Lapurdi
Labourd extends from the Pyrenees to the river Adour, along the Bay of Biscay. To the south are Gipuzkoa and Navarre in Spain, to the east is Lower Navarre, and to the north are the Landes. It has an area of almost 900 km (347 sq mi) and a population of over 200,000 (115,154 in 1901; 209,913 in 1990), making it the most populous of the three French Basque provinces. Over 25% of the inhabitants speak Basque (17% in the Bayonne-Anglet-Biarritz zone, 43% in the rest). Labourd has also long had a Gascon-speaking tradition, notably along the banks of the river Adour but also more diffusely throughout the whole viscounty (about 20% in Bayonne-Anglet-Biarritz).
The main town of Labourd is Bayonne, although the capital up to the French Revolution was Ustaritz, 13 km away, where local Basque leaders assembled. Other important towns are Biarritz, Anglet (between Bayonne and Biarritz), Hendaye, Ciboure and Saint-Jean-de-Luz along the coast, and Hasparren inland. The area is famous for the five-day Fêtes de Bayonne and the red peppers of Espelette. Many tourists come to the coast, especially to Biarritz, and to the hills and mountains of the interior for walking and agri-tourism. La Rhune (Larrun in Basque), a 900 m high mountain, lies south of Saint-Jean-de-Luz on the border with Spain.
The traditional buildings of Labourd have low-roofed, half-timbered features, stone lintels, and red, white and green paint. The house of Edmond Rostand, Villa Arnaga at Cambo-les-Bains, is such a house and is now a museum dedicated to the author of Cyrano de Bergerac and to Basque traditions.
Lapurdian (Lapurtera) is a dialect of the Basque language spoken in the region.
History
Ancient Labourd was inhabited by the Tarbelli, an Aquitanian tribe. They had the fortified town of Lapurdum, which eventually would become modern Bayonne and give its name to the region.
In the Middle Ages, it formed part of the Duchy of Vasconia, which eventually came to be called Gascony.
After the early 9th century, the area of the river Adour was referred to as the County of Vasconia. According to many authorities, Duke Sancho VI of Gascony ceded Labourd and its ports, Bayonne and Biarritz, to King Sancho III of Navarre around 1023, and Sancho in turn bestowed it on his majordomo, Lope Sánchez, as viscount. This Lope was supposedly the king's relative, being a nephew of King Ramiro Garcés of Viguera. This oft-repeated story has no basis in contemporary documents, and there is no evidence that Navarre extended its territory north of the Pyrenees prior to the late 12th century.
Around 1125, Bayonne was chartered by Duke William IX of Aquitaine. In 1130–31, King Alfonso the Battler of Aragon and Navarre attacked Bayonne over a dispute on jurisdictions with the Duke of Aquitaine, William X the Saint.
Labourd was ruled directly, between 1169 and 1199, by Richard Lionheart, who gave a second charter to Bayonne c. 1174 and, c. 1175, returning to the merchants of this city the duties they paid in the tolls of Poitou, Aquitaine and Gascony. This caused an uprising of Gascons and Basques (including Labourdins from outside Bayonne), but Richard defeated all the cities that had revolted.
Richard married the Navarrese princess Berengaria of Navarre in 1191, which favored the trade between Navarre and Bayonne (and England). This marriage also included a jurisdictional transaction that shaped the borders of the Northern Basque Country: Lower Navarre was definitively annexed to Navarre, while Labourd and Soule remained as parts of Angevin Aquitaine. This pact was materialized in 1193 in form of the sale of their rights by the legitimate viscounts of Labourd, who had established their seat in Ustaritz. From that point, Ustaritz was the capital of Labourd, instead of Bayonne, until the suppression of the province in 1790.
John I of England, gave to Bayonne the Municipal Law, that created the figures of mayor, 12 jurors, 12 councilors and 75 advisors.
Labourd passed to French hands in 1451, just before the end of the Hundred Years' War. Since then and until the French Revolution, Labourd was largely self-ruled as an autonomous French province.
In 1610, Labourd suffered a major witch-hunt at the hands of the judge Pierre de Lancre after feuds between the elites (merchant bourgeoisie vs nobility) and different social layers (nobility vs common people) took a turn for the worse over elements of superstition and alleged public morality, which ended up with some 70 supposed sorginak burnt at the stake (see Basque witch trials).
In 1790, France suppressed the historical provinces, including Labourd, incorporating them into the newly created département of Basses-Pyrénées, together with Béarn. Dominique Joseph Garat and his older brother were then representing the Biltzar (Assembly) of Labourd's third estate in Paris. Like the other Basque representatives, he opposed the new administrative layout (but eventually voted for it) and the inclusion of the Basques in the same department with Bayonne and Béarn.
During the War of the Pyrenees, Labourd had its customary trade with the Southern Basque Country interrupted, and was shaken by indiscriminate repression unleashed by the Convention (1793-1794) resulting in mass deportation to the Landes of Gascony, seizure of landholdings, and the death of an estimated 1,600 civilians from the bordering towns of Sara, Itxassou, Ascain, Biriatu, etc. The abuses included the establishment of new, alien names to the villages and towns of Labourd, but they were soon after reverted to their usual names.
In the last decades, petitions have asked for the separation from Béarn and the creation of a Basque département, together with the other two historical Basque provinces of Lower Navarre and Soule.
-
Status of French customs in 1732 roughly clinging to linguistic boundaries; Labourd including Bayonne shows an autonomous fiscal system
-
Aerial view over northern Labourd from Mount Baigura
-
Ainhoa village houses showing some aspects of traditional Basque architecture
Mariner activities
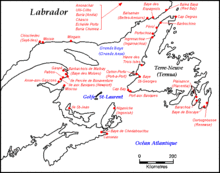
(click to enlarge)
Labourd, like the other coastal territories of the Basque Country, played an important role in early European exploitation of the Atlantic Ocean.
The earliest document (a bill) that mentions the whale oil or blubber dates from 670. In 1059, Labourdin whalers already gave to the viscount the oil of the first captured animal. It seems that Basques disliked the taste of whales but made good business selling their meat and oil to the French, Castilian and Flemish. Basque whalers used for this activity the longboats known as traineras, that only allowed whaling near the coast or based in a larger ship.
It seems that it was this industry, along with cod-fishing, is what brought Basque sailors to the North Sea and eventually to Newfoundland. Basque whaling in Newfoundland and Labrador began in the 1530s. By at least the early 17th century Basque whalers had reached Iceland.
The development of the rudder in Europe seems also a Basque and specifically Labourdine development. Three masted ships appear in a fresco of Estella (Navarre), dating to the 12th century, seals preserved in the Navarrese and Parisian historical archives also show similar ships. The rudder itself is first mentioned as steer "a la Navarraise" or "a la Bayonaise".
After Navarre lost San Sebastian and Hondarribia to Castile in 1200, it signed a treaty with Bayonne that made it the "port of Navarre" for nearly three centuries, a role that extended also into the Early Modern Age, after Navarre had been annexed by Castile (but both provinces remained autonomous).
See also
Notes
- ^ Gonzalo Martínez Díez, Sancho III el Mayor (Madrid: Marcial Pons Historia, 2007), pp. 114–15.
- ^ This created the strange situation that befell a string of villages hemmed in-between the new Labourd, the new Lower Navarre, Bearn and the province of Lannes, Sames, Bidache, Guiche and to a lesser extent Came, which lasted about four centuries
References
- Urzainqui, Tomás, and Olaizola, Juan M. de (1998). La Navarra marítima. Pamiela. ISBN 84-7681-284-1.
External links
 Media related to Labourd at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Labourd at Wikimedia Commons



