Maurice (emperor)
Maurice's reign was troubled by almost constant warfare. After he became emperor, he brought the war with Sasanian Persia to a victorious conclusion. The empire's eastern border in the South Caucasus was vastly expanded and, for the first time in nearly two centuries, the Romans were no longer obliged to pay the Persians thousands of pounds of gold annually for peace.
Afterward, Maurice campaigned extensively in the Balkans against the Avars—pushing them back across the Danube by 599. He also conducted campaigns across the Danube, the first Roman emperor to do so in over two centuries. In the west, he established two large semi-autonomous provinces called exarchates, ruled by exarchs, or viceroys of the emperor. In Italy Maurice established the Exarchate of Italy in 584, the first real effort by the empire to halt the advance of the Lombards. With the creation of the Exarchate of Africa in 591 he further solidified the power of Constantinople in the western Mediterranean.
Maurice's successes on battlefields and in foreign policy were counterbalanced by mounting financial difficulties of the empire. Maurice responded with several unpopular measures which alienated both the army and the general populace. In 602, a dissatisfied officer named Phocas usurped the throne, having Maurice and his six sons executed. This event would prove a disaster for the empire, sparking a twenty-six-year war with a resurgent Sassanid Persia which would leave both empires devastated prior to the Muslim conquests.
Maurice's reign is a relatively well-documented era of late antiquity, in particular by the historian Theophylact Simocatta. The Strategikon, a manual of war which influenced European and Middle Eastern military traditions for well over a millennium, is traditionally attributed to Maurice.
Life
Origins and early life
Maurice was born in Arabissus in Cappadocia in 539. His father was Paul. He had one brother, Peter, and two sisters, Theoctista and Gordia, the latter of whom was later the wife of the general Philippicus. He is recorded to have been a native Greek speaker, unlike the previous emperors since Anastasius I Dicorus. Sources call him a native Cappadocian Greek and the first emperor "from the race of the Greeks".
Maurice first came to Constantinople as a notarius to serve as secretary to Tiberius, the comes excubitorum (commander of the Excubitors, the imperial bodyguard). When Tiberius was named Caesar in 574, Maurice was appointed to succeed him as comes excubitorum.
Persian War and accession to the throne

In late 577, despite a complete lack of military experience, Maurice was named as magister militum per Orientem, effectively commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army in the east. He succeeded General Justinian in the ongoing war against Sassanid Persia. At about the same time he was raised to the rank of patrikios, the empire's senior honorific title, which was limited to a small number of holders.
In 578, a truce in Mesopotamia came to an end and the main focus of the war shifted to that front. After Persian raids in Mesopotamia, Maurice mounted attacks on both sides of the Tigris, captured the fortress of Aphumon and sacked Singara. Sassanid emperor Khosrow sought peace in 579, but died before an agreement could be reached and his successor Hormizd IV (r. 579–590) broke off the negotiations. In 580, Byzantium's Arab allies the Ghassanids scored a victory over the Lakhmids, Arab allies of the Sassanids, while Byzantine raids again penetrated east of the Tigris. Around this time the future Khosrow II was put in charge of the situation in Armenia, where he succeeded in convincing most of the rebel leaders to return to Sassanid allegiance, although Iberia remained loyal to the Byzantines.
The following year an ambitious campaign by Maurice, supported by Ghassanid forces under al-Mundhir III, targeted Ctesiphon, the Sassanid capital. The combined force moved south along the river Euphrates accompanied by a fleet of ships. The army stormed the fortress of Anatha and moved on until it reached the region of Beth Aramaye in central Mesopotamia, near Ctesiphon. There they found the bridge over the Euphrates destroyed by the Persians.
In response to Maurice's advance, Sassanid general Adarmahan was ordered to operate in northern Mesopotamia, threatening the Roman army's supply line. Adarmahan pillaged Osrhoene, and was successful in capturing its capital, Edessa. He then marched his army toward Callinicum on the Euphrates. With the possibility of a march to Ctesiphon gone Maurice was forced to retreat. The retreat was arduous for the tired army, and Maurice and al-Mundhir exchanged recriminations for the expedition's failure. However, they cooperated in forcing Adarmahan to withdraw, and defeated him at Callinicum.
The mutual recriminations were not laid to rest by this. Despite his successes, al-Mundhir was accused by Maurice of treason during the preceding campaign. Maurice claimed that al-Mundhir had revealed the Byzantine plan to the Persians, who then proceeded to destroy the bridge over the Euphrates. The chronicler John of Ephesus explicitly calls this assertion a lie, as the Byzantine intentions must have been plain to the Persian commanders.
Both Maurice and al-Mundhir wrote letters to Emperor Tiberius, who tried to reconcile them. Maurice visited Constantinople himself, where he was able to persuade Tiberius of al-Mundhir's guilt. The charge of treason is almost universally dismissed by modern historians; Irfan Shahîd says that it probably had more to do with Maurice's dislike of the veteran and militarily successful Arab ruler. This was compounded by the Byzantines' habitual distrust of the "barbarian" and supposedly innately traitorous Arabs, as well as by al-Mundhir's staunchly Monophysite faith. Al-Mundhir was arrested the following year on suspicion of treachery, triggering war between Byzantines and Ghassanids and marking the beginning of the end of the Ghassanid kingdom.

In June of 582 Maurice scored a decisive victory against Adarmahan near Constantina. Adarmahan barely escaped the field, while his co-commander Tamkhosrau was killed. In the same month Emperor Tiberius was struck down by an illness which shortly thereafter killed him. In this state Tiberius initially named two heirs, each of whom was to marry one of his daughters. Maurice was betrothed to Constantina, and Germanus, related through blood to the great emperor Justinian I, was married to Charito. It appears that the plan was to divide the empire in two, with Maurice receiving the eastern provinces and Germanus the western.
According to John of Nikiû, Germanus was Tiberius' favored candidate for the throne but declined out of humility. On 5 August, Tiberius was on his deathbed and civilian, military and ecclesiastical dignitaries awaited the appointment of his successor. He then chose Maurice and named him Caesar, after which he adopted the name "Tiberius". Maurice was crowned emperor soon after, on 13 August. Tiberius had reportedly prepared a speech on the matter but at this point was too weak to speak. The quaestor sacri palatii (the senior judicial official of the empire) read it for him. The speech proclaimed Maurice as Augustus and sole successor to the throne. On 14 August 582 Tiberius died and his last words were spoken to his successor: "Let my sovereignty be delivered to thee with this girl. Be happy in the use of it, mindful always to love equity and justice." Maurice became sole emperor, marrying Constantina in the autumn.
Shortly after his ascension the advantage he had gained at the Battle of Constantina was lost when his successor as magister militum of the east, John Mystacon, was defeated at the River Nymphios by Kardarigan. The situation was difficult: Maurice ruled a bankrupt Empire; it was at war with Persia; he was paying extremely high tribute to the Avars, 80,000 gold solidi a year; and the Balkan provinces were being thoroughly devastated by the Slavs.

Maurice had to continue the war against the Persians. In 586 his troops defeated them at the Battle of Solachon south of Dara. In 588, a mutiny by unpaid Byzantine troops against their new commander, Priscus, seemed to offer the Sassanids a chance for a breakthrough, but the mutineers themselves repulsed the ensuing Persian offensive. Later in the year they secured a major victory before Martyropolis. The Sassanid commander, Maruzas, was killed, several of the Persian leaders were captured along with 3,000 other prisoners, and only a thousand men survived to reach refuge at Nisibis. The Byzantines secured much booty, including the Persian battle standards, and sent them, along with Maruzas' head, to Maurice in Constantinople.
In 590, two Parthian brothers, Vistahm and Vinduyih, overthrew King Hormizd IV and made the latter's son, Prince Khosrow II, the new king. The former Persian commander-in-chief, Bahram Chobin, who had rebelled against Hormizd IV, claimed the throne for himself and defeated Khosrow. Khosrow and the two Parthians fled to the Byzantine court. Although the Senate unanimously advised against it, Maurice helped Khosrow regain his throne with an army of 35,000 men. In 591 the combined Byzantine-Persian army under generals John Mystacon and Narses defeated Bahram Chobin's forces near Ganzak at the Battle of the Blarathon. The victory was decisive; Maurice finally brought the war to a successful conclusion with the re-accession of Khosrow.
Subsequently, Khosrow was adopted by the emperor in order to seal their alliance. The adoption was made through a rite of adoptio per arma, which ordinarily assumed the Christian character of its partakers. However, the chief Byzantine bishops, "despite their best attempts", failed to convert Khosrow. Khosrow rewarded Maurice by ceding to the empire western Armenia up to the lakes Van and Sevan, including the large cities of Martyropolis, Tigranokert, Manzikert, Ani, and Yerevan. Maurice's treaty brought a new status-quo to the east territorially. Byzantium was enlarged to an extent never before achieved by the empire. During the new "perpetual peace" millions of solidi were saved by the remission of tribute to the Persians.
Balkan war
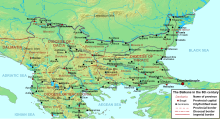
The Avars arrived in the Carpathian Basin in 568. Almost immediately they launched an attack on Sirmium, the keystone to the Byzantine defences on the Danube, but were repulsed. They then sent 10,000 Kotrigur Huns to invade the Byzantine province of Dalmatia. There followed a period of consolidation, during which the Byzantines paid them 80,000 gold solidi a year. In 579, his treasury empty, Tiberius II stopped the payments.
The Avars retaliated with another siege of Sirmium. The city fell in c. 581. After the capture of Sirmium, the Avars demanded 100,000 solidi a year. Refused, they used the strategically important city as a base of operations against several poorly defended forts along the Danube and began pillaging the northern and eastern Balkans. The Slavs began settling the land from the 580s on.
In 584, the Slavs threatened the capital and in 586 the Avars besieged Thessalonica, while the Slavs went as far as the Peloponnese. After his victory on the eastern frontier in 591, Maurice was free to focus on the Balkans. He launched several campaigns against the Slavs and Avars. In 592 his troops retook Singidunum (modern Belgrade) from the Avars. His commander-in-chief Priscus defeated the Slavs, Avars and Gepids south of the Danube in 593. The same year he crossed the Danube into modern-day Wallachia to continue his series of victories. In 594, Maurice replaced Priscus with his rather inexperienced brother Peter, who, despite initial failures, scored another victory in Wallachia. Priscus, now in command of another army further upstream, defeated the Avars again in 595. The latter now only dared to attack peripherally, in Dalmatia two years later. In the same year the Byzantines concluded a peace treaty with the Avar leader Bayan I, which allowed the Byzantines to send expeditions into Wallachia.
In 598, Maurice broke the treaty to permit a retaliation campaign inside the Avar homeland. In 599 and 601 the Byzantine forces wreaked havoc amongst the Avars and Gepids. In 602, the Slavs suffered a crushing defeat in Wallachia. The Byzantine troops were now able to hold the Danube line again. Meanwhile, Maurice was making plans for repopulating devastated areas in the Balkans by using Armenian settlers. Maurice also planned to lead further campaigns against the Avar Khaganate, so as to either destroy them or force them into submission.
Domestic policy
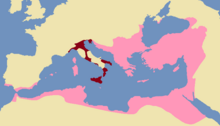
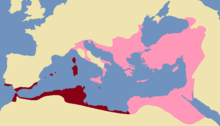
In the west, Maurice organised the threatened Byzantine dominions in Italy into the Exarchate of Italy. The Late Roman administrative system provided for a clear distinction between civil and military offices, primarily to lessen the possibility of rebellion by over-powerful provincial governors. In 584, Maurice created the office of exarch, which combined the supreme civil authority of a praetorian prefect and the military authority of a magister militum and enjoyed considerable autonomy from Constantinople. The Exarchate was successful in slowing the Lombard advance in Italy. In 591, he created a second Exarchate in Byzantine North Africa, along similar lines.
In 597, an ailing Maurice wrote his last will, in which he described his ideas of governing the empire. His eldest son, Theodosius, would rule the eastern provinces from Constantinople; his second son, Tiberius, would rule the western exarchates from Rome. Some historians believe he intended for his younger sons to rule from Alexandria, Carthage, and Antioch. His intent was to maintain the unity of the empire; this idea bears a strong resemblance to the Tetrarchy of Diocletian. However, Maurice's violent death prevented these plans from coming to fruition.
In religious matters, Maurice was tolerant towards Monophysitism, although he was a supporter of the Council of Chalcedon. He clashed with Pope Gregory I over the latter's defence of Rome against the Lombards.
Maurice's efforts to consolidate the empire slowly but steadily succeeded, especially after the peace with Persia. His initial popularity apparently declined during his reign, mostly because of his fiscal policies. In 588 he announced a cut in military wages by a quarter, leading to a serious mutiny by troops on the Persian front. He refused to pay a small ransom in 599 or 600 to free 12,000 Byzantine soldiers taken prisoner by the Avars. The prisoners were killed, and a protesting military delegation, headed by an officer named Phocas, was humiliated and rejected in Constantinople.
Family
Maurice's marriage produced nine known children:
- Theodosius (4 August 583/585 – after 27 November 602). According to John of Ephesus, he was the first heir born to a reigning emperor since the reign of Theodosius II (408–450). He was appointed Caesar in 587 and co-emperor on 26 March 590.
- Tiberius (died 27 November 602)
- Petrus (died 27 November 602)
- Paulus (died 27 November 602)
- Justin (died 27 November 602)
- Justinian (died 27 November 602)
- Anastasia (died c. 605)
- Theoctista (died c. 605)
- Cleopatra (died c. 605)
A daughter, Miriam/Maria, is recorded by the 12th-century chronicler Michael the Syrian and other eastern sources as married to Khosrow II but not in any Byzantine Greek ones; she is probably legendary.
His brother Petrus (c. 550 – 602) became the curopalates and was killed at the same time as Maurice. Petrus married Anastasia Aerobinda (born c. 570), daughter of Areobindus (born c. 550), and had female issue. Maurice's nephew Domitian of Melitene was probably a son of Petrus.
Death
In 602, Maurice, with the lack of money as always dictating policy, decreed that the army should stay for winter beyond the Danube. The exhausted troops mutinied against the emperor. Probably misjudging the situation, Maurice repeatedly ordered his troops to start a new offensive rather than return to winter quarters. His troops gained the impression that Maurice no longer understood the military situation and proclaimed Phocas their leader. They demanded that Maurice abdicate and proclaim as successor either his son Theodosius or General Germanus. Both men were accused of treason. As riots broke out in Constantinople, the emperor, taking his family with him, left the city on a warship heading to Nicomedia. Theodosius was put ashore with direction to seek support from the Persians, but apparently never reached his destination. Phocas entered Constantinople in November and was crowned emperor. His troops captured Maurice and his remaining family, and brought them to the Harbor of Eutropius at Chalcedon.
Maurice was murdered at the harbor of Eutropius on 27 November 602. The deposed emperor was forced to watch his five younger sons executed before he was beheaded himself.
Empress Constantina and her three daughters were temporarily spared and sent to a monastery. The palace eunuch Scholasticus aided their escape to St. Sophia, but the church turned them over to Phocas, who sent them back to the monastery. A few years later, they were all executed at the harbor of Eutropius when Constantina was found guilty of a conspiracy against Phocas. The entire family of Maurice and Constantina was buried at the monastery of St. Mamas or Nea Metanoia that had been founded by Maurice's sister Gordia. The Persian king Khosrow II used this coup and the murder of his patron as an excuse for a renewed war against the empire.
Legacy

Assessment
Maurice is seen as an able emperor and commander-in-chief, though the description of him by Theophylact may exaggerate these traits. He possessed insight, public spirit, and courage. He proved his expertise on military and foreign affairs during his campaigns against the Persians, Avars and Slavs, and during peace negotiations with Khosrow II. His administrative reforms reveal him as a farsighted statesman, all the more since they outlasted his death by centuries and were the basis for the later introduction of themes as military districts.
Maurice promoted science and the arts and he is traditionally named as author of the military treatise Strategikon, which is praised in military circles as the only sophisticated combined arms theory until World War II. Some historians now believe the Strategikon is the work of his brother or another general in his court, however.
His greatest weakness was his inability to judge how unpopular his decisions were. The historian C. W. Previté-Orton listed a number of character flaws in the emperor's personality:
His fault was too much faith in his own excellent judgment without regard to the disagreement and unpopularity which he provoked by decisions in themselves right and wise. He was a better judge of policy than of men.
It was this flaw that cost him throne and life, and thwarted most of his efforts to prevent the disintegration of the empire of Justinian I. The death of Maurice was a turning point. The war against Persia which it caused weakened both empires, enabling the Slavs to permanently settle the Balkans and paving the way for the Arab-Muslim expansion.
His court still used Latin alongside Greek, as did the army and administration. Historian A. H. M. Jones characterises the death of Maurice as the end of the era of Classical Antiquity, as the turmoil that shattered the empire over the next four decades permanently and thoroughly changed society and politics.
Legends
Maurice, Emperor of the Romans, With His Six Sons | |
|---|---|
 From the Mutinensis gr. 122 codex | |
| Emperor | |
| Venerated in | Eastern Orthodoxy |
| Major shrine | Church of the Holy Apostles, Constantinople modern day Istanbul, Turkey |
| Feast | 28 November |
| Attributes | Imperial Vestment |
The first legendary accounts of Maurice's life are recorded in the ninth century, in the work of the Byzantine historian Theophanes the Confessor. According to his chronicle Chronographia, the death of the imperial family is due to divine intervention: Christ asked the emperor to choose between a long reign or death and acceptance in the kingdom of heaven. Maurice preferred the second choice.
The same story has been recorded in a short Syriac hagiography on the life of the emperor. It is of East Syrian origin. This was later sanctified by the Eastern Orthodox Church. According to the Syriac author, the emperor asked in prayer to receive a punishment in this world and a "perfect reward" in the kingdom of heaven. The choice was offered by an angel. Anthony Alcock has published an English translation.
According to another legend in the same text, Maurice prevented a nurse from substituting one of his sons so as to save at least one of the heirs of the empire.
It has been proposed that the name of the Albanian folk hero Muji derives from that of Emperor Maurice (Murik, Muji). Similarly, the name of the folk hero's wife, Ajkuna (or Kuna), corresponds to that of the Empress Aelia Constantina, the wife of Maurice, if we take into account the laws of phonetic evolution of the Albanian language since Late Antiquity. Though this proposition remains a matter of debate.
See also
Notes
- ^ Sometimes, Mauricius is spelled as Mauritius.
- ^ The full imperial titulature of Maurice, attested in a letter to Childebert II, was Imperator Caesar Flavius Mauricius Tiberius fidelis in Christo mansuetus maximus beneficus pacificus Alamannicus Gothicus [Francicus Germanicus] Anticus Alanicus Vandalicus Erulicus Gepidicus Afric[an]us pius felix inclitus victor ac triumfator semper Augustus ("Emperor Caesar Flavius Maurice Tiberius, faithful in Christ, mild, majestic, bountiful, peaceable; victor over the Alamanni, Goths, [Franks and Germans,] the Antae, Vandals, Heruls, Gepids, in Africa; pious, fortunate, renowned, victorious and triumphant, ever august").
- ^ Commemorated on 28 November according to the Typikon of the Great Church and on 28 August, according to the Palestinian-Georgian Synaxarion.
References
- ^ Geary, Patrick (2015). Readings in Medieval History, Fifth Edition. University of Toronto Press. p. 186. ISBN 978-1442634411.
Given the seventeenth of June, in the nineteenth year of the reign of our most religious lord, Mauritius Tiberius Augustus, the eighteenth year of the consulship of our said lord, and the fourth indiction.
- ^ Roger Shaler Bagnall; Klaas Anthony Worp (2004). Chronological Systems of Byzantine Egypt (2nd ed.). Brill. p. 261. ISBN 978-9004136540.
The formula is Oxyrhynchite, but our one Mephite and one Arsinoite document also show it. In Oxyrhynchos, Νέος is consistently absent up to 588, with the names in the order Tiberius Mauricius; after that one finds Mauricius Novus Tiberius in almost all examples.
- ^ Bury 1889, pp. 165–166.
- ^ Rösch 1978, p. 169.
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris 1992, p. 855.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, p. 227.
- ^ Stark, Freya (2012). Rome on the Euphrates: The Story of a Frontier. Tauris Parke Paperbacks. p. 390. ISBN 978-1-84885-314-0.
Byzantium reverted to Greek (Maurice, born in Cappadocia, was its first Greek emperor); and trade and diplomacy were honored from the very founding of the Imperial city as never in Rome before.
- ^ Corradini, Richard (2006). Texts and identities in the early Middle Ages. Verl. der Österr. Akad. der Wiss. p. 57. ISBN 978-3-7001-3747-4.
Emperor Maurice who is said to be the first emperor "from the race of the Greeks," ex Graecorum genere.
- ^ Stark 2012, p. 390.
- ^ Corradini 2006, p. 57.
- ^ Rosser 2011, p. 199.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991, p. 1318.
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris 1992, p. 856.
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris1992, pp. 856–857.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 160–162.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 162–163
- ^ Shahîd 1995, pp. 413–419; Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 163–165
- ^ Shahîd 1995, p. 414.
- ^ Shahîd 1995, p. 416; Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 165
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 164
- ^ Shahîd 1995, pp. 439–443
- ^ Shahîd 1995, pp. 444–455
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 163–166
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris 1992, pp. 859, 1215
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 166
- ^ Treadgold 1997, p. 226.
- ^ "John, Bishop of Nikiu: Chronicle. Chapter XCV (95), 25–26. 1916 translation by R. H. Charles". Archived from the original on 9 January 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2008.
- ^ Chronicon Paschale (Olympiad 340)
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris 1992, pp. 859–860.
- ^ Paul the Deacon, III, ch. 15
- ^ Lynda Garland, Sophia, Wife of Justin II Archived 30 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 166–167.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1956, pp. 74–75.
- ^ Norwich 1988, p. 275.
- ^ Mitchell 2007, p. 406.
- ^ Petersen 2013, p. 379.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 170
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1956, p. 73.
- ^ Norwich 1988, pp. 273–274.
- ^ Payne 2015, p. 164.
- ^ Norwich 1988, p. 273.
- ^ Petersen 2013, p. 378.
- ^ Mitchell 2007, p. 405.
- ^ Petersen 2013, pp. 378–379.
- ^ Norwich 1988, p. 274.
- ^ Pohl 2002, p. 154.
- ^ The Armenian History attributed to Sebēos, Part 1, translation and notes, trans. R.W. Thomson; comm. J.D. Howard-Johnston, Translated Texts for Historians 31 (Liverpool, 1999) p. 56
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1956, p. 75.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1956, p. 74.
- ^ Fortescuen, Adrian (1911). . In Herbermann, Charles (ed.). Catholic Encyclopedia. Vol. 10. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1956, p. 76.
- ^ Norwich 1988, pp. 275–278.
- ^ Norwich 1988, p. 277.
- ^ "Roman Emperors – DIR Constantina". www.roman-emperors.org. Archived from the original on 22 July 2018. Retrieved 8 May 2018.
- ^ Whitby 1988, p. 18.
- ^ Baum (2004), pp. 24–26
- ^ Whitby 1988, p. 5.
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris 1992, p. 411.
- ^ Howard-Johnston 2021, pp. 16–18.
- ^ Martindale, Jones & Morris 1992, p. 860. Some sources give 23 November, but, as the Chronicon Paschale (O.345) points out, this was the date of Phocas' coronation..
- ^ Norwich 1988, p. 278.
- ^ Garland, Lynda (1999). "Constantina (Wife of the emperor Maurice)". roman-emperors.org. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ Ostrogorsky 1956, p. 24.
- ^ McCotter, Stephen (2003). "'The Nation which Forgets its Defenders will Itself be Forgotten': Emperor Maurice and the Persians". Queen's University of Belfast. deremilitari.org. Archived from the original on 20 November 2008. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- ^ Previté-Orton 1952, p. 203.
- ^ Davis 1990, p. 260.
- ^ Jenkins 1987, p. 24.
- ^ Norwich 1988, pp. 278–279.
- ^ Theophanes (1997) [c.815]. Chronicle, translated by Cyril Mango & Roger Scott. Clarendon Press. p. 410 (AM 6094).
- ^ Whitby 1988, p. 21.
- ^ Brock 1976, p. 29.
- ^ Wortley 1980.
- ^ Turnhout: Brepols, 1981, pp. 774–775.
- ^ Alcock 2018.
- ^ Nau, 1981, pp. 776–778.
- ^ Akademia e Shkencave te Kosoves; Shuka Gj. (2023). "Nenshtresa ne tri kenge te Ciklit te Kosoves". Studime Shoqerore (9): 245–285.
Sources
- Alcock, Anthony (2018). "Maurice the Emperor: A Short Syriac Text". Academia.edu.
- Baum, Wilhelm (2004). Christian, queen, myth of love, a woman of late antiquity, historical reality and literary effect. Gorgias Press LLC. ISBN 1-59333-282-3.
- Brock, Sebastian P. (1976). "Syriac Sources for Seventh-Century History". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies. 2 (1): 17–36. doi:10.1179/030701376790206207. S2CID 162305771.
- Bury, J.B. (1889). A History of the Later Roman Empire from Arcadius to Irene, 395 A.D. to 800 A.D. Vol. II. MacMillan & Co. OCLC 168739195.
- Corradini, Richard (2006). Texts and identities in the early Middle Ages. Wien: Verl. der Österr. Akad. der Wiss. ISBN 978-3700137474.
- Davis, Leo Donald (1990). The first seven ecumenical councils (325–787): their history and theology. Liturgical Press. ISBN 0-8146-5616-1.
- Greatrex, Geoffrey; Lieu, Samuel N. C. (2002). The Roman Eastern Frontier and the Persian Wars (Part II, 363–630 AD). New York, London: Routledge (Taylor & Francis). ISBN 978-0-415-14687-6.
- Howard-Johnston, James (2021). The Last Great War of Antiquity. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198830191.
- Jenkins, Romilly James Heald (1987). Byzantium: The Imperial Centuries, AD 610-1071. University of Toronto Press. ISBN 0-8020-6667-4.
- Kazhdan, Alexander, ed. (1991). "Maurice". Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 1318. ISBN 978-0-19-504652-6.
- Martindale, J.R.; Jones, A.H.M.; Morris, J., eds. (1992). The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire, Volume III: A.D. 527–641. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-20160-5.
- Mitchell, Stephen (2007). A History of the Later Roman Empire. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4051-0856-0.
- Norwich, John (1988). Byzantium: The Early Centuries. London: Viking. ISBN 978-0670802517. OCLC 18834505.
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of The Byzantine State. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press. OCLC 422217218.
- Paul the Deacon (2011). Peters, Edward (ed.). History of the Lombards. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0812205589.
- Payne, Richard E. (2015). A State of Mixture: Christians, Zoroastrians, and Iranian Political Culture in Late Antiquity. Univ of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-29245-1.
- Petersen, Leif Inge Ree (2013). Siege Warfare and Military Organization in the Successor States (400–800 AD) Byzantium, the West and Islam. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-9004254466.
- Pohl, Walter (2002). The Avars: a Steppe People in Central Europe, 567–822 AD (in German). Munich: Beck. ISBN 9783406489693.
- Previté-Orton, Charles William (1952). The shorter Cambridge medieval history. Cambridge: University Press. OCLC 263439650.
- Rösch, Gerhard (1978). Onoma Basileias: Studien zum offiziellen Gebrauch der Kaisertitel in spätantiker und frühbyzantinischer Zeit. Byzantina et Neograeca Vindobonensia (in German). Verlag der österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. ISBN 978-3-7001-0260-1.
- Rosser, John H. (2011). Historical Dictionary of Byzantium. Boston: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0810874770.
- Shahîd, Irfan (1995). Byzantium and the Arabs in the Sixth Century, Volume 1. Washington, District of Columbia: Dumbarton Oaks. ISBN 978-0-88402-214-5.
- Stark, Freya (2012). Rome on the Euphrates: The Story of a Frontier. London: Tauris Parke Paperbacks. ISBN 978-1848853140.
- Treadgold, Warren T. (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-2630-6.
- Walford, Edward, transl. (1846) The Ecclesiastical History of Evagrius: A History of the Church from AD 431 to AD 594, Reprinted 2008. Evolution Publishing, Merchantville, NJ ISBN 978-1-889758-88-6.
- Whitby, Michael (1988). The Emperor Maurice and his Historian – Theophylact Simocatta on Persian and Balkan Warfare. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822945-2.
- Wortley, J. (1980). "The legend of the Emperor Maurice". Actes du XVe Congrès International d'Etudes byzantines, Athènes, 1976. Vol. IV. Athens. pp. 382–391.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
Further reading
- The Christian Roman Empire series. Merchantville, NJ: Evolpub.com. 2007. ISBN 978-1-889758-87-9. Retrieved 27 November 2013.
- Shlosser, Franziska E. (1994). The Reign of the Emperor Maurikios (582–602). A reassessment (Historical Monographs 14). Montreal: McGill University. ISBN 978-9607100788.
- Whitby, Michael; Whitby, Mary (1986). The History of Theophylact Simocatta. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822799-1.
- Whitby, Michael (2015). "Maurice". Encyclopaedia Iranica. Columbia University Press. OCLC 59605200.