Allin to the Henderson Grant land to lay out a town and mark off land for the respective investors. The location they selected for the town was the site of an existing settlement that sat high above the Ohio River called Red Banks. The new town was subsequently named Henderson.
Henderson County was created out of Christian County in December 1798, and was officially established in May 1799. Henderson was designed as its county seat. The county initially encompassed a larger area than it does today. It was reduced in size when Hopkins County was formed in 1806, when Union County was established in 1811, and when Webster County was established in 1860.
In August 1799, serial killers Micajah and Wiley Harpe came to the house of Moses Stegall, near what is now Dixon in Webster County, and murdered his wife, child, and a visitor. Moses Stegall later tracked down the brothers, and killed Micajah Harpe, cutting off his head and hanging it in a tree as a warning to other outlaws. Wiley Harpe was captured and hanged four years later in Mississippi.
During the 19th century, a cultivar of dark tobacco raised in Henderson County became very popular in Great Britain and continental Europe. Henderson became the largest dark-tobacco market in the world, generating considerable wealth in Henderson County. Around 1880, Henderson had 17 stemmeries in the city and 18 in the county. Stemmeries were where tobacco was stripped from its stem and made ready for use. However, tobacco production in Henderson County declined through the 20th century and early 21st century, with few farmers still raising the labor-intensive crop.
A peninsula across the Ohio from Henderson, which now forms Union Township, Vanderburgh County, Indiana, was the subject of Handly's Lessee v. Anthony, a U.S. Supreme Court case in 1820. An area known as "Green River Island" is part of Kentucky, even though it is on the Indiana side of the Ohio River. The Ellis Park Race Course is located there.
A workplace shooting occurred at an Atlantis Plastics factory in Henderson, Kentucky, United States on June 25, 2008. The gunman, 25-year-old Wesley Neal Higdon, shot and killed five people and critically injured a sixth, before taking his own life. The mass murder is the worst in the history of Henderson County, surpassing the triple homicides that took place in 1799 and 1955.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 466 square miles (1,210 km), of which 437 square miles (1,130 km) is land and 30 square miles (78 km) (6.4%) is water. The county's northern border with Indiana is mostly formed by the Ohio River, though some of the county lies north of the river.
Adjacent counties
- Posey County, Indiana (northwest)
- Vanderburgh County, Indiana (north)
- Warrick County, Indiana (northeast)
- Daviess County (east)
- McLean County (southeast)
- Webster County (south)
- Union County (west)
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | 1,468 | — | |
| 1810 | 4,703 | 220.4% | |
| 1820 | 5,714 | 21.5% | |
| 1830 | 6,659 | 16.5% | |
| 1840 | 9,548 | 43.4% | |
| 1850 | 12,171 | 27.5% | |
| 1860 | 14,262 | 17.2% | |
| 1870 | 18,457 | 29.4% | |
| 1880 | 24,515 | 32.8% | |
| 1890 | 29,536 | 20.5% | |
| 1900 | 32,907 | 11.4% | |
| 1910 | 29,352 | −10.8% | |
| 1920 | 27,609 | −5.9% | |
| 1930 | 26,295 | −4.8% | |
| 1940 | 27,020 | 2.8% | |
| 1950 | 30,715 | 13.7% | |
| 1960 | 33,519 | 9.1% | |
| 1970 | 36,031 | 7.5% | |
| 1980 | 40,849 | 13.4% | |
| 1990 | 43,044 | 5.4% | |
| 2000 | 44,829 | 4.1% | |
| 2010 | 46,250 | 3.2% | |
| 2020 | 44,793 | −3.2% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 44,119 | −1.5% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 | |||
As of the census of 2000, there were 44,829 people, 18,095 households, and 12,576 families residing in the county. The population density was 102 per square mile (39/km). There were 19,466 housing units at an average density of 44 per square mile (17/km). The racial makeup of the county was 91.16% White, 7.10% Black or African American, 0.16% Native American, 0.33% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.39% from other races, and 0.86% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino people of any race were 0.97% of the population.
There were 18,095 households, out of which 32.40% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.40% were married couples living together, 11.60% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.50% were non-families. 26.40% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.60% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.43 and the average family size was 2.93.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 24.60% under the age of 18, 8.40% from 18 to 24, 30.00% from 25 to 44, 23.90% from 45 to 64, and 13.10% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.60 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.60 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $35,892, and the median income for a family was $44,703. Males had a median income of $33,838 versus $22,572 for females. The per capita income for the county was $18,470. About 9.70% of families and 12.30% of the population were below the poverty line, including 17.20% of those under age 18 and 10.10% of those age 65 or over.
Communities
Cities
Census-designated places
- Anthoston
- Poole (partially in Webster County)
- Spottsville
Other unincorporated places
Ghost town
Notable people
- John James Audubon, ornithologist, painter and naturalist, lived in Henderson 1810–1819
- LaVerne Butler, Kentucky clergyman and university president; born in Henderson County in 1926
- Happy Chandler, 44th and 49th governor of Kentucky; born in the farming community of Corydon, Kentucky in 1898
- Ewing Galloway, journalist and one-time county prosecutor; born in Little Dixie, Kentucky in 1880
- W. C. Handy, musician and composer who became known as the "father of the blues"; lived in Henderson during the 1890s, performing in bands
- Grandpa Jones, country entertainer; born in 1913 in the small farming community of Niagara, Kentucky
- Gary L. Littrell, Command Sergeant Major, born in Henderson in 1944
- Luther Skaggs Jr., Marine corporal; born in Henderson, Kentucky in 1923
Politics
The county voted "No" on 2022 Kentucky Amendment 2, an anti-abortion ballot measure, by 54% to 46%, and backed Donald Trump with 62% of the vote to Joe Biden's 37% in the 2020 presidential election.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party(ies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2024 | 12,592 | 63.96% | 6,837 | 34.73% | 259 | 1.32% |
| 2020 | 12,730 | 61.51% | 7,639 | 36.91% | 328 | 1.58% |
| 2016 | 12,159 | 61.69% | 6,707 | 34.03% | 844 | 4.28% |
| 2012 | 10,296 | 55.29% | 8,091 | 43.45% | 235 | 1.26% |
| 2008 | 9,523 | 47.95% | 10,049 | 50.60% | 289 | 1.46% |
| 2004 | 10,467 | 55.97% | 8,101 | 43.32% | 133 | 0.71% |
| 2000 | 7,698 | 48.00% | 8,054 | 50.22% | 287 | 1.79% |
| 1996 | 5,092 | 34.39% | 8,051 | 54.38% | 1,663 | 11.23% |
| 1992 | 5,125 | 31.78% | 8,270 | 51.28% | 2,731 | 16.94% |
| 1988 | 6,911 | 47.27% | 7,648 | 52.31% | 61 | 0.42% |
| 1984 | 7,389 | 51.88% | 6,795 | 47.71% | 58 | 0.41% |
| 1980 | 5,074 | 37.15% | 8,082 | 59.17% | 503 | 3.68% |
| 1976 | 4,053 | 33.45% | 7,916 | 65.32% | 149 | 1.23% |
| 1972 | 6,231 | 60.68% | 3,889 | 37.87% | 149 | 1.45% |
| 1968 | 3,512 | 32.74% | 5,062 | 47.19% | 2,152 | 20.06% |
| 1964 | 2,734 | 25.35% | 8,022 | 74.38% | 29 | 0.27% |
| 1960 | 5,302 | 48.79% | 5,565 | 51.21% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1956 | 5,085 | 46.92% | 5,501 | 50.76% | 252 | 2.33% |
| 1952 | 4,929 | 45.25% | 5,913 | 54.28% | 51 | 0.47% |
| 1948 | 1,904 | 24.13% | 5,499 | 69.70% | 486 | 6.16% |
| 1944 | 2,683 | 31.22% | 5,887 | 68.49% | 25 | 0.29% |
| 1940 | 2,455 | 26.65% | 6,727 | 73.03% | 29 | 0.31% |
| 1936 | 1,811 | 20.50% | 6,835 | 77.38% | 187 | 2.12% |
| 1932 | 2,485 | 27.98% | 6,100 | 68.69% | 296 | 3.33% |
| 1928 | 5,443 | 57.03% | 4,068 | 42.62% | 33 | 0.35% |
| 1924 | 4,902 | 53.67% | 4,046 | 44.30% | 186 | 2.04% |
| 1920 | 4,161 | 35.51% | 7,272 | 62.06% | 285 | 2.43% |
| 1916 | 2,218 | 36.41% | 3,699 | 60.73% | 174 | 2.86% |
| 1912 | 1,157 | 21.51% | 3,098 | 57.58% | 1,125 | 20.91% |
See also
References
- ^ "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 6, 2022.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ "Henderson County". The Kentucky Encyclopedia. 2000. Archived from the original on September 4, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2014.
- ^ The Register of the Kentucky State Historical Society, Volume 1. Kentucky State Historical Society. 1903. pp. 35.
- ^ Kleber, John E. (1992). The Kentucky Encyclopedia. The University Press of Kentucky. p. 423. ISBN 0-8131-1772-0. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
- ^ Hogan, Roseann Reinemuth (1992). Kentucky Ancestry: A Guide to Genealogical and Historical Research. Ancestry Publishing. p. 250. ISBN 9780916489496. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ Dixon, Abby (November 11, 2020). "Henderson's Tobacco History". Henderson Tourist Commission. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
- ^ White, Doug (October 2, 2017). "Growing tobacco: Henderson family one of few left doing it here". The Gleaner. Henderson, Kentucky. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
- ^ Handly's Lessee v. Anthony, 18 U.S. 374 (1820)
- ^ Lenz, Ryan (June 25, 2008). "6 dead in Henderson, Ky., plastics plant shooting". Associated Press. Archived from the original on June 28, 2008.
- ^ Smith, Beth (June 26, 2008). "Rampage at Atlantis Plastics ends with six dead". Henderson Gleaner. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved August 15, 2014.
- ^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on August 12, 2014. Retrieved August 16, 2014.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Counties: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2023". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 14, 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 16, 2014.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved August 16, 2014.
- ^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 16, 2014.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 27, 2010. Retrieved August 16, 2014.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ "LaVerne Butler". Lexington Herald Leader, December 18, 2010. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- ^ "November 8, 2022 - Official 2022 General Election Results" (PDF). Commonwealth of Kentucky State Board of Elections. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 24, 2022. Retrieved December 30, 2024.
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved April 9, 2018.