Hugh Trumble
A tall and thin off spinner, Trumble delivered the ball at a quicker pace than most spin bowlers, using his height and uncommonly long fingers to his greatest advantage. He was at his best on the softer pitches of England, but his accuracy and variations in pace enabled him to take wickets on the harder pitches of Australia as well. He was a dependable lower order batsman and a fine fielder in the slips. He was recognised as a shrewd thinker about the game and was popular with team-mates and opponents, with a penchant for practical jokes.
Trumble made his Test debut during the Australian cricket team's tour of England in 1890, but was unable to secure a permanent place in the Australian side until the 1896 tour of England. When the Australian team next toured England in 1899, Trumble scored 1,183 runs and took 142 wickets; only George Giffen before him had achieved the "double" of 1,000 runs and 100 wickets as part of a touring team in England. He was appointed captain of Australia in 1901–02, when Joe Darling was unavailable due to farming commitments. He retired after the 1902 Australian tour of England but was coaxed back in 1903–04. In his last Test match, against England, Trumble took a hat-trick, his second, in front of his home town supporters in Melbourne.
Off the field, Trumble worked for the National Bank of Australasia, rising to the position of manager of a local branch despite his cricket commitments interrupting his banking career. In 1911, he was appointed secretary of the Melbourne Cricket Club, overseeing the development of the Melbourne Cricket Ground (MCG) into a stadium capable of holding over 70,000 spectators. He held this post until his death in 1938 from a heart attack, aged 71.
Early life and career
Trumble was born in the inner Melbourne neighbourhood of Collingwood, Victoria in 1867, the son of William, born in Ireland and superintendent of an insane asylum, and Scottish-born Elizabeth (née Clark). His elder brother, Billy, also played Test cricket for Australia and his younger brother, Thomas, was a public servant who served as Secretary for the Department of Defence from 1918 to 1927, and then official secretary to the High Commissioner for Australia in London.
Trumble spent part of his early life in the western Victorian town of Ararat before returning to Melbourne, settling in suburban Camberwell. He was educated at Hawthorn Grammar School and played his early cricket for Kew Cricket Club. Encouraging his sons' early love of cricket, William Trumble—a keen cricketer who bowled leg breaks for South Melbourne Cricket Club—set out a cricket pitch at the family home. He placed a feather on a good length and urged his sons to aim at it when bowling. Known for his accuracy, Hugh later said, "Of course I couldn't repeatedly hit the feather, but I soon reached the stage when I was always pretty close to it"
Trumble transferred to the Melbourne Cricket Club for the 1887–88 cricket season and was an immediate success. He took 36 wickets that season, finishing with an average of 6.77 runs per wicket; the best in the club, beating his teammate and Australian Test bowler Fred Spofforth. He made his first-class cricket debut for Victoria that same season, selected to play against a touring English XI led by Middlesex batsman George Vernon. His first match for Victoria against Australian opposition was against New South Wales at the Melbourne Cricket Ground. Bowling with Spofforth, in the first innings Trumble took seven wickets for 52 runs.
Test cricket
Early struggle
Early in the 1889–90 Australian season, Trumble endured a period where he was not able to take wickets consistently. With selection of the Australian team to tour England in 1890 due at this time, Trumble was anxious about this poor run of form. Noting his anxiety while playing, a friend offered him a beer during the lunch break to revive his spirits. Previously a teetotaler, Trumble enjoyed his first taste and ordered another before re-entering the field of play. Feeling relaxed, although wondering about his steadiness of step, Trumble took a succession of wickets to ensure his selection in the Australian team. Trumble finished the season with 27 wickets at an average of 14.20 per wicket.
The 1890 Australian team touring England was relatively inexperienced. The team missed the all-round ability of George Giffen, who had refused to join the squad, thinking it unlikely the tour would be a sporting or financial success. The Australians won 13 matches on tour, losing 16 and drawing 9. Trumble made his Test cricket debut in the First Test against the English team at Lord's Cricket Ground. He took only one wicket, dismissing Bobby Peel caught and bowled for 1. Batting at number eleven in the first innings he made 1 not out and in the second, 5 runs batting at number ten. Despite this lack of success, he retained his spot in the team for the Second Test at The Oval where he failed to take a wicket. He was selected for the Third Test at Old Trafford but continuous rain saw the match abandoned without a ball being bowled. Trumble played 28 first-class matches during the tour, scoring 288 runs at an average of 8.47 and took 52 wickets at an average of 21.75. Wisden Cricketers' Almanack wrote, "Reports from Australia had led us to expect a great deal of ... Trumble" but his "straightness and regular length [were] insufficient to compensate for an obvious lack of 'devil' and variety".
Trumble was not selected for the Australian team to play Lord Sheffield's touring English team in 1891–92. He did not return to the Australian team until his selection in the squad to tour England in 1893. Before the Test matches he took 14 wickets for 116 runs (14/116) against the Players followed by 12/84 against Kent at Gravesend. He played in all three Test matches in 1893, taking 6 wickets at an average of 39.00. Trumble scored 58 runs in the Tests with a highest score of 35 but had more success in the other matches, scoring 774 runs, including one century in all first-class matches on tour. Wisden noted that "An immense improvement on his form of three years before was shown by Hugh Trumble, who bowled consistently well all through the tour" and "... the reports of Hugh Trumble's improvement in batting were amply borne out, his hitting in many matches being remarkably fine".
When Andrew Stoddart's English team visited Australia in 1894–95, Trumble played only one Test, the Second at the Melbourne Cricket Ground. In the first innings, England scored 75 runs with Trumble taking 3 wickets. England fought back in their second innings, scoring 475 runs to win the Test by 94 runs; Trumble failed to take a wicket.
Established cricketer

Trumble was selected in the Australian team to tour England in 1896, despite a poor domestic season in 1895–96 that saw his place in the touring squad seriously questioned by pundits. The leading cricket journalist, Tom Horan said that as much as he personally liked Trumble, he could not see him as a member of a team for the England tour that season. It was, however, during this tour that Trumble finally established a permanent place in the Australian line up. Wisden said of Trumble when listing him as one of its Cricketers of the Year, "...it was not until his third visit, during the past season, that Trumble convinced Englishmen he was entitled to rank among the great bowlers of Australia". In that season, Trumble took 148 wickets at an average of 15.81. He was seen as Australia's leading bowler who "was able to inspire [the English] batsmen with a feeling of apprehension". Wisden's summary of the 1896 Australian tour said of Trumble, "His great strength lay in the combination of spin with extreme accuracy" and "he was on all wickets distinctly the best bowler on the [Australian] side".
England won the First Test at Lord's by 6 wickets, Trumble taking one wicket in each innings. The Second Test at Old Trafford was more closely fought. Despite K. S. Ranjitsinhji scoring a "marvellous" 154 and Tom Richardson "bowling in his finest form" the Australians managed to hold on for a 3 wicket victory. The Australians required 125 runs to win in their second innings and were expected to make this target easily. Richardson's skilful bowling however saw Trumble and Kelly batting together with only 3 wickets in hand but with 25 runs still to make. Against excellent bowling and in a tense atmosphere, the pair managed to bat Australia home with the last runs taking an hour to score, mainly in singles. Trumble made 17 not out to follow his 24 runs in the first innings and his 4 wickets. With the series tied at one Test apiece, the Third and final Test was played at The Oval in London. On a pitch damaged by rain, the English batted first and were dismissed for 145. Trumble took 6 wickets for 59 runs, including a 9-over spell of 5 wickets for 10 runs. England fought back to bowl the Australians out for 119. In turn, the Australians restricted England to 84 runs with Trumble taking 6 wickets for 30, to leave Australia requiring 111 runs in their second innings to win the match. Bobby Peel and Jack Hearne combined to bowl Australia out for 44 runs to win the Test by 66 runs and retain the Ashes for England . In the three Tests, Trumble took 18 wickets at an average of 18.83 runs per wicket.
Trumble played in every Test of the 1897–98 series against the touring English, who were again captained by Stoddart. England won the First Test in Sydney by 9 wickets with Trumble's 70 runs the highest score in the Australian first innings. Under the captaincy of Harry Trott, Australia fought back to win the Second Test in Melbourne by an innings and 55 runs. Trumble took 8 wickets in the match and in partnership with Monty Noble bowled the English out for 150 runs in the second innings. Australia won the Third Test in Adelaide by an innings and 13 runs; Trumble made 37 runs in the Australian innings and took 1 wicket for the match. In the Fourth Test, Trumble combined with Clem Hill in a 165 run partnership for the seventh wicket, described by Wisden as the turning point in the innings. Australia won the match by 8 wickets. Australia won the Fifth Test and the series four Tests to one. For the series overall, Trumble took 19 wickets at an average of 28.15 runs per wicket and scored 170 runs at an average of 36.20.
The 1899 Australian tour saw Trumble score 1,183 runs and take 142 wickets; he was only the second Australian, after George Giffen, to score 1,000 runs and take 100 wickets in an English season as part of a touring team. In the Test series, Trumble took 15 wickets at an average of 25.00 and made 232 runs at an average of 38.66. Wisden said of Trumble's batting that season, "[Trumble] played so consistently well as to make it clear that if he had not been a bowler he would have been a great batsman". Dry pitches saw his bowling average fall off a little from the 1896 tour but Wisden stated that he "bowled quite as well as in 1896" and "[he] never seemed easy to hit, and whenever the ground gave him least advantage ... he was deadly". Australia won the Second Test by 10 wickets and with the other Tests finishing in draws, they retained the Ashes in a one Test to nil series victory. Trumble played particularly well in the Third Test at Headingley, where he took 5 wickets for 60 runs and was the highest run-scorer in the Australian second innings with 56.
Hat-tricks and captaincy
At the age of 34, Trumble was chosen to captain the Australian team against England in 1901–02 when Joe Darling withdrew to manage his farm in Tasmania after the first three Tests. Australia won the two remaining Tests—the only occasions that Trumble would captain his country in Test cricket—to win the series four Tests to one. Earlier, in the Second Test at the Melbourne Cricket Ground, Trumble took a "hat-trick"; only five hat-tricks had been taken in the previous 24 years of Test cricket. He dismissed Arthur Jones, John Gunn and Sydney Barnes in successive balls to complete an Australian victory by 229 runs. In the Third Test in Adelaide, Trumble captured 6 wickets for 74 runs in the England second innings and made 62 not out to help the Australians win the match by 4 wickets. After this success with the bat, Trumble—in his new role as captain—promoted himself to open the batting alongside Victor Trumper. He made only 6 runs, handing the opening batsman role to Reggie Duff for the second innings. Australia won the Test by 7 wickets with Trumble not required to bat a second time. In the Fifth Test, again in Melbourne, Trumble took 5 wickets for 62 runs to help restrict England to a lead of 45 runs after the first innings. In the second innings Trumble took another 3 wickets and, combined with Noble's 6 wickets, helped Australia win by 32 runs. Trumble and Noble were the most successful Australian bowlers during the series. Together they took 60 wickets in the Tests: Noble 32 at an average of 19.00 and Trumble 28 at an average of 20.03.

Trumble's last cricketing tour of England was in 1902, with Darling returning to captain the Australian team. Early in the tour, Trumble broke his thumb at practice, causing him to miss the first month of the English season. Despite this, when he returned for the final three Tests he took 26 wickets. In the Fourth Test at Old Trafford, Trumble took 10 wickets. This included 6 wickets in the second innings when he combined with Jack Saunders to bowl England out for 120; securing an Australian victory by 3 runs. Trumble, recalling his final over of the match, said "With the ball greasy [wet] and my boots unable to get a proper foothold on slippery turf, it was the most trying over I ever bowled." In the Fifth Test at The Oval, Trumble made 64 runs in the first innings and followed this with 8 wickets for 65 runs in the English first innings. He took another 4 wickets in the English second innings, but this was not sufficient to prevent an English victory by one wicket. Darling bowled Trumble unchanged from the Pavilion end throughout both innings of the match. Wisden praised Trumble's bowling saying "Trumble, paying us his fifth visit, bowled perhaps better than ever", but remarked that "it must be said that the wet weather and soft wickets were all in his favour"
After playing in one Test match against the South African team on a stopover when returning from England to Australia, Trumble retired from Test cricket, aged 35. When Australia lost to the English tourists in the First Test in Sydney in 1903–04, Trumble was persuaded to return for the Second Test under the captaincy of Noble. He was immediately successful taking 4 wickets for 107 runs in the first innings and 5 for 34 in the second, but was unable to prevent England from winning the Test by 185 runs Selected for the remaining four Tests, his 24 wickets in four Tests made Trumble the most successful Australian bowler in the series. The writer Roland Perry described Trumble's final Test match as "the most dramatic and memorable farewell performance ever by a bowler". In front of his home town supporters in Melbourne, he took 7 wickets for 28 runs, including a hat-trick, to bowl Australia to victory; Wisden describing his bowling in the second innings as "practically unplayable". The hat-trick, his second in Test cricket, consisted of the dismissals of Bernard Bosanquet, Plum Warner and Dick Lilley on 7 March. He went on to take the wicket of Ted Arnold, ending the match and his career in international cricket.
Style and personality
Always the same, whether on the winning or the losing side, Hugh Trumble is ... one of the most popular of Australian cricketers.
— Wisden Cricketers' Almanack,
Trumble was tall and thin, 6 feet 4 inches (193 cm) in height. His long face featured prominent ears and a large nose, while his long arms and uncommonly long and strong fingers assisted his bowling. The cricket writer Ray Robinson said of Trumble: "El Greco, with his lengthening touch would have liked to draw Trumble. Hugh's lantern shaped head set on a column of a neck would have given the Spaniard a halfway start." English cricketer and author Plum Warner called him "That great camel, Hughie Trumble."

When bowling, Trumble made the most of his height, bringing the ball over the full extent of his right arm. His action was described by his team-mate and bowling partner, Monty Noble, as "sidelong and insinuating, with his neck craned like a gigantic bird". He bowled off spinners with an impeccable length at medium pace and was able to swing the new ball. He had a well-disguised slower ball, hoodwinking batsmen such as Stanley Jackson, who said, "You old devil. You get me caught-and-bowled whenever you like but I'll pick that slow one sooner or later." He preferred English pitches, saying he hardly saw one on which he could not get some turn and the temperate weather allowed him to bowl all day. In Australia, Trumble had to work harder for his wickets on firmer pitches, relying on his change of pace and consistent accuracy; he claimed he could land the ball on a saucer 17 metres (19 yd) away five times out of six. Johnnie Moyes named him as an "immortal of the art" who succeeded by "attacking the batsman's strength". W. G. Grace called him "the best bowler Australia has sent us". While Trumble was able to score 1,183 runs during the 1899 tour of England, the demands of bowling did not allow him to consistently score heavily. His long, prehensile fingers helped him make a reputation as a fine slips fieldsman and he was the first to take 20 catches in an Australian season. English cricketer Johnny Douglas said, "Trumble should not be allowed on the cricket field—his natural place would be up trees in the bush." He practised slip fielding by catching a tennis ball thrown against a brick wall; he believed this practise trained him not to "snatch" at the ball but allow it to fall into his safe hands.
Trumble was known for his cleverness on the field. C. B. Fry said of him, "He is the most long-headed, observant and acute judge of the game, a perfect master of the whole art of placing fieldsmen and changing bowlers." On one occasion when captaining his state side, Victoria, he deliberately bowled two wides that his fieldsmen allowed to roll to the boundary to score four runs for his opponents. This was done to save his tired bowlers from having to bowl again immediately, as his opponents would have been required to follow-on (bat twice in a row), at the time compulsory. When questioned by an onlooker about the dubious sportsmanship of the action, he replied, "I had to do it, old chap, but I wonder what my father will think of it?" Trumble was respected by his teammates and opponents; New Zealand cricketer, Dan Reese, who played against and alongside Trumble said, "His subtle humour, his fund of cricket stories, his kindness, and, above all, his judgment, made him a man of exceptional character."
He was popular with team-mates and opponents alike, with a weakness for practical jokes. On board a ship travelling to England, Trumble offered to coach unsuspecting fellow travellers in various deck sports such as quoits. Accepting Trumble's advice, they were made to contort themselves into a number of ludicrous positions to the amusement of his team-mates and other onlookers in the know. To prolong the joke, in his own games Trumble would adopt the same peculiar stance and method he advocated.
Legacy and statistical analysis
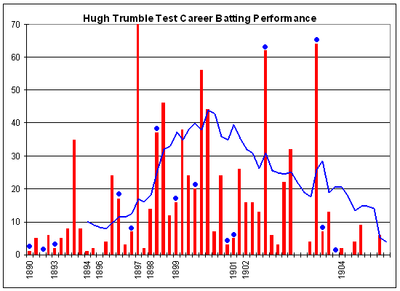
"The first of the great off spinners of the Test-match age", in 32 Tests, Trumble took 141 wickets at an average of just over 20 runs per wicket. He took 5 wickets in an innings on nine occasions and 10 wickets in a match three times. On retirement, he had taken more wickets in Test cricket than any other player; a record he held for nearly 10 years until surpassed by Sydney Barnes. It wasn't until Dennis Lillee 75 years later that anyone was able to better Trumble's 141 wickets against England. While mainly a bowler, Trumble batted well enough to make 851 runs in Test cricket at an average of 19.79 with a highest score of 70. Trumble was also prolific at first-class level. He took 929 wickets, including 5 wickets in an innings on 69 occasions, and as a batsman, he made 5,395 runs with three centuries and a highest score of 107. For Melbourne Cricket Club, he took just under 400 wickets and scored more than 3,000 runs; winning the club best bowling average on six occasions and the best batting average once.
Trumble was particularly effective in England. After taking 52 wickets on his first tour of England in 1890, his other four visits to England—in 1893, 1896, 1899 and 1902—saw him take over 100 wickets in first-class matches. In 1899, he scored 1,183 runs making him one of only four Australians, with George Giffen, Warwick Armstrong (both three times) and Jack Gregory, to take over 100 wickets and make over 1,000 runs on a tour of England.
The ICC player rankings have been applied retrospectively to cricket history and Trumble achieved the top ranking as a bowler. By June 1896, he was ranked fifth in the world and never again slipped lower; from 1899 until his retirement he was the first or second best bowler in the world according to the ratings. As a batsman, Trumble's ranking peaked at twelfth in the world after the Third Test in Adelaide in 1901–02.
Trumble was the first player to take two hat-tricks in Test cricket. Both hat-tricks were taken against England at the Melbourne Cricket Ground, where Trumble played his club cricket. Hat-tricks are extremely rare; in over 131 years of Test cricket to March 2008, there had only been 37 Test hat-tricks and only Jimmy Matthews and Wasim Akram been able to repeat Trumble's feat of taking a second.
Off the playing field

Trumble joined the National Bank of Australasia in 1887 to begin a career in banking. While the bank often allowed him time to practice, his frequent absences with cricket meant his career progression was slow; after each of his five tours of England he returned to find junior bank officers promoted over him. Nevertheless, he was appointed accountant at the Richmond branch in 1903 and after his retirement from cricket in 1908, manager of the Kew branch.
A loyal clubman, Trumble served on the committee of the Melbourne Cricket Club (MCC) from 1900–01 to 1910–11 and was made a life member in 1904. In 1911 he resigned from the bank to become MCC club secretary; a position he held for 27 years until his death. In this role, he played a leading part in reconciling the club and the Victorian Cricket Association after a period of some friction between the two bodies. He was instrumental in attracting quality cricketers to the club including Bert Ironmonger, whom Trumble saw play on a visit to Queensland. During his term as secretary, the Melbourne Cricket Ground was expanded to a capacity of over 70,000 spectators.
Trumble was a prominent writer about and elder statesman of the game and was conspicuous in his support for journalists calling at any hour. From time to time, Trumble acted as a selector of the Victorian cricket team. In 2001, Trumble was selected in the Melbourne Cricket Club Team of the Century, and in 2004 he was inducted into the Australian Cricket Hall of Fame for his contribution to the sport in Australia.
In 1899, aged 31, Trumble met and fell in love with Florence Christian, aged 19 from Queensland. The couple were married in 1902, with the wedding timed to allow a honeymoon trip accompanying the Australian cricket tour of England. An injury to his thumb freed Trumble from cricket commitments for a while, to his new wife's delight. Together, the couple had eight children; six sons and two daughters. One son, Robert, a renowned musician and writer, dedicated his first book, The Golden Age of Cricket, to his father. Trumble died aged 71, from a heart attack in his home in the Melbourne eastern suburb of Hawthorn.
References
Citations
- ^ Pierce, Peter (1990). "Trumble, Hugh (1867–1938)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Canberra: National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. ISBN 978-0-522-84459-7. ISSN 1833-7538. OCLC 70677943. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ^ Hyslop, Robert (1990). "Trumble, Thomas (1872–1954)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Canberra: National Centre of Biography, Australian National University. ISBN 978-0-522-84459-7. ISSN 1833-7538. OCLC 70677943. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ^ In the Australian government, a departmental secretary such as the Secretary of the Department of Defence is the senior public servant in a government department; as opposed to the Minister for Defence, a political position. See Australian Public Service#Organisational Structure for further detail on the split between the two roles.
- ^ Fiddian, Marc (1992). "Hugh Trumble". extract from Australian All-Rounders – From Giffen to Gilmour. Victorian Premier Cricket. Archived from the original on 22 July 2008. Retrieved 17 February 2008.
- ^ Perry, pp. 90–93.
- ^ Reese, Daniel (1948). Was It All Cricket?. London: George Allen and Unwin. p. 71.
- ^ "Victoria v GF Vernon's XI: GF Vernon's XI in Australia 1887/88". CricketArchive. Retrieved 17 February 2008.
- ^ "Victoria v New South Wales: Other First-Class matches 1887/88". CricketArchive. Retrieved 17 February 2008.
- ^ Robinson, pp. 88–94.
- ^ "First-class Bowling in Each Season by Hugh Trumble". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ Pollard (1988), p. 405.
- ^ Robinson, p. 62.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1890 (1st Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1890 (2nd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "The Ashes – 3rd Test 1890 season: England v Australia". Cricinfo. 1891. Retrieved 3 May 2008.
- ^ "First-class Batting and Fielding for Australians: Australia in England 1890". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "First-class Bowling for Australians: Australia in England 1890". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "The Australians in England, 1890". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1891. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "The Australians in England, 1893". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1894. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "Players v Australians: Australia in England 1893". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "Kent v Australians: Australia in England 1893". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "Test Bowling for Australia: Australia in England 1893". CricketArchive. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "Test Batting and Fielding for Australia: Australia in England 1893". CricketArchive. Retrieved 3 May 2008.
- ^ "First-class Batting and Fielding for Australia: Australia in England 1893". CricketArchive. Retrieved 3 May 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: AE Stoddart's XI in Australia 1894/95 (2nd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "Cricketer of the year – 1897: Hugh Trumble". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1897. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "The Australians in England, 1896". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1897. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "First-class Bowling for Australians: Australia in England 1896". CricketArchive. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1896 (1st Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "Second Test: England v Australia 1896". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1897. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1896 (2nd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "Third Test: England v Australia 1896". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1897. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1896 (3rd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "Test Bowling for Australia: Australia in England 1896". CricketArchive. Retrieved 5 April 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: AE Stoddart's XI in Australia 1897/98 (1st Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: AE Stoddart's XI in Australia 1897/98 (2nd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: AE Stoddart's XI in Australia 1897/98 (3rd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 4 May 2008.
- ^ "Fourth Test: Australia v England 1897–98". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1899. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Australia 4 England 1: England in Australia, 1897–98". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1899. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Test Bowling for Australia: AE Stoddart's XI in Australia 1897/98". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Test Batting and Fielding for Australia: AE Stoddart's XI in Australia 1897/98". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Test Bowling for Australia: Australia in England 1899". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Test Batting and Fielding for Australia: Australia in England 1899". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Pardon, Sydney (1900). "The Australians in England, 1899". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1899 (3rd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ "Test matches: Hat-tricks". Cricinfo Records. Cricinfo. Retrieved 3 May 2008.
- ^ Meher-Homji, p. 28.
- ^ "Australia v England: AC MacLaren's XI in Australia 1901/02 (3rd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: AC MacLaren's XI in Australia 1901/02 (4th Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: AC MacLaren's XI in Australia 1901/02 (5th Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Test Bowling for Australia: AC MacLaren's XI in Australia 1901/02". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Robinson, p. 84. "The 1902 team was widely recognised as such not only its own batting, bowling and fielding merits, but because it met England at full strength."
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1902 (4th Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "England v Australia: Australia in England 1902 (5th Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Fifth Test match: England v Australia 1902". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1903. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "The Australians in England 1902". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1903. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: Marylebone Cricket Club in Australia 1903/04 (2nd Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ "Australia v England: Marylebone Cricket Club in Australia 1903/04 (5th Test)". CricketArchive. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ "Fifth Test match: Australia v England 1903–04". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1905. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Pollard (1988), pp. 1069–1071.
- ^ "Obituary: Hugh Trumble". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack – online archive. John Wisden & Co. 1939. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ "Statsguru – H Trumble – Test matches – All-round analysis". Cricinfo. Retrieved 15 April 2008.
- ^ Martin-Jenkins, Christopher (4 December 2007). "The greatest match-winner despite that freakish action". London: The Times. Retrieved 1 October 2024.
- ^ "Hugh Trumble". CricketArchive. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Basevi, Travis; Binoy, George (29 November 2005). "A record Bradman never had". Cricinfo Magazine. Cricinfo. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Steen, Rob (24 January 2008). "The men with the most". The Wisden Cricketer. Cricinfo. Retrieved 3 May 2008.
- ^ Williams, Ken (2000). "For Club and Country" (PDF). Melbourne Cricket Club. pp. 27–28. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ "Hugh Trumble Bowling Test Ranking Statistics". LG ICC Rankings. Retrieved 6 May 2008.
- ^ "Hugh Trumble Batting Test Ranking Statistics". LG ICC Rankings. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ Searle, Percival (1949). "Trumble, Hugh (1867–1938)". Dictionary of Australian Biography. Angus and Robertson. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
- ^ Haigh, p. 200.
- ^ "2000–01 Cricket News – MCC Team of the Century". Melbourne Cricket Club. Archived from the original on 21 August 2006. Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- ^ "Australian Cricket Hall of Fame: Inductees". Melbourne Cricket Ground. Archived from the original on 20 May 2013. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ^ Thompson, Anne (15 March 2004). "A past master". The Age. Retrieved 10 April 2008.
Bibliography
- Haigh, Gideon (2001). The Big Ship: Warwick Armstrong and the making of modern cricket. Melbourne: Text. ISBN 1-877008-84-2.
- Meher-Homji, Kersi (1995). Hat-Tricks. Sydney: Kangaroo Press. ISBN 0-86417-736-4.
- Perry, Roland (2003). Captain Australia: A history of the celebrated captains of Australian Test cricket. Sydney: Random House Australia. ISBN 1-74051-174-3.
- Pollard, Jack (1986). The pictorial history of Australian cricket (revised ed.). Melbourne: JM Dent. ISBN 0-86770-043-2.
- Pollard, Jack (1988). Australian Cricket: The game and the players. Sydney: Angus & Robertson. ISBN 0-207-15269-1.
- Robinson, Ray; Haigh, Gideon (1996). On top down under: Australia's cricket captains (revised ed.). Adelaide: Wakefield. ISBN 1-86254-387-9.
External links