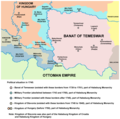
Military Border
| History of Croatia |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
|
|
| History of Hungary |
|---|
 |
|
|
| History of Serbia |
|---|
 |
|
|
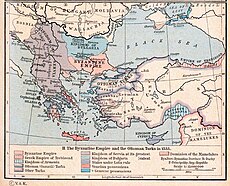
The Military Frontier (German: Militärgrenze; Serbo-Croatian: Војна крајина, Vojna krajina, Војна граница, Vojna granica; Hungarian: Katonai határőrvidék; Romanian: Granița Militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and later the Austrian and Austro-Hungarian Empire. It acted as the cordon sanitaire against incursions from the Ottoman Empire.
The establishment of the new defense system in Hungary and Croatia took place in the 16th century, following the election of Ferdinand I as king. Six districts under special military administration were established in Hungary and Croatia. The Croatian Military Frontier and the Slavonian Military Frontier came under the jurisdiction of the Croatian Sabor and ban. In 1627, they were placed under the direct control of the Habsburg military. For more than two centuries, they would retain complete civilian and military authority over the area, up to the abolition of the Military Frontier in 1881.
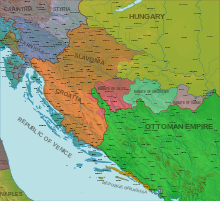
During the 17th century, the territory was expanded towards the East and new sections were created. By then, it stretched from Croatia proper in the west to eastern Transylvania in the east and included parts of present-day Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Romania and Hungary. During this period, the defence system was also changed, from a conventional garrison model to one of 'soldier-settler' communities.
The inhabitants of the area were known as the Grenzer (or frontiersmen). They were mostly Serbian, Croatian, German, Vlach and other colonists. In exchange for land-grants, religious freedom and favorable tax rates, they colonized the area and served as the bulwark for the monarchy against Ottoman incursions. Germans had been recruited by Hungary in the late 18th century to resettle and develop the Danube River Valley, and became known as Donauschwaben. The military regiments formed by the settlers had a vested reason to stand and fight and were familiar with local terrain and conditions. They soon gained a formidable military reputation.
Background
The Ottoman wars in Europe caused the border of the Kingdom of Hungary – and subsequently that of the Habsburg monarchy – to shift towards the northwest. Much of the old Croatian territory either became Ottoman land or bordered the new Ottoman domain.
In 1435, in an attempt to strengthen the defences against the Ottomans and Venice, King Sigismund founded the so-called tabor, a military encampment, each in Croatia, Slavonia and Usora. In 1463 King Matthias Corvinus founded the banovina of Jajce and Srebrenik, and in 1469 the military captaincy of Senj, modeled after the Ottoman captaincies in the Province of Bosnia. All these actions aimed to improve defence, but ultimately proved unsuccessful. But, they did lead to development of the Pandur infantry and the Hussar cavalry.
Vlachs known as "Martolos" and "Voynuks" were the most dangerous military element under Ottomans, while Vlachs and Serbs which fled from the Ottomans in the 15th century had a similar military tradition which Habsburgs begin to use on their side of the border. They were joined by some Vlachs from Bosnia and thus under the Habsburgs a special system of land ownership and military organization was created ie Military Frontier. This military border was an area of some major war campaigns, but mostly consisted of eternal clashes between the Ottoman Vlachs and the Habsburg Vlachs.
History
16th century
After the Croatian Parliament elected the Austrian Habsburgs as kings of Croatia in 1526, Ferdinand I promised the Croatian Parliament that he would give them 200 cavalrymen and 200 infantrymen, and that he would pay for another 800 cavalrymen who would be commanded by the Croatians. Soon the Habsburg monarchy founded another captaincy in Bihać. In the short term, all this was ineffective, as in 1529 the Ottomans swept through the area, captured Buda and besieged Vienna, wreaking havoc throughout the Croatian border areas.
The Habsburgs aimed at holding the Ottoman forces on Hungarian and Croatian territory before they could reach Austria, but did not have a clear defense plan. In the 1530s, significant reinforcements were sent only to the most important forts on the border with the Ottoman Empire. In the 1540s and following the Ottoman campaign of 1552, several conferences were held in which a new defense strategy was adopted. Separate defense zones were to be established in parts of Hungary and Croatia around the border forts. Austrian and Bohemian provinces were obligated to help finance this new system, beginning in the 1550s. At the end of the 1560s, the new border system consisted of around 100–120 forts and extended from the Adriatic Sea to Transylvania. It was organized into six Border Fortress Captain Generalcies (Grenzgeneralat):
- The Croatian and Adriatic Border Fortress Captain Generalcy (kroatische und Meergrenze), centred initially in Bihać, and from 1579 in Karlovac;
- The Slavonian or Wendish Captain Generalcy (slawonische/windische Grenze), centred in Varaždin, after 1578 known as the Wendish-Bajcsavár Captain Generalcy;
- The Kanizsa Captain Generalcy (kanischarische Grenze), centred in Kanizsa. Renamed the Captain Generalcy across from Kanizsa (gegenüber von Kanischa liegende Grenze) following the loss of Kanizsa in 1600;
- The Györ Captain Generalcy (Raaber/raaberische Grenze), protecting Vienna;
- The Captain Generalcy Defending the Mining Towns (bergstädtische Grenze), centred in Léva, and in Érsekújvár after 1589;
- The Upper Hungary or Kassa Captain Generalcy (oberungarische Grenze), centred in Kassa.
In addition, there were four District Captain Generalcies (Kreisgeneralat).
From the 1530s, immigration to the Military Frontier began to include a large number of Martolos, Vlach military colonists and other irregulars who were part of the Ottoman military system, they were mostly Christians and some were Muslims.
The new military expenditures became a considerable concern, and the Congress of Inner Austrian lands in Bruck an der Mur in 1578 defined the obligations of each land in covering the military expenses and defined the priorities in improving the defensive strategy. It was determined that the Duchy of Styria will finance the Slavonian and Hungarian Frontiers, and the Duchy of Carniola will finance the Croatian Frontier. The Duchy of Carinthia put their finances at the disposal of Styria and Carniola, to direct the money where needed. In the 2nd half of the 16th century, there were around 20,000 troops stationed in Hungarian and Croatian border forts.
By the end of the 16th century Slavicized Vlachs, other Vlachs and Serbs flee from Ottoman territory to Military Frontier and Dalmatia. At the same time the Croatian Military Frontier became known as the Karlovac generalate, and from the 1630s the Upper Slavonian Military Frontier was known as the Varaždin generalat. During the 16th and 17th centuries, the military administration of the Frontier was moved away from the Croatian ban and the Sabor (Parliament) and instead instated in the high command of Archduke Charles and the War Council in Graz.
17th century
Despite the financial support of the Inner Austrian nobility, the financing of the Military Frontier was not efficient enough. The military leadership in Graz decided to try solutions other than mercenary units. In the 1630s the Imperial Court decided to give land and certain privileges to immigrants into the Frontier (the uskok guerrillas as well as refugees from Ottoman-controlled lands) at the area of Žumberak. In return they would serve in the Imperial army. The remaining local population was also encouraged to remain by receiving the status of free peasants (rather than serfs) and other privileges. These new units were organized into ten or more voivodeships per each captaincy.
In 1627, the Military Frontier was removed from the control of the Croatian Sabor and put under direct rule of the Habsburg military. It would have complete civilian and military authority over it until abolition of the Military Frontiers. In November 1630, Emperor Ferdinand II proclaimed the so-called Statuta Valachorum ("Vlach Statute"), which regulated the status of so-called Vlach settlers (which included Croats, Serbs and Vlachs) from the Ottoman Empire with regard to military command, their obligations, and rights to internal self-administration. Over time, the population of the Frontier (as it was then) became mixed between the autochthonous Croats and Croatian serfs who had fled the Ottoman territories, and the numerous minority of the Serb and Vlach (who were later assimilated into Croats and Serbs) refugees who strove to expand their rights as a major contributor in the defense of the land. By creating the new military class in the Frontier, the territory of the Frontier eventually became fully detached from the Croatian Parliament and the ban. As freedom of faith was granted to them, they preserved their Orthodox faith in spite of their living in a Catholic country. Eventually, the whole male population of the Military Frontier became professional soldiers who served the Empire on several fronts and through many European wars, even after the relaxation of the Ottoman threat.

During the 17th century territory of the Military Frontier was expanded towards the East and new sections were created. By then, it stretched from Croatia in the west to eastern Transylvania in the east and included parts of present-day Croatia, Serbia, Romania and Hungary. The area was settled primarily with Croatian, Serbian and German colonists (known as grenzer and graničari) who, in return for land grants, served in the military units defending the empire against Ottomans. The majority of immigrants were Serbs, and some were ethnic Croats, mainly from Bosnia. A large migration of Serbs to Habsburg lands was undertaken by Patriarch Arsenije III Čarnojević. The large community of Serbs concentrated in Banat, southern Hungary, and the Military Frontier included merchants and craftsmen in the cities, but mainly refugees who were peasants.
The 17th century was a relatively peaceful period, during which only smaller raids were made from the Province of Bosnia. After the Ottoman army was repelled at the Battle of Vienna in 1683, the Great Turkish War ended with much of the former Croatian lands under Habsburg control. Despite this, the Frontier system was retained, and expanded onto former Ottoman territories in Lika, Kordun, Banija, lower Slavonia, Syrmia, Bačka, Banat, Pomorišje, and Transylvania. The Habsburg Empire valued the ability to centrally control the area and to draft cheap and numerous army units.
After the Treaty of Karlowitz of 1699, the Seressaner troops were established with both military and police duties. They were not paid, but were exempted from taxes. Over the following century, each regiment had one section of Seressaners that organized border patrols towards Bosnia, particularly on difficult terrain, and stopped incursions of bandits.
Orthodox Christians who settled Military Frontier from the Ottoman Empire were called in sources as "Vlachs schismatics" and Vlachs or Uskoks, other names which are mentioned are "Valachi seu Rasciani" "Valachi seu Serviani", "Valachi seu Graeci", Vlachs or Morlachs, "Illirica gens graeci ritus" and "homines Ritus Ruthenici seu Graeci". During the 17th and first half of the 18th century Catholic natives and Catholics immigrated from Bosnia and Kingdom of Croatia also converted to Orthodoxy. Most documents state that the Vlachs arriving "from Turkey" or "from Bosnia", ie the Bosnia Eyalet.
18th century
When in 1699 and 1718 the lands of Croatia and Hungary returned, which was previously occupied by the Ottomans, the vast majority of that area became the Military Frontier. Throughout the entire region of this frontier various ethnic groups were settled including Croats, Serbs, Albanians and others which were also all together called Vlachs. From 1718 to 1739 the Military Frontier also included the Habsburg-controlled northern parts of present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina. In the mid-18th century the Frontier was once again reorganized and modelled after the Imperial army and its regular regiments. In 1737 the Vlach Statute was formally abolished. All previous captaincies and voivodships were discarded, and the area was instead subdivided into general-commands, regiments and companies:

After 1767, every twelfth inhabitant of the Military Frontier was a soldier – in contrast to every 62nd inhabitant in the rest of the Habsburg Monarchy. The Frontier soldiers became a professional military, ready to move to all European battlefields. Due to further immigration of refugees from the Ottoman domain, and to the expansion of the territory to places previously controlled by the Ottomans, the population of the Frontier became even more mixed. There were still many autochthonous Serbs and Croats in Slavonia and in parts of present-day Vojvodina (in Syrmia, Bačka and Banat). However, at this time they became outnumbered by the Serb, Croat and Vlach refugees/immigrants. Some Germans, Poles, Magyars and Slovaks also came to the Frontier, mostly as administrative personnel, and a number of other settlers and military personnel arrived from other parts of the Habsburg Empire – Czechs, Poles, Slovaks, Ukrainians, Rusyns and others.
In 1783 the Croatian and Slavonian frontiers came under the unified control of the Croatian General Command headquartered in Zagreb.
The Serbian Free Corps of 5,000 soldiers had been established in Banat, composed of refugees who had fled earlier conflicts in the Ottoman Empire. The Corps would fight for the liberation of Serbia and for unification under Habsburg rule. Several freikorps operated along the Habsburg-Ottoman frontier. The Austrians used the Corps in two failed attempts to seize Belgrade, in late 1787 and in early 1788.
Serbia was subsequently liberated, and organized into a Habsburg protectorate. On 8 October 1789 Ernst Gideon von Laudon took over Belgrade. Austrian forces occupied Serbia, and many Serbs fought in the Habsburg free corps, gaining organizational and military skills. By 1791, however, the Austrians were forced into withdrawal across the Danube and Sava rivers, joined by thousands of Serb families who feared Ottoman persecution. The Treaty of Sistova (1791) ended the Austro-Turkish War of 1787.
In 1787 the civil administration became separate from the military, but this was reversed in 1800.
19th century
By the end of the 18th century, it had already become apparent for some time that the Ottomans were on the decline and were not likely to attempt any further invasions north of the Sava River. The Military Frontier thus began to outlive its usefulness. In 1848, Josip Jelačić, Ban of Croatia, became the commander of the Military Frontier. He pressed for the unification of Croatia, Slavonia, Dalmatia, and the Croatian-Slavonian Frontier. Although he did not have the power to abolish it, he secured approval for reforms and in 1848 the Military Frontier sent representatives to the Croatian Sabor, however, this was revoked in the 1850s. From 1850 the Frontier, Croatia and Slavonia formally constituted a single land, but with separate administration and representation. The whole area of Military Frontier was under military administration. All population, regardless of age and sex, belonged to the army and was subject to austrian military legislation. The Main Command had its headquarters in Zagreb, but remained directly subordinate to the Ministry of War in Vienna.
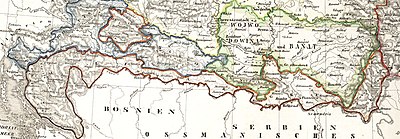
The Croatian Parliament made numerous pleas to demilitarize the Frontier after the Turkish wars subsided. The demilitarization began in 1869 and on 8 August 1873, under Franz Joseph, the Banat Frontier was abolished and incorporated into the Kingdom of Hungary, while part of the Croatian Frontier (Križevci and Đurđevac regiments) was already incorporated into Croatia-Slavonia on 1 August 1871. The decree in which the rest of the Croatian and Slavonian frontiers were incorporated into Croatia-Slavonia was proclaimed on 15 July 1881, while incorporation began on 1 August 1881, when Ban of Croatia Ladislav Pejačević took over from the Zagreb General Command.
Administration
Divisions
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the frontier was divided into several districts:
| Division | Period | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Danube Military Frontier | 1702–1751 | Comprised parts of southern Bačka (including Palanka, Petrovac, Petrovaradinski Šanac, Titel, etc.) and northern Syrmia (including Petrovaradin, Šid, etc.). After the abolishment of this section of the Frontier, one part of its territory was placed under civil administration and another part was joined with other sections of the Frontier. |
| Tisa Military Frontier | 1702–1751 | Comprised parts of north-eastern Bačka (including Sombor, Subotica, Kanjiža, Senta, Bečej, etc.). After the abolishment of this section of the Frontier, most of its territory was placed under civil administration, while one small area in the south remained under military administration as part of the Šajkaš Battalion. |
| Mureș Military Frontier | 1702–1751 | This frontier included the region of Pomorišje, the area on the northern bank of the river Mureș. After the abolishment of this section, its entire territory was placed under civil administration. |
| Sava Military Frontier | 1702–1751 | It was located along the Sava river. |
| Banat Military Frontier | 1751–1873 | It was located on the present-day Serbian-Romanian border. It was divided into Serbian (Illyrian), German (Volksdeutscher) and Romanian (Vlach) sections. |
| Slavonian Military Frontier | 1745–1881 | It was located along Posavina, from eastern Croatia, following the river Sava, along the border with Bosnia-Herzegovina and Serbia, and stretched into Syrmia, until inflow into Danube near Zemun (today part of Belgrade). Its north-eastern border followed the Danube up until the Petrovaradin. |
| Croatian Military Frontier | 1553–1881 | It was located on the border of Croatia and Bosnia. This part of the Military Frontier included the geographic regions of Lika, Kordun, Banovina (named after "Banska krajina"), and bordered the Adriatic Sea to the west, Venetian Republic to the south, Habsburg Croatia to the west, and the Ottoman Empire to the east. It extended onto the Slavonian Military Frontier near the confluence of the rivers Una and Sava. |
| Šajkaš Battalion | 1763–1873 | It was a small part of the Frontier that was formed in 1763 from parts of the previously abolished Danube and Tisa sections of the frontier. In 1852, Šajkaš battalion was transformed into Titel infantry battalion. It was abolished in 1873, and its territory was incorporated into Bačka-Bodrog County. |
| Transylvanian Military Frontier | 1762–1851 | It was located in the eastern and southern parts of Transylvania. It was composed of two Székely and two Romanian regiments. The establishment of the frontier was followed by the Mádéfalva Massacre or Siculicidium. |
Maps
-
Map of Military Frontier sections in Syrmia, Bačka, and Pomorišje in 1699-1718
-
Map of Military Frontier sections in Syrmia, Bačka, and Pomorišje in 1718-1744
-
Map of Military Frontier sections in Syrmia, Bačka, and Pomorišje in 1744-1750
-
Map of Military Frontier sections in Syrmia, Bačka, and Banat in 1751-1873
-
Map of Military Frontier sections in Banat, Syrmia, and Bačka (18th-19th century)
-
Map of Military Frontier sections in Banat, Syrmia, and Bačka in 1849 - Banatian and Slavonian military frontier and Schajkasch Battalion
-
Map of the Slavonian Military Frontier in 1849
-
Map of the Croatian Military Frontier in 1868
Demographics
1828
In 1828 the population included:
- 543,154 (50.60%) Eastern Orthodox
- 434,344 (40.46%) Roman Catholics
- 53,073 (4.95%) Greek Catholics
- 42,659 (3.98%) Protestants
- 450 (0.05%) Jews
1846
An Austrian statistical yearbook for 1846 notes that 1,226,408 residents lived in the Military Frontier:
- 598,603 (48.82%) Eastern Orthodox
- 514,545 (41.96%) Roman Catholics
- 62,743 (5.12%) Greek Catholics
- 49,980 (4.08%) Protestants
- 537 (0.05%) Jews
1857
The first modern population census in the Austrian Empire was conducted in 1857 and recorded the religion of the population. The population of the Military Frontier numbered 1,062,072 inhabitants, while the religious structure of the Military Frontier was:
- 587,269 (55.30%) Eastern Orthodox
- 448,703 (42.26%) Roman Catholics
- 20,139 (1.91%) Protestants
- 5,533 (0.53%) Greek Catholics
- 404 (0.05%) Jews
Population data by divisions:
Croatian-Slavonian Military Frontier (Total 675,817)
- 396,843 (58.72%) Roman Catholics
- 272,755 (40.36%) Eastern Orthodox
- 5,486 (0.81%) Greek Catholics
- 733 (0.11%) others
Banat Military Frontier (Total 386,255)
- 314,514 (81.43%) Eastern Orthodox
- 51,860 (13.43%) Roman Catholics
- 19,418 (5.03%) Evangelicals
- 393 (0.1%) Jews
- 70 (0.01%) others
Legacy
Many Serbs emigrated to the north toward the southern regions of Hungary during the period when the territory of Serbia was largely under Ottoman rule. In order to attract Serbs into Hungary, emperor Leopold I decreed that they would be allowed to elect their own ruler, or Vojvoda, from which the name Vojvodina derives. In 1690, about 30,000 to 70,000 Serbs settled eastern Slavonia, Bačka and Banat in what became known as the Great Serbian Migrations. Later the Habsburgs did not allow Serbs to elect their own vojvoda; they incorporated the region into the military frontiers of eastern Slavonia and the Banat. However, the strong Serb presence in the region resulted in Vojvodina serving as the cradle of the Serbian renaissance during the 19th century.
From October 1990, eight months before Croatia declared independence (June 25, 1991) from Yugoslavia, the Serbs who lived in the region of the former Military Frontier (Vojna Krajina) started an insurrection and adopted the name (Krajina) for their unrecognised Republic of Serbian Krajina. The occupied territory was virtually identical to the Military Frontier's territory, however also including some territories that were never a part of former Military Frontier, such as northern Dalmatia with town of Knin. Other territories that had constituted the Military Frontier remained under control of Republic of Croatia. Croatian forces regained control over Serb occupied territories after Operation Storm in 1995 (see the Croatian War of Independence for more information).
See also
References
- ^ Aleksa Djilas (1991). The Contested Country: Yugoslav Unity and Communist Revolution, 1919–1953. Harvard University Press. pp. 11–. ISBN 978-0-674-16698-1.
- ^ Frucht, Richard (2004). Eastern Europe, An Introduction to the People, Lands, and Culture. ABC-CLIO. p. 422. ISBN 1576078000.
- ^ Stoianovich, Traian (1992). Balkan Worlds: The First and Last Europe. Routledge. p. 152. ISBN 1563240335.
- ^ Hálfdanarson, Guðmundur (2003). Racial Discrimination and Ethnicity in European History. PLUS, Università di Pisa. ISBN 9788884922809.
- ^ Macartney, Carlile Aylmer, ed. (2017). Hungary: From Ninth Century Origins to the 1956 Uprising. Routledge. p. 116. ISBN 978-1138525542.
- ^ Malcolm, Noel (1996). Bosnia: A Short History. NYU Press. p. 98. ISBN 0814755615.
- ^ Pál, Fodor; Geza, David; Gábor, Agoston; Klára, Hegyi; József, Kelenik; Kybinyi, András [in Hungarian]; Géza, Pálffy (2000). Ottomans, Hungarians, and Habsburgs in Central Europe: The Military Confines in the Era of Ottoman Conquest (Ottoman Empire and Its Heritage). Brill. p. 62. ISBN 9004119078.
- ^ Calic, Marie-Janine [in German] (2019). The Great Cauldron: A History of Southeastern Europe. Harvard University Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0674983922.
- ^ Banac, Ivo (1984). The National Question in Yugoslavia: Origins, History, Politics. Cornell University Press. p. 43. ISBN 0801416752.
- ^ Kaser, Karl (2012). Household and Family in the Balkans: Two Decades of Historical Family Research at University of Graz. LIT Verlag. pp. 123–124. ISBN 978-3643504067.
- ^ Malcolm, Noel (1995). Povijest Bosne - kratki pregled [History of Bosnia - a brief overview] (in Croatian). Zagreb, Dani-Sarajevo: Erasmus Gilda, Novi Liber. p. 98.99. ISBN 953-6045-03-6.
- ^ Fine 1994, p. 595.
- ^ Pálffy 2012, p. 38.
- ^ Pálffy 2012, pp. 40–41.
- ^ Pálffy 2012, pp. 43–44.
- ^ Pálffy 2012, pp. 45–46.
- ^ Bracewell, Catherine Wendy (2011). The Uskoks of Senj: Piracy, Banditry, and Holy War in the Sixteenth-Century Adriatic. Cornell University Press. pp. 27–31. ISBN 978-0801477096.
- ^ Štefanec 2011, pp. 349, 355–356.
- ^ Pálffy 2012, p. 52.
- ^ Aleksa Djilas (1991). The Contested Country: Yugoslav Unity and Communist Revolution, 1919–1953. Harvard University Press. pp. 11–. ISBN 978-0-674-16698-1.
- ^ "Statuta Valachorum (prevod)". Archived from the original on 2021-11-22. Retrieved 2016-03-23.
- ^ Historical Atlas of Central Europe, Paul Robert Magocsi, p. 34
- ^ Jelavich 1983, p. 145.
- ^ Zlatko Kudelić, 2010, Čaplovičeva povijest Marčanske biskupije, https://hrcak.srce.hr/56775 #page=137-138
- ^ Ilona Czamańska; (2015) The Vlachs – several research problems p. 13; BALCANICA POSNANIENSIA XXII/1 IUS VALACHICUM I, [1]
- ^ Plamen Mitev (2010). Empires and Peninsulas: Southeastern Europe Between Karlowitz and the Peace of Adrianople, 1699–1829. LIT Verlag Münster. pp. 171–. ISBN 978-3-643-10611-7.
- ^ Fine 2005, p. 370-371.
- ^ Karl Kaser: Freier Bauer und Soldat: die Militarisierung der agrarischen Gesellschaft and der kroatisch-slowanischen Militärgrenze (1535–1881), Böhlau Verlag Wien, 1997, p. 369
- ^ Gunther Erich Rothenberg: The Military Border in Croatia, 1740–1881: a study of an imperial institution, University of Chicago Press, 1966, p. 63
- ^ Paul W. Schroeder (1996). The Transformation of European Politics, 1763–1848. Oxford University Press. pp. 58–59. ISBN 978-0-19-820654-5.
- ^ Društvo, Srpsko Učeno (1866). Glasnik Srpskoga učenog društva. Vol. 20. pp. 69–.
- ^ R. S. Alexander (30 January 2012). Europe's Uncertain Path 1814–1914: State Formation and Civil Society. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 19–. ISBN 978-1-4051-0052-6.
- ^ Tanner, Marcus (2001). Croatia : A Nation Forged in War (2nd ed.). New Haven; London: Yale University Press, p. 86-87
- ^ Tanner, (2001). Croatia, p. 104
- ^ Horvat 1906, pp. 157.
- ^ Valentic 1978, pp. 53.
- ^ Horvat 1906, pp. 289–290.
- ^ Versuch einer Darstellung der oesterreichischen Monarchie in statistischen Tafeln, p. 7
- ^ Uebersichts-Tafeln zur Statistik der österreichischen Monarchie: besonderer Abdruck des X. und XI. Heftes der "Statistischen Mittheilungen". 1850, page 2
- ^ Bundesministerium für Inneres 1859, p. 179.
- ^ Bundesministerium für Inneres 1859, p. 172.
- ^ Bundesministerium für Inneres 1859, p. 176.
- ^ Miller 1997, p. 10.
Sources
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472082604.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (2005). When Ethnicity Did Not Matter in the Balkans: A Study of Identity in Pre-Nationalist Croatia, Dalmatia, and Slavonia in the Medieval and Early-Modern Periods. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472025600.
- Horvat, Rudolf (1906). Najnovije doba hrvatske povjesti [The latest era of Croatian history] (in Croatian). Matica hrvatska. (Wikisource)
- Valentic, Mirko (1978). Vojna Krajina u austrijskoj politici 1849-1860 [Military Border in Austrian politics in 1849-1860] (in Croatian).
- Bundesministerium für Inneres (1859). Statistische Übersichten Über Die Bevölkerung und Den Viehstand Von Österreich. Nach Der Zählung Vom 31. Oktober 1857 [Statistical surveys of the population and livestock of Austria. According to the census of October 31, 1857] (in German).
- Jelavich, Barbara (1983). History of the Balkans: Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521252492.
- Kulauzov, Maša (2008). "The emergence, development and demilitarization of the military border of the Austrian Monarchy" (in Serbian). Matica srpska.
- Miller, Nicholas J. (1997). Between Nation and State: Serbian Politics in Croatia Before the First World War. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press. ISBN 9780822939894.
- Pálffy, Géza (2012). "The Habsburg Defense System in Hungary Against the Ottomans in the Sixteenth Century: A Catalyst of Military Development in Central Europe". In Davies, Brian (ed.). Warfare in Eastern Europe, 1500-1800. Brill Publishers. ISBN 9789004221987.
- Štefanec, Nataša (2011). Država ili ne. Ustroj Vojne krajine 1578. godine i hrvatsko-slavonski staleži u regionalnoj obrani i politici [State or Not. Organization of the Military Border in 1578 and Croatian-Slavonian Estates in Regional Defense and Politics] (in Croatian). Zagreb: Srednja Europa. ISBN 978-953-6979-73-8.
Bibliography
- Bataković, Dušan T., ed. (2005). Histoire du peuple serbe [History of the Serbian People] (in French). Lausanne: L'Age d'Homme. ISBN 9782825119587.
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781405142915.
- Dabić, Vojin S. (1992). "Wanderungen der Serben nach Kroatien und Slawonien vom Anfang des XVI bis Ende des XVII Jahrhunderts". Историјски часопис. 38 (1991): 43–76.
- Dabić, Vojin S. (2011). "The Habsburg-Ottoman War of 1716-1718 and Demographic Changes in the War-Afflicted Territories". The Peace of Passarowitz, 1718. West Lafayette: Purdue University Press. pp. 191–208. ISBN 9781557535948.
- Fodor, Pál; Dávid, Géza, eds. (2000). Ottomans, Hungarians, and Habsburgs in Central Europe: The Military Confines in the Era of Ottoman Conquest. BRILL. ISBN 9004119078.
- Ilić-Mandić, Jelena (2020). "The Local Elite in Central Government Service: Banat Military Frontier Officers in the 18th Century". The Habsburg State-wide and the regions in the Southern Danube basin (16th-20th centuries). Wien: New academic press. pp. 99–121.
- Ilić-Mandić, Jelena (2021). "Forging the Wallachian Military Border, 1769-1772" (PDF). Banatica. 31 (2): 251–273.
- Ilić-Mandić, Jelena (2022a). "Making the Border and Frontiersmen: Militarisation in Temeswarer Banat, 1764-1775". From medieval frontiers to early modern borders in Central and South-Eastern Europe. Berlin: Peter Lang Publishing. pp. 207–228. ISBN 9783631880111.
- Ilić-Mandić, Jelena (2022b). "The Military Frontier and Emigration Challenges in the 18th Century" (PDF). Migrations in the Slavic Cultural Space From the Middle Ages to the Present Day. Lódź: Wydawnictwo Universytetu Lódzkiego. pp. 45–62.
- Dragutin Pavličević (1984). Vojna krajina: povijesni pregled, historiografija, rasprave. Sveučilišna naklada Liber.
- Walter Berger: Baut dem Reich einen Wall. Das Buch vom Entstehen der Militärgrenze wider die Türken. Leopold Stocker Verlag, 1979 ISBN 3-7020-0342-8
- Jakob Amstadt: Die k.k. Militaergrenze 1522 – 1881 (mit einer Gesamtbibliographie). Dissertation, University of Würzburg, 1969
- Heeresgeschichtliches Museum (Hrsg.): Die k. k. Militärgrenze (Beiträge zu ihrer Geschichte). ÖBV, 1973 (Schriften des Heeresgeschichtlichen Museums, 6) ISBN 3-215-73302-1
- Mirko Valentić: Vojna krajina i pitanje njezina sjedinjenja s Hrvatskom 1849–1881, CHP, 1981, Zagreb
- Alexander Buczynski: Gradovi Vojne krajine 1–2, HIP, 1997, Zagreb
- Milan Kruhek: Krajiške utvrde Hrvatskog kraljevstva, HIP, 1995, Zagreb
- Drago Roksandić: Vojna Hrvatska (1809.-1813.), 1–2, ŠK, 1988, Zagreb
- Drago Roksandić: Etnos, konfesija, tolerancija, SKD Prosvjeta, 2004, Zagreb
- Potiska i pomoriška vojna granica (1702–1751), Muzej Vojvodine, Novi Sad, 2003.
External links