Moghul Empire
The Mughal Empire is conventionally said to have been founded in 1526 by Babur, a Timurid chieftain from Transoxiana, who employed aid from the neighbouring Safavid and Ottoman Empires to defeat the sultan of Delhi, Ibrahim Lodi, in the First Battle of Panipat, and to sweep down the plains of North India. The Mughal imperial structure, however, is sometimes dated to 1600, to the rule of Babur's grandson, Akbar. This imperial structure lasted until 1720, shortly after the death of the last major emperor, Aurangzeb, during whose reign the empire also achieved its maximum geographical extent. Reduced subsequently to the region in and around Old Delhi by 1760, the empire was formally dissolved by the British Raj after the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Although the Mughal Empire was created and sustained by military warfare, it did not vigorously suppress the cultures and peoples it came to rule; rather it equalized and placated them through new administrative practices, and diverse ruling elites, leading to more efficient, centralised, and standardized rule. The base of the empire's collective wealth was agricultural taxes, instituted by the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. These taxes, which amounted to well over half the output of a peasant cultivator, were paid in the well-regulated silver currency, and caused peasants and artisans to enter larger markets.
The relative peace maintained by the empire during much of the 17th century was a factor in India's economic expansion. The burgeoning European presence in the Indian Ocean and an increasing demand for Indian raw and finished products generated much wealth for the Mughal court. There was more conspicuous consumption among the Mughal elite, resulting in greater patronage of painting, literary forms, textiles, and architecture, especially during the reign of Shah Jahan. Among the Mughal UNESCO World Heritage Sites in South Asia are: Agra Fort, Fatehpur Sikri, Red Fort, Humayun's Tomb, Lahore Fort, Shalamar Gardens, and the Taj Mahal, which is described as "the jewel of Muslim art in India, and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage".
Name
The closest to an official name for the empire was Hindustan, which was documented in the Ain-i-Akbari. Mughal administrative records also refer to the empire as "dominion of Hindustan" (Wilāyat-i-Hindustān), "country of Hind" (Bilād-i-Hind), "Sultanate of Al-Hind" (Salṭanat(i) al-Hindīyyah) as observed in the epithet of Emperor Aurangzeb or endonymous identification from emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar as "Land of Hind" (Hindostān) in Hindustani. Contemporary Chinese chronicles referred to the empire as Hindustan (Héndūsītǎn). In the west, the term "Mughal" was used for the emperor, and by extension, the empire as a whole.
The Mughal designation for their dynasty was Gurkani (Gūrkāniyān), a reference to their descent from the Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur, who took the title Gūrkān 'son-in-law' after his marriage to a Chinggisid princess. The word Mughal (also spelled Mogul or Moghul in English) is the Indo-Persian form of Mongol. The Mughal dynasty's early followers were Chagatai Turks and not Mongols. The term Mughal was applied to them in India by association with the Mongols and to distinguish them from the Afghan elite which ruled the Delhi Sultanate. The term remains disputed by Indologists. In Marshall Hodgson's view, the dynasty should be called Timurid/Timuri or Indo-Timurid.
History
Babur and Humayun (1526–1556)
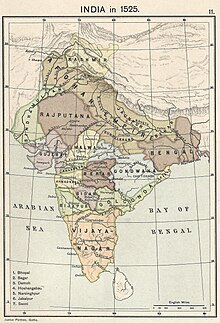
The Mughal Empire was founded by Babur (reigned 1526–1530), a Central Asian ruler who was descended from the Persianized Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur (the founder of the Timurid Empire) on his father's side, and from Genghis Khan on his mother's side. Paternally, Babur belonged to the Turkicized Barlas tribe of Mongol origin. Ousted from his ancestral domains in Central Asia, Babur turned to India to satisfy his ambitions. He established himself in Kabul and then pushed steadily southward into India from Afghanistan through the Khyber Pass. Babur's forces defeated Ibrahim Lodi, Sultan of Delhi, in the First Battle of Panipat in 1526. Through his use of firearms and cannons, he was able to shatter Ibrahim's armies despite being at a numerical disadvantage, expanding his dominion up to the mid Indo-Gangetic Plain. After the battle, the centre of Mughal power shifted to Agra. In the decisive Battle of Khanwa, fought near Agra a year later, the Timurid forces of Babur defeated the combined Rajput armies of Rana Sanga of Mewar, with his native cavalry employing traditional flanking tactics.
The preoccupation with wars and military campaigns, however, did not allow the new emperor to consolidate the gains he had made in India. The instability of the empire became evident under his son, Humayun (reigned 1530–1556), who was forced into exile in Persia by the rebellious Sher Shah Suri (reigned 1540–1545). Humayun's exile in Persia established diplomatic ties between the Safavid and Mughal courts and led to increasing Persian cultural influence in the later restored Mughal Empire. Humayun's triumphant return from Persia in 1555 restored Mughal rule in some parts of India, but he died in an accident the next year.
Akbar to Aurangzeb (1556–1707)

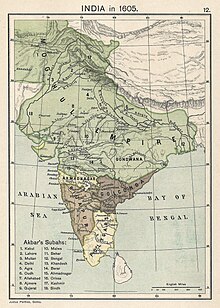
Akbar (reigned 1556–1605) was born Jalal-ud-din Muhammad in the Umarkot Fort, to Humayun and his wife Hamida Banu Begum, a Persian princess. Akbar succeeded to the throne under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped consolidate the Mughal Empire in India. Through warfare, Akbar was able to extend the empire in all directions and controlled almost the entire Indian subcontinent north of the Godavari River. He created a new ruling elite loyal to him, implemented a modern administration, and encouraged cultural developments. He increased trade with European trading companies. India developed a strong and stable economy, leading to commercial expansion and economic development. Akbar allowed freedom of religion at his court and attempted to resolve socio-political and cultural differences in his empire by establishing a new religion, Din-i-Ilahi, with strong characteristics of a ruler cult. He left his son an internally stable state, which was in the midst of its golden age, but before long signs of political weakness would emerge.
Jahangir (born Salim, reigned 1605–1627) was born to Akbar and his wife Mariam-uz-Zamani, an Indian princess. Salim was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti. He "was addicted to opium, neglected the affairs of the state, and came under the influence of rival court cliques". Jahangir distinguished himself from Akbar by making substantial efforts to gain the support of the Islamic religious establishment. One way he did this was by bestowing many more madad-i-ma'ash (tax-free personal land revenue grants given to religiously learned or spiritually worthy individuals) than Akbar had. In contrast to Akbar, Jahangir came into conflict with non-Muslim religious leaders, notably the Sikh guru Arjan, whose execution was the first of many conflicts between the Mughal Empire and the Sikh community.

Shah Jahan (reigned 1628–1658) was born to Jahangir and his wife Jagat Gosain. His reign ushered in the golden age of Mughal architecture. During the reign of Shah Jahan, the splendour of the Mughal court reached its peak, as exemplified by the Taj Mahal. The cost of maintaining the court, however, began to exceed the revenue coming in. His reign was called "The Golden Age of Mughal Architecture". Shah Jahan extended the Mughal Empire to the Deccan by ending the Ahmadnagar Sultanate and forcing the Adil Shahis and Qutb Shahis to pay tribute.
Shah Jahan's eldest son, the liberal Dara Shikoh, became regent in 1658, as a result of his father's illness. Dara championed a syncretistic Hindu-Muslim culture, emulating his great-grandfather Akbar. With the support of the Islamic orthodoxy, however, a younger son of Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb (r. 1658–1707), seized the throne. Aurangzeb defeated Dara in 1659 and had him executed. Although Shah Jahan fully recovered from his illness, Aurangzeb kept Shah Jahan imprisoned until he died in 1666. Aurangzeb brought the empire to its greatest territorial extent, and oversaw an increase in the Islamicization of the Mughal state. He encouraged conversion to Islam, reinstated the jizya on non-Muslims, and compiled the Fatawa 'Alamgiri, a collection of Islamic law. Aurangzeb also ordered the execution of the Sikh guru Tegh Bahadur, leading to the militarization of the Sikh community. From the imperial perspective, conversion to Islam integrated local elites into the king's vision of a network of shared identity that would join disparate groups throughout the empire in obedience to the Mughal emperor. He led campaigns from 1682 in the Deccan, annexing its remaining Muslim powers of Bijapur and Golconda, though engaged in a prolonged conflict in the region which had a ruinous effect on the empire. The campaigns took a toll on the Mughal treasury, and Aurangzeb's absence led to a severe decline in governance, while stability and economic output in the Mughal Deccan plummeted.
Aurangzeb is considered the most controversial Mughal emperor, with some historians arguing his religious conservatism and intolerance undermined the stability of Mughal society, while other historians question this, noting that he built Hindu temples, employed significantly more Hindus in his imperial bureaucracy than his predecessors did, and opposed bigotry against Hindus and Shia Muslims. Despite these allegations, it has been acknowledged that Emperor Aurangzeb enacted repressive policies towards non-Muslims. A major rebellion by the Marathas took place following this change, precipitated by the unmitigated state-building of its leader Shivaji in the Deccan.
Decline (1707–1857)

Aurangzeb's son, Bahadur Shah I, repealed the religious policies of his father and attempted to reform the administration. "However, after he died in 1712, the Mughal dynasty began to sink into chaos and violent feuds. In 1719 alone, four emperors successively ascended the throne", as figureheads under the rule of a brotherhood of nobles belonging to the Indian Muslim caste known as the Sadaat-e-Bara, whose leaders, the Sayyid Brothers, became the de facto sovereigns of the empire.
During the reign of Muhammad Shah (reigned 1719–1748), the empire began to break up, and vast tracts of central India passed from Mughal to Maratha hands. As the Mughals tried to suppress the independence of Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah I in the Deccan, he encouraged the Marathas to invade central and northern India. The Indian campaign of Nader Shah, who had previously reestablished Iranian suzerainty over most of West Asia, the Caucasus, and Central Asia, culminated with the Sack of Delhi shattering the remnants of Mughal power and prestige, and taking off all the accumulated Mughal treasury. The Mughals could no longer finance the huge armies with which they had formerly enforced their rule. Many of the empire's elites now sought to control their affairs and broke away to form independent kingdoms. But lip service continued to be paid to the Mughal Emperor as the highest manifestation of sovereignty. Not only the Muslim gentry, but the Maratha, Hindu, and Sikh leaders took part in ceremonial acknowledgements of the emperor as the sovereign of India.
Meanwhile, some regional polities within the increasingly fragmented Mughal Empire involved themselves and the state in global conflicts, leading only to defeat and loss of territory during conflicts such as the Carnatic wars and Bengal War.
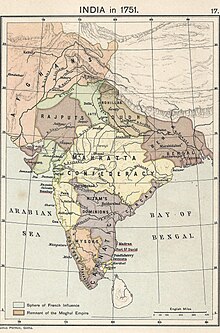
The Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II (1759–1806) made futile attempts to reverse the Mughal decline. Delhi was sacked by the Afghans, and when the Third Battle of Panipat was fought between the Maratha Empire and the Afghans (led by Ahmad Shah Durrani) in 1761, in which the Afghans were victorious, the emperor had ignominiously taken temporary refuge with the British to the east. In 1771, the Marathas recaptured Delhi from the Rohillas, and in 1784 the Marathas officially became the protectors of the emperor in Delhi, a state of affairs that continued until the Second Anglo-Maratha War. Thereafter, the British East India Company became the protectors of the Mughal dynasty in Delhi. The British East India Company took control of the former Mughal province of Bengal-Bihar in 1793 after it abolished local rule (Nizamat) that lasted until 1858, marking the beginning of the British colonial era over the Indian subcontinent. By 1857 a considerable part of former Mughal India was under the East India Company's control. After a crushing defeat in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 which he nominally led, the last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was deposed by the British East India Company and exiled in 1858 to Rangoon, Burma.

Causes of decline
Historians have offered numerous accounts of the several factors involved in the rapid collapse of the Mughal Empire between 1707 and 1720, after a century of growth and prosperity. A succession of short-lived incompetent and weak rulers, and civil wars over the succession, created political instability at the centre. The Mughals appeared virtually unassailable during the 17th century, but, once gone, their imperial overstretch became clear, and the situation could not be recovered. The seemingly innocuous European trading companies, such as the British East Indies Company, played no real part in the initial decline; they were still racing to get permission from the Mughal rulers to establish trades and factories in India.
In fiscal terms, the throne lost the revenues needed to pay its chief officers, the emirs (nobles) and their entourages. The emperor lost authority as the widely scattered imperial officers lost confidence in the central authorities and made their deals with local men of influence. The imperial army bogged down in long, futile wars against the more aggressive Marathas, and lost its fighting spirit. Finally came a series of violent political feuds over control of the throne. After the execution of Emperor Farrukhsiyar in 1719, local Mughal successor states took power in region after region.
Administration and state
The Mughal Empire had a highly centralised, bureaucratic government, most of which was instituted during the rule of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. The central government was headed by the Mughal emperor; immediately beneath him were four ministries. The finance/revenue ministry, headed by an official called a diwan, was responsible for controlling revenues from the empire's territories, calculating tax revenues, and using this information to distribute assignments. The ministry of the military (army/intelligence) was headed by an official titled mir bakhshi, who was in charge of military organisation, messenger service, and the mansabdari system. The ministry in charge of law/religious patronage was the responsibility of the sadr as-sudr, who appointed judges and managed charities and stipends. Another ministry was dedicated to the imperial household and public works, headed by the mir saman. Of these ministers, the diwan held the most importance, and typically acted as the wazir (prime minister) of the empire.
Administrative divisions
The empire was divided into Subah (provinces), each of which was headed by a provincial governor called a subadar. The structure of the central government was mirrored at the provincial level; each suba had its own bakhshi, sadr as-sudr, and finance minister that reported directly to the central government rather than the subahdar. Subas were subdivided into administrative units known as sarkars, which were further divided into groups of villages known as parganas. The Mughal government in the pargana consisted of a Muslim judge and local tax collector. Parganas were the basic administrative unit of the Mughal Empire.
Mughal administrative divisions were not static. Territories were often rearranged and reconstituted for better administrative control, and to extend cultivation. For example, a sarkar could turn into a subah, and Parganas were often transferred between sarkars. The hierarchy of division was ambiguous sometimes, as a territory could fall under multiple overlapping jurisdictions. Administrative divisions were also vague in their geography—the Mughal state did not have enough resources or authority to undertake detailed land surveys, and hence the geographical limits of these divisions were not formalised and maps were not created. The Mughals instead recorded detailed statistics about each division, to assess the territory's capacity for revenue, based on simpler land surveys.
Capitals
The Mughals had multiple imperial capitals, established throughout their rule. These were the cities of Agra, Delhi, Lahore, and Fatehpur Sikri. Power often shifted back and forth between these capitals. Sometimes this was necessitated by political and military demands, but shifts also occurred for ideological reasons (for example, Akbar's establishment of Fatehpur Sikri), or even simply because the cost of establishing a new capital was marginal. Situations where two simultaneous capitals happened multiple times in Mughal history. Certain cities also served as short-term, provincial capitals, as was the case with Aurangzeb's shift to Aurangabad in the Deccan. Kabul was the summer capital of Mughals from 1526 to 1681.
The imperial camp, used for military expeditions and royal tours, also served as a kind of mobile, "de facto" administrative capital. From the time of Akbar, Mughal camps were huge in scale, accompanied by numerous personages associated with the royal court, as well as soldiers and labourers. All administration and governance were carried out within them. The Mughal Emperors spent a significant portion of their ruling period within these camps.
After Aurangzeb, the Mughal capital definitively became the walled city of Shahjahanabad (Old Delhi).
Law

The Mughal Empire's legal system was context-specific and evolved throughout the empire's rule. Being a Muslim state, the empire employed fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence) and therefore the fundamental institutions of Islamic law such as those of the qadi (judge), mufti (jurisconsult), and muhtasib (censor and market supervisor) were well-established in the Mughal Empire. However, the dispensation of justice also depended on other factors, such as administrative rules, local customs, and political convenience. This was due to Persianate influences on Mughal ideology and the fact that the Mughal Empire governed a non-Muslim majority. Scholar Mouez Khalfaoui notes that legal institutions in the Mughal Empire systemically suffered from the corruption of local judges.
Legal ideology
The Mughal Empire followed the Sunni Hanafi system of jurisprudence. In its early years, the empire relied on Hanafi legal references inherited from its predecessor, the Delhi Sultanate. These included the al-Hidayah (the best guidance) and the Fatawa al-Tatarkhaniyya (religious decisions of the Emire Tatarkhan). During the Mughal Empire's peak, the Fatawa 'Alamgiri was commissioned by Emperor Aurangzeb. This compendium of Hanafi law sought to serve as a central reference for the Mughal state that dealt with the specifics of the South Asian context.
The Mughal Empire also drew on Persian notions of kingship. Particularly, this meant that the Mughal emperor was considered the supreme authority on legal affairs.
Courts of law
Various kinds of courts existed in the Mughal Empire. One such court was that of the qadi. The Mughal qadi was responsible for dispensing justice; this included settling disputes, judging people for crimes, and dealing with inheritances and orphans. The qadi also had additional importance in documents, as the seal of the qadi was required to validate deeds and tax records. Qadis did not constitute a single position, but made up a hierarchy. For example, the most basic kind was the pargana (district) qadi. More prestigious positions were those of the qadi al-quddat (judge of judges) who accompanied the mobile imperial camp, and the qadi-yi lashkar (judge of the army). Qadis were usually appointed by the emperor or the sadr-us-sudr (chief of charities). The jurisdiction of the qadi was availed by Muslims and non-Muslims alike.
The jagirdar (local tax collector) was another kind of official approach, especially for high-stakes cases. Subjects of the Mughal Empire also took their grievances to the courts of superior officials, who held more authority and punitive power than the local qadi. Such officials included the kotwal (local police), the faujdar (an officer controlling multiple districts and troops of soldiers), and the most powerful, the subahdar (provincial governor). In some cases, the emperor dispensed justice directly. Jahangir was known to have installed a "chain of justice" in the Agra Fort that any aggrieved subject could shake to get the attention of the emperor and bypass the inefficacy of officials.
Self-regulating tribunals operating at the community or village level were common, but sparse documentation of them exists. For example, it is unclear how panchayats (village councils) operated in the Mughal era.
Economy
The Mughal economy was large and prosperous. India was producing 24.5% of the world's manufacturing output up until 1750. Mughal India's economy has been described as a form of proto-industrialization, like that of 18th-century Western Europe before the Industrial Revolution.
Modern historians and researchers generally agree that the character of the Mughal Empire's economic policy resembles the laissez-faire system in dealing with trade and billions to achieve the economic ends.
The Mughals were responsible for building an extensive road system and creating a uniform currency. The empire had an extensive road network, which was vital to the economic infrastructure, built by a public works department set up by the Mughals which designed, constructed and maintained roads linking towns and cities across the empire, making trade easier to conduct.
The main base of the empire's collective wealth was agricultural taxes, instituted by the third Mughal emperor, Akbar. These taxes, which amounted to well over half the output of a peasant cultivator, were paid in the well-regulated silver currency, and caused peasants and artisans to enter larger markets. In circa 1595, Modern historians estimated the state's annual revenues of the Mughal Empire were around 99,000,000 rupees.
Coinage

The Mughals adopted and standardised the rupee (rupiya, or silver) and dam (copper) currencies introduced by Sur Emperor Sher Shah Suri during his brief rule. The Mughals minted coins with high purity, never dropping below 96%, and without debasement until the 1720s.
Despite India having its stocks of gold and silver, the Mughals produced minimal gold of their own but mostly minted coins from imported bullion, as a result of the empire's strong export-driven economy, with global demand for Indian agricultural and industrial products drawing a steady stream of precious metals into India.
Labour
The historian Shireen Moosvi estimates that in terms of contributions to the Mughal economy, in the late 16th century, the primary sector contributed 52%, the secondary sector 18% and the tertiary sector 29%; the secondary sector contributed a higher percentage than in early 20th-century British India, where the secondary sector only contributed 11% to the economy. In terms of the urban-rural divide, 18% of Mughal India's labour force were urban and 82% were rural, contributing 52% and 48% to the economy, respectively.
According to Moosvi, Mughal India had a per-capita income, in terms of wheat, 1.24% higher in the late 16th century than British India did in the early 20th century. This income, however, would have to be revised downwards if manufactured goods, like clothing, would be considered. Compared to food per capita, expenditure on clothing was much smaller though, so relative income between 1595 and 1596 should be comparable to 1901–1910. However, in a system where wealth was hoarded by elites, wages were depressed for manual labour. While slavery also existed, it was limited largely to household servants.
Agriculture
Indian agricultural production increased under the Mughal Empire. A variety of crops were grown, including food crops such as wheat, rice, and barley, and non-food cash crops such as cotton, indigo and opium. By the mid-17th century, Indian cultivators began to extensively grow two new crops from the Americas, maize and tobacco.
The Mughal administration emphasised the agrarian reform that began under the non-Mughal emperor Sher Shah Suri, which Akbar adopted and furthered with more reforms. The civil administration was organised hierarchically based on merit, with promotions based on performance. The Mughal government funded the building of irrigation systems across the empire, which produced much higher crop yields and increased the net revenue base, leading to increased agricultural production.
A major Mughal reform introduced by Akbar was a new land revenue system called zabt. He replaced the tribute system, previously common in India and used by Tokugawa Japan at the time, with a monetary tax system based on a uniform currency. The revenue system was biased in favour of higher value cash crops such as cotton, indigo, sugar cane, tree crops, and opium, providing state incentives to grow cash crops, in addition to rising market demand. Under the zabt system, the Mughals also conducted extensive cadastral surveying to assess the area of land under plough cultivation, with the Mughal state encouraging greater land cultivation by offering tax-free periods to those who brought new land under cultivation. The expansion of agriculture and cultivation continued under later Mughal emperors, including Aurangzeb.
Mughal agriculture was in some ways advanced compared to European agriculture at the time, exemplified by the common use of the seed drill among Indian peasants before its adoption in Europe. Geared sugar rolling mills first appeared in Mughal India, using the principle of rollers as well as worm gearing, by the 17th century.
Industrial manufacturing
South Asia during the Mughal's rule was a very fertile ground for manufacturing technologies coveted by the Europeans before the Industrial Revolution. Up until 1750, India produced about 25% of the world's industrial output.
Manufactured goods and cash crops from the Mughal Empire were sold throughout the world. The growth of manufacturing industries in the Indian subcontinent during the Mughal era in the 17th–18th centuries has been referred to as a form of proto-industrialization, similar to 18th-century Western Europe before the Industrial Revolution.
In early modern Europe, there was significant demand for products from Mughal India, particularly cotton textiles, as well as goods such as spices, peppers, indigo, silks, and saltpetre (for use in munitions). European fashion, for example, became increasingly dependent on Mughal Indian textiles and silks.
Textile industry

The largest manufacturing industry in the Mughal Empire was textile manufacturing, particularly cotton textile manufacturing, which included the production of piece goods, calicos, and muslins. The cotton textile industry was responsible for a large part of the empire's international trade. India had a 25% share of the global textile trade in the early 18th century, and it represented the most important manufactured goods in world trade in the 18th century. The most important centre of cotton production was the Bengal province, particularly around its capital city of Dhaka.
The production of cotton was advanced by the diffusion of the spinning wheel across India shortly before the Mughal era, lowering the costs of yarn and helping to increase demand for cotton. The diffusion of the spinning wheel and the incorporation of the worm gear and crank handle into the roller cotton gin led to greatly expanded Indian cotton textile production during the Mughal era.
Bengal Subah

The Bengal Subah province was especially prosperous from the time of its takeover by the Mughals in 1590 until the British East India Company seized control in 1757. Historian C. A. Bayly wrote that it was probably the Mughal Empire's wealthiest province. Domestically, much of India depended on Bengali products such as rice, silks and cotton textiles. Overseas, Europeans depended on Bengali products such as cotton textiles, silks, and opium. The province was a leading producer of grains, salt, fruits, liquors and wines, precious metals and ornaments.
After 150 years of rule by Mughal viceroys, Bengal gained de facto independence as a dominion under Murshid Quli Khan, the first Nawab of Bengal in 1717. The Nawabs permitted European companies to set up trading posts across the region, which regarded Bengal as the richest place for trade.
Shipbuilding industry
Mughal India had a large shipbuilding industry, which was also largely centred in the Bengal province. Economic historian Indrajit Ray estimates the shipbuilding output of Bengal during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries at 223,250 tons annually, compared with 23,061 tons produced in nineteen colonies in North America from 1769 to 1771. He also assesses ship repairing as very advanced in Bengal.
Demographics
Population
India's population growth accelerated under the Mughal Empire, with an unprecedented economic and demographic upsurge which boosted the Indian population by 60% to 253% in 200 years during 1500–1700. The Indian population had a faster growth during the Mughal era than at any known point in Indian history before the Mughal era. By the time of Aurangzeb's reign, there were a total of 455,698 villages in the Mughal Empire.
The following table gives population estimates for the Mughal Empire, compared to the total population of South Asia including the regions of modern India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, and compared to the world population:
| Year | Mughal Empire population |
Total Indian population |
% of South Asian population |
World population |
% of world population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | — | 100,000,000 | — | 425,000,000 | — |
| 1600 | 115,000,000 | 130,000,000 | 89 | 579,000,000 | 20 |
| 1700 | 158,400,000 | 160,000,000 | 99 | 679,000,000 | 23 |
Urbanization
According to Irfan Habib Cities and towns boomed under the Mughal Empire, which had a relatively high degree of urbanization for its time, with 15% of its population living in urban centres. This was higher than the percentage of the urban population in contemporary Europe at the time and higher than that of British India in the 19th century; the level of urbanization in Europe did not reach 15% until the 19th century.
Under Akbar's reign in 1600, the Mughal Empire's urban population was up to 17 million people, 15% of the empire's total population. This was larger than the entire urban population in Europe at the time, and even a century later in 1700, the urban population of England, Scotland and Wales did not exceed 13% of its total population, while British India had an urban population that was under 13% of its total population in 1800 and 9% in 1881, a decline from the earlier Mughal era. By 1700, Mughal India had an urban population of 23 million people, larger than British India's urban population of 22.3 million in 1871.
Those estimates were criticised by Tim Dyson, who considers them exaggerations. According to Dyson, urbanization of the Mughal Empire was less than 9%.
The historian Nizamuddin Ahmad (1551–1621) reported that, under Akbar's reign, there were 120 large cities and 3200 townships. Several cities in India had a population between a quarter-million and half-million people, with larger cities including Agra (in Agra Subah) with up to 800,000 people, Lahore (in Lahore Subah) with up to 700,000 people, Dhaka (in Bengal Subah) with over 1 million people, and Delhi (in Delhi Subah) with over 600,000 people.
Cities acted as markets for the sale of goods, and provided homes for a variety of merchants, traders, shopkeepers, artisans, moneylenders, weavers, craftspeople, officials, and religious figures. However, several cities were military and political centres, rather than manufacturing or commerce centres.
Culture

Generally, classical historiographies depicted the Mughal Empire's origin as a sedentarized agrarian society. However, modern historians such as André Wink, Jos J. L. Gommans, Anatoly Khazanov, Thomas J. Barfield, and others, argued the Mughals originated from nomadic culture. Pius Malekandathil argued instead that although it was true that the Mughal had their origin as nomadic civilization, they became more sendentarized as time passed, as exemplified by their military tradition. The Mughal Empire was definitive in the early-modern and modern periods of South Asian history, with its legacy in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Afghanistan seen in cultural contributions such as:


- Centralised imperial rule that consolidated the smaller polities of South Asia.
- The amalgamation of Persian art and literature with Indian art.

- The development of Mughlai cuisine, an amalgamation of South Asian, Iranian and Central Asian culinary styles.
- The development of Mughal clothing, jewellery and fashion, utilizing richly decorated fabrics such as muslin, silk, brocade and velvet.
- The influence of the Persian language over Old Hindi led to the development of the Hindustani language.
- The introduction of sophisticated Iranian-style waterworks and horticulture through Mughal gardening.
- The introduction of Turkish baths into the Indian subcontinent.
- The evolution and refinement of Mughal and Indian architecture, and, in turn, the development of later Rajput and Sikh palatial architecture. A famous Mughal landmark is the Taj Mahal.
- The development of the Pehlwani style of Indian wrestling, a combination of Indian malla-yuddha and Persian varzesh-e bastani.
- The construction of Maktab schools, where youth were taught the Quran and Islamic law such as the Fatawa 'Alamgiri in their indigenous languages.
- The development of Hindustani classical music, and instruments such as the sitar.

Customs
The procession of marriage among the royals of the Mughal Empire was recorded with many reports of extravagant gifts. One occasion was during the marriage of a son of emperor Akbar, Salim, with the daughter of a ruler of Bijapur, Raja Bhagwant Das, where the gift presented by Bhagwant Das consisted of many horses, 100 elephants, many male and female slaves of Abyssinian, Caucasian, and native Indian origins, who brought with them various gold and silver utensils as dowry.
Architecture
The Mughals made a major contribution to the Indian subcontinent with the development of their distinctive architectural style. This style was derived from earlier Indo-Islamic architecture as well as from Iranian and Central Asian architecture (particularly Timurid architecture), while incorporating further influences from Hindu architecture. Mughal architecture is distinguished, among other things, by bulbous domes, ogive arches, carefully-composed and polished façades, and the use of hard red sandstone and marble as construction materials.
Furthermore, William Dalrymple mentioned that during the final days of the Mughal fall of Delhi in 1857, an ice house structure existed in Delhi. Emperor Shah Jahan has recorded establishing an ice-house in Sirmaur, north of Delhi.
Many monuments were built during the Mughal era by the Muslim emperors, especially Shah Jahan, including the Taj Mahal—a UNESCO World Heritage Site considered "the jewel of Muslim art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage", attracting 7–8 million unique visitors a year. The palaces, tombs, gardens and forts built by the dynasty stand today in Agra, Aurangabad, Delhi, Dhaka, Fatehpur Sikri, Jaipur, Lahore, Kabul, Sheikhupura, and many other cities of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Bangladesh, such as:

| India | Pakistan | Bangladesh | Afghanistan |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Art and literature

The Mughal artistic tradition, mainly expressed in painted miniatures, as well as small luxury objects, was eclectic, borrowing from Iranian, Indian, Chinese and Renaissance European stylistic and thematic elements. Mughal emperors often took in Iranian bookbinders, illustrators, painters and calligraphers from the Safavid court due to the commonalities of their Timurid styles, and due to the Mughal affinity for Iranian art and calligraphy. Miniatures commissioned by the Mughal emperors initially focused on large projects illustrating books with eventful historical scenes and court life, but later included more single images for albums, with portraits and animal paintings displaying a profound appreciation for the serenity and beauty of the natural world. For example, Emperor Jahangir commissioned brilliant artists such as Ustad Mansur to realistically portray unusual flora and fauna throughout the empire.
The literary works Akbar and Jahangir ordered to be illustrated ranged from epics like the Razmnama (a Persian translation of the Hindu epic, the Mahabharata) to historical memoirs or biographies of the dynasty such as the Baburnama and Akbarnama, and Tuzk-e-Jahangiri. Richly finished albums (muraqqa) decorated with calligraphy and artistic scenes were mounted onto pages with decorative borders and then bound with covers of stamped and gilded or painted and lacquered leather. Aurangzeb (1658–1707) was never an enthusiastic patron of painting, largely for religious reasons, and took a turn away from the pomp and ceremonial of the court around 1668, after which he probably commissioned no more paintings.

Language
According to Mughal court historian Aminai Qazvini, by the time of Shah Jahan, the emperor was only familiar with a few Turki words and showed little interest in the study of the language as a child. Though the Mughals were of Turko-Mongol origin, their reign enacted the revival and height of the Persian language in the Indian subcontinent, and by the end of the 16th-century Turki (Chagatai) was understood by relatively few at court. Accompanied by literary patronage was the institutionalisation of Persian as an official and courtly language; this led to Persian reaching nearly the status of a first language for many inhabitants of Mughal India. Historian Muzaffar Alam argues that the Mughals used Persian purposefully as the vehicle of an overarching Indo-Persian political culture, to unite their diverse empire. Persian had a profound impact on the languages of South Asia; one such language, today known as Hindustani, developed in the imperial capital of Delhi in the late Mughal era. It began to be used as a literary language in the Mughal court from the reign of Shah Jahan, who described it as the language of his dastans (prose romances) and replaced Persian as the informal language of the Muslim elite. According to contemporary poet Mir Taqi Mir, "Urdu was the language of Hindustan by the authority of the King".
Military
Gunpowder warfare

Mughal India was one of the three Islamic gunpowder empires, along with the Ottoman Empire and Safavid Persia. By the time he was invited by Lodi governor of Lahore, Daulat Khan, to support his rebellion against Lodi Sultan Ibrahim Khan, Babur was familiar with gunpowder firearms and field artillery, and a method for deploying them. Babur had employed Ottoman expert Ustad Ali Quli, who showed Babur the standard Ottoman formation—artillery and firearm-equipped infantry protected by wagons in the centre and the mounted archers on both wings. Babur used this formation at the First Battle of Panipat in 1526, where the Afghan and Rajput forces loyal to the Delhi Sultanate, though superior in numbers but without the gunpowder weapons, were defeated. The decisive victory of the Timurid forces is one reason opponents rarely met Mughal princes in pitched battles throughout the empire's history. In India, guns made of bronze were recovered from Calicut (1504) and Diu (1533). Fathullah Shirazi (c. 1582), a Persian polymath and mechanical engineer who worked for Akbar, developed an early multi-gun shot. As opposed to the polybolos and repeating crossbows used earlier in ancient Greece and China, respectively, Shirazi's rapid-firing gun had multiple gun barrels that fired hand cannons loaded with gunpowder. It may be considered a version of a volley gun.

By the 17th century, Indians were manufacturing a diverse variety of firearms; large guns, in particular, became visible in Tanjore, Dacca, Bijapur and Murshidabad.
Rocketry and explosives
In the sixteenth century, Akbar was the first to initiate and use metal cylinder rockets known as bans, particularly against war elephants, during the battle of Sanbal. In 1657, the Mughal Army used rockets during the siege of Bidar. Prince Aurangzeb's forces discharged rockets and grenades while scaling the walls. Sidi Marjan was mortally wounded when a rocket struck his large gunpowder depot, and after twenty-seven days of hard fighting, Bidar was captured by the Mughals.
In A History of Greek Fire and Gunpowder, James Riddick Partington described Indian rockets and explosive mines:
The Indian war rockets ... were formidable weapons before such rockets were used in Europe. They had bam-boo rods, a rocket body lashed to the rod and iron points. They were directed at the target and fired by lighting the fuse, but the trajectory was rather erratic. The use of mines and counter-mines with explosive charges of gunpowder is mentioned for the times of Akbar and Jahangir.
Science
A new curriculum for the madrasas that stressed the importance of uloom-i-muqalat (Rational Sciences) and introduced new subjects such as geometry, medicine, philosophy, and mathematics. The new curriculum produced a series of eminent scholars, engineers and architects.
Astronomy

While there appears to have been little concern for theoretical astronomy, Mughal astronomers made advances in observational astronomy and produced some Zij treatises. Humayun built a personal observatory near Delhi. According to Sulaiman Nadvi, Jahangir and Shah Jahan intended to build observatories too, but were unable to do so. The astronomical instruments and observational techniques used at the Mughal observatories were mainly derived from Islamic astronomy. In the 17th century, the Mughal Empire saw a synthesis between Islamic and Hindu astronomy, where Islamic observational instruments were combined with Hindu computational techniques.
During the decline of the Mughal Empire, the Hindu king Jai Singh II of Amber continued the work of Mughal astronomy. In the early 18th century, he built several large observatories called Yantra Mandirs, to rival Ulugh Beg's Samarkand observatory, and to improve on the earlier Hindu computations in the Siddhantas and Islamic observations in Zij-i-Sultani. The instruments he used were influenced by Islamic astronomy, while the computational techniques were derived from Hindu astronomy.
Metallurgy

The society within the Mughal Empire operated the Karkhanas, which functioned as workshops for craftsmen. These Karkhanas were producing arms, ammunition, and also various items for the court and emperor's need such as clothes, shawls, turbans, jewelry, gold and silverware, perfumes, medicines, carpets, beddings, tents, and for the imperial stable-harnesses for the horses in irons, copper and other metals.
Another aspect of the remarkable invention in Mughal India is the lost-wax cast, hollow, seamless, celestial globe. It was invented in Kashmir by Ali Kashmiri ibn Luqman in 998 AH (1589–90 CE). Twenty other such globes were later produced in Lahore and Kashmir during the Mughal Empire. Before they were rediscovered in the 1980s, it was believed by modern metallurgists to be technically impossible to produce hollow metal globes without any seams. A 17th-century celestial globe was also made by Diya' ad-din Muhammad in Lahore, 1668 (now in Pakistan).
List of emperors
| Portrait | Titular Name | Birth Name | Birth | Reign | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 
|
Babur بابر |
Zahir al-Din Muhammad ظهیر الدین محمد |
14 February 1483 Andijan, Uzbekistan | 20 April 1526 – 26 December 1530 | 26 December 1530 (aged 47) Agra, India |
2 
|
Humayun همایوں |
Nasir al-Din Muhammad نصیر الدین محمد |
6 March 1508 Kabul, Afghanistan | 26 December 1530 – 17 May 1540
22 February 1555 – 27 January 1556 (10 years 3 months 25 days) |
27 January 1556 (aged 47) Delhi, India |
3 
|
Akbar اکبر |
Jalal al-Din Muhammad جلال الدین محمد |
15 October 1542 Umerkot, Pakistan | 11 February 1556 – 27 October 1605
(49 years 9 months 0 days) |
27 October 1605 (aged 63) Agra, India |
4 
|
Jahangir جهانگیر |
Nur al-Din Muhammad نور الدین محمد |
31 August 1569 Agra, India | 3 November 1605 – 28 October 1627
(21 years 11 months 23 days) |
28 October 1627 (aged 58) Bhimber, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan |
5 
|
Shah Jahan شاہ جهان |
Shihab al-Din Muhammad شهاب الدین محمد |
5 January 1592 Lahore, Pakistan | 19 January 1628 – 31 July 1658
(30 years 8 months 25 days) |
22 January 1666 (aged 74) Agra, India |
6 
|
Aurangzeb اورنگزیب Alamgir |
Muhi al-Din Muhammad محی الدین محمد |
3 November 1618 Gujarat, India | 31 July 1658 – 3 March 1707
(48 years 7 months 0 days) |
3 March 1707 (aged 88) Ahmednagar, India |
7 
|
Azam Shah اعظم شاه |
Qutb al-Din Muhammad قطب الدين محمد |
28 June 1653 Burhanpur, India | 14 March 1707 – 20 June 1707 | 20 June 1707 (aged 53) Agra, India |
8 
|
Bahadur Shah بهادر شاہ |
Qutb al-Din Muhammad قطب الدین محمد |
14 October 1643 Burhanpur, India | 19 June 1707 – 27 February 1712
(4 years, 253 days) |
27 February 1712 (aged 68) Lahore, Pakistan |
9 
|
Jahandar Shah جهاندار شاہ |
Muiz al-Din Muhammad معز الدین محمد |
9 May 1661 Deccan, India | 27 February 1712 – 11 February 1713
(0 years, 350 days) |
12 February 1713 (aged 51) Delhi, India |
10
|
Farrukh Siyar فرخ سیر |
Muin al-Din Muhammad موئن الدین محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
20 August 1685 Aurangabad, India | 11 January 1713 – 28 February 1719
(6 years, 48 days) |
19 April 1719 (aged 33) Delhi, India |
11
|
Rafi ud-Darajat رفیع الدرجات |
Shams al-Din Muhammad شمس الدین محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
1 December 1699 | 28 February 1719 – 6 June 1719
(0 years, 98 days) |
6 June 1719 (aged 19) Agra, India |
12
|
Shah Jahan II شاہ جهان دوم |
Rafi al-Din Muhammad رفع الدين محمد Puppet King Under the Sayyids of Barha |
5 January 1696 | 6 June 1719 – 17 September 1719
(0 years, 105 days) |
18 September 1719 (aged 23) Agra, India |
13
|
Muhammad Shah محمد شاه |
Nasir al-Din Muhammad نصیر الدین محمد |
7 August 1702 Ghazni, Afghanistan | 27 September 1719 – 26 April 1748
(28 years, 212 days) |
26 April 1748 (aged 45) Delhi, India |
14
|
Ahmad Shah Bahadur احمد شاہ بهادر |
Mujahid al-Din Muhammad مجاهد الدین محمد |
23 December 1725 Delhi, India | 29 April 1748 – 2 June 1754
(6 years, 37 days) |
1 January 1775 (aged 49) Delhi, India |
15
|
Alamgir II عالمگیر دوم |
Aziz al-Din Muhammad عزیز اُلدین محمد |
6 June 1699 Burhanpur, India | 3 June 1754 – 29 November 1759
(5 years, 180 days) |
29 November 1759 (aged 60) Kotla Fateh Shah, India |
16
|
Shah Jahan III شاه جهان سوم |
Muhi al-Millat محی الملت |
1711 | 10 December 1759 – 10 October 1760
(282 days) |
1772 (aged 60–61) |
17
|
Shah Alam II شاه عالم دوم |
Jalal al-Din Muhammad Ali Gauhar جلال الدین علی گوهر |
25 June 1728 Delhi, India | 10 October 1760 – 31 July 1788
(27 years, 301 days) |
19 November 1806 (aged 78) Delhi, India |
18
|
Jahan Shah جهان شاه |
Bidar Bakht Mahmud Shah Bahadur Jahan Shah بیدار بخت محمود شاه بهادر جهان شاہ Puppet King Under Ghulam Qadir Rogilla |
1749 Delhi, India | 31 July 1788 – 11 October 1788
(63 days) |
1790 (aged 40–41) Delhi, India |
17
|
Shah Alam II شاه عالم دوم |
Jalal al-Din Muhammad Ali Gauhar جلال الدین علی گوهر Puppet monarch under the Maratha Confederacy |
25 June 1728 Delhi, India | 16 October 1788 – 19 November 1806
(18 years, 339 days) |
19 November 1806 (aged 78) Delhi, India |
19
|
Akbar Shah II اکبر شاه دوم |
Muin al-Din Muhammad میرزا اکبر Puppet King under the East India Company |
22 April 1760 Mukundpur, India | 19 November 1806 – 28 September 1837
(30 years, 321 days) |
28 September 1837 (aged 77) Delhi, India |
20
|
Bahadur Shah II Zafar بهادر شاه ظفر |
Abu Zafar Siraj al-Din Muhammad ابو ظفر سراج اُلدین محمد |
24 October 1775 Delhi, India | 28 September 1837 – 21 September 1857
(19 years, 360 days) |
7 November 1862 (aged 87) Rangoon, Myanmar |
See also
- History of India
- Flags of the Mughal Empire
- List of Mongol states
- Mughal-Mongol genealogy
- Islam in South Asia
References
Footnotes
- ^ Branch: Sunni
- School of jurisprudence: Hanafi
Citations
- ^ Sinopoli 1994, p. 294.
- ^ Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D. (2006). "East–West Orientation of Historical Empires and Modern States". Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 219–229. doi:10.5195/JWSR.2006.369. ISSN 1076-156X.
- ^ Rein Taagepera (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 475–504. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. ISSN 0020-8833. JSTOR 2600793. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ^ Dyson, Tim (2018). A Population History of India: From the First Modern People to the Present Day. Oxford University Press. pp. 70–71. ISBN 978-0-19-256430-6.
We have seen that there is considerable uncertainty about the size of India's population c.1595. Serious assessments vary from 116 to 145 million (with an average of 125 million). However, the true figure could even be outside of this range. Accordingly, while it seems likely that the population grew over the seventeenth century, it is unlikely that we will ever have a good idea of its size in 1707.
- ^ József Böröcz (2009). The European Union and Global Social Change. Routledge. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-135-25580-0. Retrieved 26 June 2017.
- ^ Richards 1995, pp. 73–74.
- ^ Stein 2010, pp. 159–. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some 750,000 square miles [1,900,000 km], ranging from the frontier with Central Asia in northern Afghanistan to the northern uplands of the Deccan plateau, and from the Indus basin on the west to the Assamese highlands in the east."
- ^ Richards, John F. (28 March 2012). The Mughal Empire. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-511-58406-0.
- ^ Gilbert, Marc Jason (2017), South Asia in World History, Oxford University Press, p. 62, ISBN 978-0-19-066137-3, retrieved 15 July 2019 Quote: "Babur then adroitly gave the Ottomans his promise not to attack them in return for their military aid, which he received in the form of the newest of battlefield inventions, the matchlock gun and cast cannons, as well as instructors to train his men to use them."
- ^ Stein 2010, pp. 159–. Quote: "Another possible date for the beginning of the Mughal regime is 1600 when the institutions that defined the regime were set firmly in place and when the heartland of the empire was defined; both of these were the accomplishment of Babur's grandson Akbar."
- ^ Stein 2010, pp. 159–. Quote: "The imperial career of the Mughal house is conventionally reckoned to have ended in 1707 when the emperor Aurangzeb, a fifth-generation descendant of Babur, died. His fifty-year reign began in 1658 with the Mughal state seeming as strong as ever or even stronger. But in Aurangzeb's later years the state was brought to the brink of destruction, over which it toppled within a decade and a half after his death; by 1720 imperial Mughal rule was largely finished and an epoch of two imperial centuries had closed."
- ^ Richards 1995, p. xv. Quote: "By the latter date (1720) the essential structure of the centralized state was disintegrated beyond repair."
- ^ Stein 2010, pp. 159–. Quote: "The vaunting of such progenitors pointed up the central character of the Mughal regime as a warrior state: it was born in war and it was sustained by war until the eighteenth century when warfare destroyed it."
- ^ Robb 2011, pp. 108–. Quote: "The Mughal state was geared for war and succeeded while it won its battles. It controlled territory partly through its network of strongholds, from its fortified capitals in Agra, Delhi or Lahore, which defined its heartlands, to the converted and expanded forts of Rajasthan and the Deccan. The emperor's will be frequently enforced in battle. Hundreds of army scouts were an important source of information. But the empire's administrative structure too was defined by and directed at war. Local military checkpoints or thanas kept order. Directly appointed imperial military and civil commanders (faujdars) controlled the cavalry and infantry, or the administration, in each region. The peasantry in turn were often armed, able to provide supporters for regional powers, and liable to rebellion on their account: continual pacification was required of the rulers."
- ^ Gilbert, Marc Jason (2017), South Asia in World History, Oxford University Press, pp. 75–, ISBN 978-0-19-066137-3, archived from the original on 22 September 2023, retrieved 15 July 2019 Quote: "With Safavid and Ottoman aid, the Mughals would soon join these two powers in a triumvirate of warrior-driven, expansionist, and both militarily and bureaucratically efficient early modern states, now often called "gunpowder empires" due to their common proficiency is using such weapons to conquer lands they sought to control."
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 115.
- ^ Robb 2011, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 152–.
- ^ Stein 2010, pp. 164–. Quote: "The resource base of Akbar's new order was land revenue"
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 158–. Quote: "The Mughal empire was based in the interior of a large land mass and derived the vast majority of its revenues from agriculture."
- ^ Stein 2010, pp. 164–. Quote: "... well over half of the output from the fields in his realm, after the costs of production had been met, is estimated to have been taken from the peasant producers by way of official taxes and unofficial exactions. Moreover, payments were exacted in money, and this required a well-regulated silver currency."
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 152–. Quote: "His stipulation that land taxes be paid in cash forced peasants into market networks, where they could obtain the necessary money, while the standardization of imperial currency made the exchange of goods for money easier."
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 152–. Quote: "Above all, the long period of relative peace ushered in by Akbar's power, and maintained by his successors, contributed to India's economic expansion."
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 186–. Quote: "As the European presence in India grew, their demands for Indian goods and trading rights increased, thus bringing even greater wealth to the already flush Indian courts."
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 186–. Quote: "The elite spent more and more money on luxury goods and sumptuous lifestyles, and the rulers built entire new capital cities at times."
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, pp. 186–. Quote: "All these factors resulted in greater patronage of the arts, including textiles, paintings, architecture, jewellery, and weapons to meet the ceremonial requirements of kings and princes."
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Taj Mahal". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 1 February 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ Vanina, Eugenia (2012). Medieval Indian Mindscapes: Space, Time, Society, Man. Primus Books. p. 47. ISBN 978-93-80607-19-1. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Hardy, P. (1979). "Modern European and Muslim Explanations of Conversion to Islam in South Asia: A Preliminary Survey of the Literature". In Levtzion, Nehemia (ed.). Conversion to Islam. Holmes & Meier. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-8419-0343-2. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ "Name of the Monument/ site: Tomb of Aurangzeb" (PDF). asiaurangabad.in. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2015.
- ^ Parvez, Aslam; Fārūqī, At̤har (2017). The life & poetry of Bahadur Shah Zafar. New Delhi, India: Hay House India. ISBN 978-93-85827-47-1. OCLC 993093699.
- ^ "Indian History Collective". 30 December 2023. Archived from the original on 30 December 2023.
- ^ Mosca, Matthew (2013). From Frontier Policy to Foreign Policy: The Question of India and the Transformation of Geopolitics in Qing China. Stanford University Press. pp. 78–94. ISBN 978-0-8047-8538-9. Archived from the original on 7 November 2023. Retrieved 7 November 2023.
- ^ Fontana, Michela (2011). Matteo Ricci: A Jesuit in the Ming Court. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-4422-0588-8. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Zahir ud-Din Mohammad (2002). Thackston, Wheeler M. (ed.). The Baburnama: Memoirs of Babur, Prince and Emperor. New York: Modern Library. p. xlvi. ISBN 978-0-375-76137-9.
In India the dynasty always called itself Gurkani, after Temür's title Gurkân, the Persianized form of the Mongolian kürägän, 'son-in-law,' a title he assumed after his marriage to a Genghisid princess.
- ^ John Walbridge. God and Logic in Islam: The Caliphate of Reason. p. 165.
Persianate Mogul Empire.
- ^ Hodgson, Marshall G. S. (2009). The Venture of Islam. Vol. 3. University of Chicago Press. p. 62. ISBN 978-0-226-34688-5.
- ^ Canfield, Robert L. (2002). Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective. Cambridge University Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-521-52291-5.
- ^ Huskin, Frans Husken; Dick van der Meij (2004). Reading Asia: New Research in Asian Studies. Routledge. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-136-84377-8.
- ^ Berndl, Klaus (2005). National Geographic Visual History of the World. National Geographic Society. pp. 318–320. ISBN 978-0-7922-3695-5.
- ^ Gérard Chaliand, A Global History of War: From Assyria to the Twenty-First Century, University of California Press, California 2014, p. 151
- ^ Bayley, Christopher (1990). The European Emergence. The Mughals Ascendant. Time-Life Books. p. 151. ISBN 0-7054-0982-1.
- ^ Richards 1995, p. 8.
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 116.
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 117.
- ^ Bayley, Christopher (1990). The European Emergence. The Mughals Ascendant. Time-Life Books. p. 154. ISBN 0-7054-0982-1.
- ^ Majumdar 1974, pp. 59, 65.
- ^ Richards 1995, p. 12.
- ^ Ballhatchet, Kenneth A. "Akbar". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 25 May 2023. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ^ Smith, Vincent Arthur (1917). Akbar the Great Mogul, 1542–1605. Oxford at The Clarendon Press. pp. 13–14.
- ^ Begum, Gulbadan (1902). The History of Humāyūn (Humāyūn-Nāma). Translated by Beveridge, Annette S. Royal Asiatic Society. pp. 237–239.
- ^ Stein 2010, p. 162.
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 128.
- ^ Mohammada, Malika (2007). The Foundations of the Composite Culture in India. Aakar Books. p. 300. ISBN 978-81-89833-18-3.
- ^ Gilbert, Marc Jason (2017). South Asia in World History. Oxford University Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-19-976034-3. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- ^ Muhammad-Hadi (1999). Preface to The Jahangirnama. Translated by Thackston, Wheeler M. Oxford University Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-19-512718-8.
- ^ Jahangir, Emperor of Hindustan (1999). The Jahangirnama: Memoirs of Jahangir, Emperor of India. Translated by Thackston, Wheeler M. Oxford University Press. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-19-512718-8.
- ^ Faruqui, Munis D. (2012). The Princes of the Mughal Empire, 1504–1719. Cambridge University Press. pp. 268–269. ISBN 978-1-107-02217-1.
- ^ Robb 2011, pp. 97–98.
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 267.
- ^ "BBC – Religions – Sikhism: Origins of Sikhism". BBC. 30 September 2009. Archived from the original on 17 August 2018. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ Mehta, Jaswant Lal (1984) [First published 1981]. Advanced Study in the History of Medieval India. Vol. II (2nd ed.). Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. p. 59. ISBN 978-81-207-1015-3. OCLC 1008395679.
- ^ Singhal, Damodar P. (1983). A History of the Indian People. Methuen. p. 193. ISBN 978-0-413-48730-8. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 4 May 2021.
- ^ Dara Shikoh Archived 3 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine Medieval Islamic Civilization: An Encyclopedia, by Josef W. Meri, Jere L Bacharach. Routledge, 2005. ISBN 0-415-96690-6. pp. 195–196.
- ^ Truschke 2017, p. 68.
- ^ Faruqui, Munis D. (2011). "Awrangzīb". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_ei3_COM_23859. ISSN 1873-9830.
- ^ Robb 2011, p. 98.
- ^ Abhishek Kaicker (2020). The King and the People: Sovereignty and Popular Politics in Mughal Delhi. Oxford University Press. p. 160. ISBN 978-0-19-007067-0. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ Burton-Page, J.; Islam, Riazul; Athar Ali, M.; Moosvi, Shireen; Moreland, W. H.; Bosworth, C. E.; Schimmel, Annemarie; Koch, Ebba; Hall, Margaret (24 April 2012), "Mug̲h̲als", Encyclopaedia of Islam (2nd ed.), Brill, doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_com_0778, archived from the original on 31 March 2022, retrieved 31 March 2022
- ^ Richards 1995, pp. 220–222.
- ^ Richards 1995, p. 252.
- ^ Asher & Talbot 2006, p. 225.
- ^ Copland, Ian; Mabbett, Ian; Roy, Asim; et al. (2013). A History of State and Religion in India. Routledge. p. 119. ISBN 978-1-136-45950-4.
- ^ Truschke 2017, p. 58.
- ^ Verghese, Ajay; Foa, Roberto Stefan (5 November 2018). "Precolonial Ethnic Violence:The Case of Hindu-Muslim Conflict in India" (PDF). Boston University. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ Kruijtzer, Gijs (2009). Xenophobia in Seventeenth-Century India. Leiden University Press. p. 153.
- ^ Audrey Truschke (2021). the Language of History: Sanskrit Narratives of Indo-Muslim Rule. Publisher:Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-55195-3. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ Muhammad Yasin (1958). A Social History of Islamic India, 1605–1748. Upper India Publishing House. p. 18. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2023.
became virtual rulers and 'de facto' sovereigns when they began to make and unmake emperors. They had developed a sort of common brotherhood among themselves
- ^ Columbia University Press (2000). Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture. Columbia University Press. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-231-11004-4. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ Richard M. Eaton (2013). Eaton, Richard M.; Faruqui, Munis D.; Gilmartin, David; Kumar, Sunil (eds.). Expanding Frontiers in South Asian and World History Essays in Honour of John F. Richards. Cambridge University Press. p. 21. doi:10.1017/CBO9781107300002. ISBN 978-1-107-03428-0.
I consider all this army (Marathas) as my own.....I will enter into an understanding with them and entrust the Mulukgiri(raiding) on that side of the Narmada to them.
- ^ Pagadi, Setu Madhavarao (1970). "Maratha-Nizam Relations : Nizam-Ul-Mulk's Letters". Annals of the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute. 51 (1/4): 94.
The Mughal court was hostile to Nizam-ul-Mulk..... Nizam did not interfere with the Maratha activities in Malwa and Gujarat.....Nizam-ul-Mulk considered the Maratha army...
- ^ Salma Ahmed Farooqui (2011). A Comprehensive History of Medieval India: Twelfth to the Mid-eighteenth Century. Pearson Education India. p. 309. ISBN 978-8131732021.
Even more disturbing was the fact that the assertion of independence had spread to other part of the empire too, and the governors of Hyderabad, Bengal and Awadh soon established independent kingdoms as well.
- ^ Bose, Sugata; Jalal, Ayesha (2004). Modern South Asia: History, Culture, Political Economy (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-203-71253-5.
- ^ Rathod, N.G. (1994). The Great Maratha Mahadaji Scindia. New Delhi: Sarup & Sons. p. 8. ISBN 978-81-85431-52-9.
- ^ Conermann, Stephan (2015). "Mughal Empire". Encyclopedia of Early Modern History Online. Brill. doi:10.1163/2352-0272_emho_COM_024206. Retrieved 28 March 2022.
- ^ Kirsten McKenzie; Robert Aldrich (2013). The Routledge History of Western Empires (ebook). Taylor & Francis. p. 333. ISBN 9781317999874. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ Richards, J.F. (1981). "Mughal State Finance and the Premodern World Economy". Comparative Studies in Society and History. 23 (2): 285–308. doi:10.1017/s0010417500013311. JSTOR 178737. S2CID 154809724.
- ^ Robinson, Francis (2009), "Mughal Empire", The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Islamic World, Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/acref/9780195305135.001.0001, ISBN 978-0-19-530513-5, archived from the original on 29 March 2022, retrieved 28 March 2022
- ^ Gladden, E.N. (2019). A History of Public Administration Volume II: From the Eleventh Century to the Present Day. Routledge. pp. 234–236. ISBN 978-0-429-42321-5.
- ^ Michael, Bernardo A. (2012). Statemaking and Territory in South Asia. Anthem Press. p. 67. doi:10.7135/upo9780857285324.005. ISBN 978-0-85728-532-4.
- ^ Michael, Bernardo A. (2012). Statemaking and Territory in South Asia. Anthem Press. pp. 69, 75, 77–78. doi:10.7135/upo9780857285324.005. ISBN 978-0-85728-532-4.
- ^ Sinopoli 1994, pp. 294–295.
- ^ Sinopoli 1994, pp. 304–305.
- ^ Samrin, Farah (2005). "The City of Kabul Under the Mughals". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 66: 1307. JSTOR 44145943. Archived from the original on 29 June 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ Sinopoli 1994, pp. 296 & 298.
- ^ Bosworth, Clifford Edmund (2008). Historic cities of the Islamic world. Brill. p. 127. ISBN 978-90-04-15388-2. OCLC 231801473.
- ^ Chatterjee, Nandini (1 December 2019), "Courts of law, Mughal", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Three, Brill, doi:10.1163/1573-3912_ei3_com_25171, archived from the original on 13 December 2021, retrieved 13 December 2021
- ^ Khalfaoui, Mouez. "Mughal Empire and Law". Oxford Islamic Studies Online. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ Conermann, Stephan (4 August 2015), "Mughal Empire", Encyclopedia of Early Modern History Online, Brill, doi:10.1163/2352-0272_emho_com_024206, archived from the original on 26 March 2022, retrieved 25 March 2022
- ^ Chatterjee, Nandini (2014). "Reflections on Religious Difference and Permissive Inclusion in Mughal Law". Journal of Law and Religion. 29 (3): 396–415. doi:10.1017/jlr.2014.20. hdl:10871/15975. ISSN 0748-0814. S2CID 143513602. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ Eaton, Richard M. (2019). India in the Persianate Age : 1000–1765. University of California Press. p. 272. ISBN 978-0-520-97423-4. OCLC 1243310832.
- ^ Schmidt, Karl J. (2015). An Atlas and Survey of South Asian History. Routledge. pp. 100–. ISBN 978-1-317-47681-8. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ Maddison, Angus (2003). Development Centre Studies The World Economy Historical Statistics: Historical Statistics. OECD Publishing. pp. 256–. ISBN 978-92-64-10414-3. Archived from the original on 20 January 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ Jeffrey G. Williamson & David Clingingsmith, India's Deindustrialization in the 18th and 19th Centuries Archived 29 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Global Economic History Network, London School of Economics
- ^ Roy, Tirthankar (2010). "The Long Globalization and Textile Producers in India". In Lex Heerma van Voss; Els Hiemstra-Kuperus; Elise van Nederveen Meerkerk (eds.). The Ashgate Companion to the History of Textile Workers, 1650–2000. Ashgate Publishing. p. 255. ISBN 978-0-7546-6428-4. Archived from the original on 2 July 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2017.
- ^ J.J.L. Gommans 2002, p. 75.
- ^ Streusand 2018, p. "...Mughal rulers pursued a more laissez-faire economic approach, benefiting from the prosperity of...".
- ^ A. Bayly, C.; Fibiger Bang, Peter; Scheidel, Walter, eds. (2020). The Oxford World History of Empire Volume Two: The History of Empires. Oxford University Press. p. 775. ISBN 9780197532775. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
- ^ Ali 2008.
- ^ Richards 1995, pp. 185–204.
- ^ Jorge Flores 2015, p. 73.
- ^ "Picture of original Mughal rupiya introduced by Sher Shah Suri". Archived from the original on 5 October 2002. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ^ Richards, John F. (2003). The Unending Frontier: An Environmental History of the Early Modern World. University of California Press. pp. 27–. ISBN 978-0-520-93935-6. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ Richards 1995.
- ^ Moosvi 2015, p. 433.
- ^ Maddison, Angus (1971). Class Structure and Economic Growth: India and Pakistan Since the Moghuls. Taylor & Francis. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-415-38259-5. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- ^ Moosvi 2015, p. 432.
- ^ Moosvi 2015, p. 450.
- ^ Moosvi, Shireen (December 2011). "The World of Labour in Mughal India (c. 1500–1750)". International Review of Social History. 56 (S19): 245–261. doi:10.1017/S0020859011000526.
- ^ Pagaza, Ignacio; Argyriades, Demetrios (2009). Winning the Needed Change: Saving Our Planet Earth. IOS Press. p. 129. ISBN 978-1-58603-958-5.
- ^ Ludden, David (1999). An Agrarian History of South Asia. Cambridge University Press. p. 96. ISBN 978-0-521-36424-9. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ^ Habib, Kumar & Raychaudhuri 1987, p. 214.
- ^ Irfan Habib (2011), Economic History of Medieval India, 1200–1500, p. 53 Archived 22 September 2023 at the Wayback Machine, Pearson Education
- ^ Andrew de la Garza 2016, pp. 114–115.
- ^ Jeffrey G. Williamson, David Clingingsmith (August 2005). "India's Deindustrialization in the 18th and 19th Centuries" (PDF). Harvard University. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 18 May 2017.
- ^ Om Prakash, "Empire, Mughal Archived 18 November 2022 at the Wayback Machine", History of World Trade Since 1450, edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference US, 2006, pp. 237–240, World History in Context. Retrieved 3 August 2017
- ^ Angus Maddison (1995), Monitoring the World Economy, 1820–1992, OECD, p. 30
- ^ Parthasarathi, Prasannan (2011), Why Europe Grew Rich and Asia Did Not: Global Economic Divergence, 1600–1850, Cambridge University Press, p. 2, ISBN 978-1-139-49889-0
- ^ Richard Maxwell Eaton (1996), The Rise of Islam and the Bengal Frontier, 1204–1760, p. 202 Archived 4 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, University of California Press
- ^ Irfan Habib (2011), Economic History of Medieval India, 1200–1500, p. 54 Archived 22 September 2023 at the Wayback Machine, Pearson Education
- ^ Roy, Tirthankar (November 2011). "Where is Bengal? Situating an Indian Region in the Early Modern World Economy". Past & Present (213): 115–146. doi:10.1093/pastj/gtr009.
- ^ Bayly, C. A. (1988). Indian Society and the Making of the British Empire. The New Cambridge History of India. Vol. II.1. Cambridge University Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-521-38650-0. Archived from the original on 8 February 2023. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- ^ Nanda, J. N. (2005). Bengal: The Unique State. Concept Publishing Company. p. 10. ISBN 978-81-8069-149-2. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ^ Nitish K, Sengupta (2011). Land of Two Rivers A History of Bengal from the Mahabharata to Mujib. Penguin Books India. p. 16. ISBN 9780143416784.
- ^ Ray, Indrajit (2011). Bengal Industries and the British Industrial Revolution (1757–1857). Routledge. p. 174. ISBN 978-1-136-82552-1.
- ^ Colin McEvedy; Richard Jones (1978). Atlas of World Population History (PDF). New York: Facts on File. pp. 184–185. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- ^ Angus Maddison (2001), The World Economy: A Millennial Perspective, p. 236 Archived 11 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine, OECD Development Centre
- ^ Habib, Kumar & Raychaudhuri 1987, p. 170.
- ^ Jean-Noël Biraben, 1980, "An Essay Concerning Mankind's Evolution", Population, Selected Papers, Vol. 4, pp. 1–13
- ^ Eraly, Abraham (2007). The Mughal World: Life in India's Last Golden Age. Penguin Books India. pp. 5–. ISBN 978-0-14-310262-5.
- ^ Malanima, Paolo (2009). Pre-Modern European Economy: One Thousand Years (10th–19th Centuries). Brill Publishers. p. 244. ISBN 978-90-04-17822-9.
- ^ Habib, Kumar & Raychaudhuri 1987, p. 165.
- ^ Broadberry, Stephen; Gupta, Bishnupriya (2010). "Indian GDP before 1870: Some preliminary estimates and a comparison with Britain" (PDF). Warwick University. p. 23. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 12 October 2015.
- ^ Dyson, Tim (2018). A Population History of India: From the First Modern People to the Present Day. pp. 63–65.
- ^ Habib, Kumar & Raychaudhuri 1987, p. 171.
- ^ Rob, Md. Abdur; Asaduzzaman, Md. (December 1997). "Historical Growth of Urbanization in Dhaka City". Social Science Review. 14 (2). Dhaka University: 126.
- ^ Moosvi, Shireen (2008). People, Taxation, and Trade in Mughal India. Oxford University Press. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-19-569315-7.
- ^ Chaudhuri, K. N. (2008). "Some Reflections on the Town and Country in Mughal India". Modern Asian Studies. 12 (1): 77–96. doi:10.1017/S0026749X00008155. ISSN 0026-749X. S2CID 146558617.
- ^ Faruqi, Shamsur Rahman (2003). "A Long History of Urdu Literary Culture, Part 1". In Pollock, Sheldon (ed.). Literary Cultures in History. University of California Press. p. 806. ISBN 0-520-22821-9.
- ^ Kaushik Roy & Peter Lorge 2014, p. 146.
- ^ Pius Malekandathil (2016). The Indian Ocean in the Making of Early Modern India (Illustrated ed.). Routledge. p. 194. ISBN 978-1351997454. Retrieved 19 July 2024.
...Mughal army shed most of its post-nomadic...
- ^ Mughal Empire – MSN Encarta. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009.
- ^ "Indo-Persian Literature Conference: SOAS: North Indian Literary Culture (1450–1650)". SOAS. Archived from the original on 23 September 2009. Retrieved 28 November 2012.
- ^ "Islam: Mughal Empire (1500s, 1600s)". Religions. BBC. Archived from the original on 13 August 2018. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- ^ Fatma, Sadaf (2012). "Waterworks in Mughal Gardens". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 73: 1268–1278. JSTOR 44156328.
- ^ Alter, Joseph S. (May 1992). "The sannyasi and the Indian Wrestler: The Anatomy of a Relationship". American Ethnologist. 19 (2): 317–336. doi:10.1525/ae.1992.19.2.02a00070. ISSN 0094-0496.
- ^ Alter, Joseph S. (1992). The Wrestler's Body: Identity and Ideology in North India. University of California Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-520-07697-6.
Wrestling in modern India is a synthesis of two different traditions: the Persian form of the art brought into South Asia by the Moguls, and an indigenous Hindu form.
- ^ "Mughal influence on Indian music". The Hindu. 8 February 2000. Archived from the original on 26 December 2019. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ^ Harbans Mukhia (2008). The Mughals of India. John Wiley & Sons. p. 150. ISBN 978-0470758151. Retrieved 11 July 2024.
- ^ Petersen, Andrew (1996). "Mughals". Dictionary of Islamic architecture. Routledge. pp. 199–205. ISBN 9781134613663.
- ^ Asher, Catherine Blanshard (1992). Architecture of Mughal India. The New Cambridge History of India, Part I. Vol. 4. Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–2, 15–17. ISBN 9780521267281.
- ^ Bloom, Jonathan M.; Blair, Sheila S., eds. (2009). "Architecture". The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture. Vol. 1. Oxford University Press. p. 182. ISBN 9780195309911.
- ^ William Dalrymple (2009). The Last Mughal: The Fall of Delhi, 1857. A&C Black. ISBN 978-1408806883. Retrieved 23 July 2024.
... Ice House in which Zahir was sheltering...
- ^ Keshavlal H. Kamdar (1933). History of the Mughal Rule in India, 1526-1761. M. C. Kothari. p. 141. Retrieved 8 August 2024.
- ^ Ross Marlay; Clark D. Neher (1999). Patriots and Tyrants: Ten Asian Leaders. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 269. ISBN 978-0-8476-8442-7.
- ^ Crill, Rosemary, and Jariwala, Kapil. The Indian Portrait, 1560–1860, pp. 23–27, National Portrait Gallery, London, 2010, ISBN 978-1855144095; Beach, Milo Cleveland (1987), Early Mughal painting, Harvard University Press, pp. 33–37, ISBN 978-0-674-22185-7, google books Archived 26 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Soucek, Priscilla (1987). "Persian Artists in Mughal India: Influences and Transformations". Muqarnas. 4: 166–181. doi:10.2307/1523102. JSTOR 1523102.
- ^ Blunt, Wilfrid (1948). "The Mughal Painters of Natural History". The Burlington Magazine. 90 (539): 48–50. JSTOR 869792.
- ^ Sardar, Marika (October 2003). "The Art of the Mughals After 1600". The MET. Archived from the original on 4 February 2019.
- ^ Losty, J. P. Roy, Malini (eds), Mughal India: Art, Culture and Empire, 2013, pp. 147, 149, British Library, ISBN 978-0712358705
- ^ Banarsi Prasad Saksena (1932). History Of Shahjahan Of Dihli 1932. Indian Press Limited. p. 4.
- ^ Seyller 2011, p. 329.
- ^ "2. The Culture and Politics of Persian in Precolonial Hindustan", Literary Cultures in History, University of California Press, pp. 158–167, 2019, doi:10.1525/9780520926738-007, ISBN 978-0-520-92673-8, S2CID 226770775, archived from the original on 22 September 2023, retrieved 26 July 2021
- ^ Abidi, S. A. H.; Gargesh, Ravinder (2008), Kachru, Braj B; Kachru, Yamuna; Sridhar, S. N (eds.), "Persian in South Asia", Language in South Asia, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 105, doi:10.1017/cbo9780511619069.007, ISBN 978-0-511-61906-9, archived from the original on 22 September 2023, retrieved 26 July 2021
- ^ Alam, Muzaffar (2004). The languages of political Islam : India 1200–1800. University of Chicago Press. pp. 134, 144. ISBN 0-226-01100-3. OCLC 469379391.
- ^ Faruqi, Shamsur Rahman (2003). "A Long History of Urdu Literary Culture, Part 1: Naming and Placing a Literary Culture". In Pollock, Sheldon (ed.). Literary Cultures in History. University of California Press. pp. 807–808, 811. doi:10.1525/9780520926738-019. ISBN 978-0-520-22821-4. S2CID 226765648.
- ^ Matthews, David (6 August 2014). "Urdu". Encyclopaedia Iranica. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 26 July 2021.
- ^ Arthur Dudney (2015). Delhi:Pages From a Forgotten History. Hay House. ISBN 978-93-84544-31-7. Archived from the original on 9 June 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ S. R. Sharma · (2014). Life, Times and Poetry of Mir. Partridge Publishing. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-4828-1478-1. Archived from the original on 16 July 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ Streusand 2011.
- ^ Charles T. Evans. "The Gunpowder Empires". Northern Virginia Community College. Archived from the original on 26 May 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2010.
- ^ Streusand 2011, p. 255.
- ^ Partington, James Riddick (1999) [First published 1960]. A History of Greek Fire and Gunpowder. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 226. ISBN 978-0-8018-5954-0.
- ^ Bag, A.K. (2005). "Fathullah Shirazi: Cannon, Multi-barrel Gun and Yarghu". Indian Journal of History of Science. 40 (3): 431–436. ISSN 0019-5235.
- ^ Partington, James Riddick (1999) [First published 1960]. A History of Greek Fire and Gunpowder. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 225. ISBN 978-0-8018-5954-0.
- ^ Swati Shiwal; Dolamani Sahu (2022). "Political History of the Mughals: Influence on South Asia". IJRTS Journal of Research. 23 (23): 113. ISSN 2347-6117. Retrieved 16 July 2024.
- ^ Andrew Lambert and narrator Stephen Kemble (6 November 2008). Ancient Discoveries: Ancient Tank Tech. History Channel.
Mughal Emperor Akbar ... in this battle a rocket hits one of the elephants and the inevitable happens, he stampedes, the other elephants stampede, a very large Gujarati army is defeated by a much smaller Mughal army
- ^ Ghulam Yazdani (1995). Bidar: Its History and Monuments (1 ed.). Motilal Banarsidass. p. 15. ISBN 8120810716.
- ^ Khan, Nasir Raza. Art and Architectural Traditions of India and Iran: Commonality and Diversity. Routledge, 2022.
- ^ Nasir Raza Khan (2022). Art and Architectural Traditions of India and Iran Commonality and Diversity. Routledge India. ISBN 9781032134819. Retrieved 20 March 2024.
... Shirazi and others revised the syllabi of the madrasas. In the new syllabi ...
- ^ Sharma, Virendra Nath (1995), Sawai Jai Singh and His Astronomy, Motilal Banarsidass Publ., pp. 8–9, ISBN 978-81-208-1256-7
- ^ Baber, Zaheer (1996), The Science of Empire: Scientific Knowledge, Civilization, and Colonial Rule in India, State University of New York Press, pp. 82–89, ISBN 978-0-7914-2919-8
- ^ "A Celestial Globe, Made by Mughal Astrolabist Muhammad Salih of Thatta, Dated 1074 AH/1663 AD". www.orientalartauctions.com. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ Verma, Tripta (1994). Karkhanas Under the Mughals, from Akbar to Aurangzeb: A Study in Economic Development. Pragati Publications. p. 18. ISBN 978-81-7307-021-1.
- ^ Sharma, Sri Ram (1951). Mughal Government and Administration. Hind Kitabs. p. 61.
- ^ Sumit (2012). "An Eighteenth Century Survey of Jaipur "Chhapakhana" Based on Jaipur "Karkhanajat" Records". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 73: 421–430. ISSN 2249-1937. JSTOR 44156233.
- ^ Savage-Smith, Emilie (1985), Islamicate Celestial Globes: Their History, Construction, and Use, Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC
- ^ "Celestial globe". National Museums Scotland. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Allan, J.; Haig, Sir T. Wolsely; Dodwell, H. H. (1934). Dodwell, H. H. (ed.). The Cambridge Shorter History of India. Cambridge University Press. p. 398.
Sources
- Ali, M. Athar (2008). "The Mughal Polity – A Critique of Revisionist Approaches". Modern Asian Studies. 27 (5). Cambridge University Press: 699–710. doi:10.1017/S0026749X00001256. ISSN 1469-8099. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
- Andrew de la Garza (2016). The Mughal Empire at War Babur, Akbar and the Indian Military Revolution, 1500-1605. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-317-24531-5. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- Asher, Catherine B.; Talbot, Cynthia (2006). India before Europe. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-80904-5. OCLC 61303480.
- J.J.L. Gommans (2002). Mughal Warfare Indian Frontiers and Highroads to Empire 1500–1700. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781134552757. Archived from the original on 2 January 2011. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
- Habib, Irfan; Kumar, Dharma; Raychaudhuri, Tapan (1987). The Cambridge Economic History of India (PDF). Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- Jorge Flores (2015). The Mughal Padshah: A Jesuit Treatise on Emperor Jahangir's Court and Household. Volume 6 of Rulers & Elites. Brill. p. 74. ISBN 978-9004307537. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
- Kaushik Roy; Peter Lorge (2014). Chinese and Indian Warfare - From the Classical Age to 1870 (ebook). Taylor & Francis. p. 196. ISBN 978-1-317-58710-1. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- Majumdar, R.C. (1974). The Mughul Empire. Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan.
- Moosvi, Shireen (2015) [First published 1987]. The economy of the Mughal Empire, c. 1595: a statistical study (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-908549-1. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 13 June 2019.
- Richards, John F. (1995). The Mughal Empire. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-56603-2.
- Robb, Peter (2011), A History of India, Macmillan International Higher Education, ISBN 978-0-230-34424-2
- Seyller, John (2011). "A Mughal Manuscript of the "Diwan" of Nawa'i". Artibus Asiae. 71 (2): 325–334.
- Sinopoli, Carla M. (1994). "Monumentality and Mobility in Mughal Capitals". Asian Perspectives. 33 (2): 293–308. ISSN 0066-8435. JSTOR 42928323. Archived from the original on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- Stein, Burton (2010), A History of India, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-1-4443-2351-1, retrieved 15 July 2019
- Streusand, Douglas E. (2011). Islamic Gunpowder Empires: Ottomans, Safavids, and Mughals. Philadelphia: Westview Press. ISBN 978-0-8133-1359-7.
- Streusand, Douglas E. (2018). Islamic Gunpowder Empires Ottomans, Safavids, and Mughals. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780429979217. Retrieved 24 April 2024.
- Truschke, Audrey (2017). Aurangzeb: The Life and Legacy of India's Most Controversial King. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-1-5036-0259-5.
Further reading
- Alam, Muzaffar. Crisis of Empire in Mughal North India: Awadh & the Punjab, 1707–48 (1988)
- Ali, M. Athar (1975), "The Passing of Empire: The Mughal Case", Modern Asian Studies, 9 (3): 385–396, doi:10.1017/s0026749x00005825, JSTOR 311728, S2CID 143861682, on the causes of its collapse
- Black, Jeremy. "The Mughals Strike Twice", History Today (April 2012) 62#4 pp. 22–26. full text online
- Blake, Stephen P. (November 1979), "The Patrimonial-Bureaucratic Empire of the Mughals", Journal of Asian Studies, 39 (1): 77–94, doi:10.2307/2053505, JSTOR 2053505, S2CID 154527305
- Dale, Stephen F. The Muslim Empires of the Ottomans, Safavids and Mughals (Cambridge U.P. 2009)
- Dalrymple, William (2007). The Last Mughal: The Fall of a Dynasty : Delhi, 1857. Random House Digital, Inc. ISBN 978-0-307-26739-9.
- Faruqui, Munis D. (2005), "The Forgotten Prince: Mirza Hakim and the Formation of the Mughal Empire in India", Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient, 48 (4): 487–523, doi:10.1163/156852005774918813, JSTOR 25165118, on Akbar and his brother
- Gordon, S. The New Cambridge History of India, II, 4: The Marathas 1600–1818 (Cambridge, 1993).
- Habib, Irfan. Atlas of the Mughal Empire: Political and Economic Maps (1982).
- Markovits, Claude, ed. (2004) [First published 1994 as Histoire de l'Inde Moderne]. A History of Modern India, 1480–1950 (2nd ed.). London: Anthem Press. ISBN 978-1-84331-004-4. Archived from the original on 22 September 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- Metcalf, B.; Metcalf, T.R. (2006), A Concise History of Modern India (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-68225-1, archived from the original on 2 July 2023, retrieved 19 October 2015
- Majumdar, Ramesh Chandra (1974). The Mughul Empire. B.V. Bhavan.
- Richards, J.F. (April 1981), "Mughal State Finance and the Premodern World Economy", Comparative Studies in Society and History, 23 (2): 285–308, doi:10.1017/s0010417500013311, JSTOR 178737, S2CID 154809724
- Robb, P. (2001), A History of India, London: Palgrave, ISBN 978-0-333-69129-8
- Srivastava, Ashirbadi Lal. The Mughul Empire, 1526–1803 (1952) online.
- Stein, B. (1998), A History of India (1st ed.), Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-631-20546-3
Culture
- Berinstain, V. Mughal India: Splendour of the Peacock Throne (London, 1998).
- Busch, Allison. Poetry of Kings: The Classical Hindi Literature of Mughal India (2011) excerpt and text search Archived 29 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Parodi, Laura E. (2021). "Kabul, a Forgotten Mughal Capital: Gardens, City, and Court at the Turn of the Sixteenth Century". Muqarnas Online. 38 (1): 113–153. doi:10.1163/22118993-00381P05. S2CID 245040517.
- Diana Preston; Michael Preston (2007). Taj Mahal: Passion and Genius at the Heart of the Moghul Empire. Walker & Company. ISBN 978-0-8027-1673-6.
- Schimmel, Annemarie. The Empire of the Great Mughals: History, Art and Culture (Reaktion 2006)
- Welch, S.C.; et al. (1987). The Emperors' album: images of Mughal India. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 978-0-87099-499-9. Archived from the original on 27 September 2018. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
Society and economy
- Chaudhuri, K.N. (1978), "Some Reflections on the Town and Country in Mughal India", Modern Asian Studies, 12 (1): 77–96, doi:10.1017/s0026749x00008155, JSTOR 311823, S2CID 146558617
- Habib, Irfan. Atlas of the Mughal Empire: Political and Economic Maps (1982).
- Habib, Irfan. Agrarian System of Mughal India (1963, revised edition 1999).
- J. C. Sharman (2019). Empires of the Weak: The Real Story of European Expansion and the Creation of the New World Order. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691182797.
- Heesterman, J.C. (2004), "The Social Dynamics of the Mughal Empire: A Brief Introduction", Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient, 47 (3): 292–297, doi:10.1163/1568520041974729, JSTOR 25165051
- Khan, Iqtidar Alam (1976), "The Middle Classes in the Mughal Empire", Social Scientist, 5 (1): 28–49, doi:10.2307/3516601, JSTOR 3516601
- Masanori Sato (佐藤正哲); Nariaki Nakazato (中里成章); Tsukasa Mizushima (水島司) (1998). ムガル帝国から英領インドへ [From the Mughal Empire to British India]. 世界の歴史14 (in Japanese). 中央公論社.
- second publishment ムガル帝国から英領インドへ [From the Mughal Empire to British India]. Chuokoron-Shinsha World History 14. 2009.
- Rothermund, Dietmar. An Economic History of India: From Pre-Colonial Times to 1991 (1993)
- Oleg Igorevich Krassov (2022). Land Law in Asian Countries (ebook). Norma. p. 75. ISBN 9785001562566. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
Primary sources
- Bernier, Francois (1891). Travels in the Mogul Empire, A.D. 1656–1668. Archibald Constable, London.
- Hiro, Dilip, ed, Journal of Emperor Babur (Penguin Classics 2007)
- The Baburnama: Memoirs of Babur, Prince and Emperor ed. by W.M. Thackston Jr. (2002); this was the first autobiography in Islamic literature
- Jackson, A.V. et al., eds. History of India (1907) v. 9. Historic accounts of India by foreign travellers, classic, oriental, and occidental, by A.V.W. Jackson online edition
- Jouher (1832). The Tezkereh al vakiat or Private Memoirs of the Moghul Emperor Humayun Written in the Persian language by Jouher A confidential domestic of His Majesty. Translated by Major Charles Stewart. John Murray, London.
Older histories
- Elliot, Sir H.M., Edited by Dowson, John. The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period; published by London Trubner Company 1867–1877. (Online Copy at Packard Humanities Institute – Other Persian Texts in Translation; historical books: Author List and Title List)
- Adams, W.H. Davenport (1893). Warriors of the Crescent. London: Hutchinson.
- Holden, Edward Singleton (1895). The Mogul emperors of Hindustan, A.D. 1398–A.D. 1707. New York : C. Scribner's Sons.
- Malleson, G.B. (1896). Akbar and the rise of the Mughal empire. Oxford : Clarendon Press.
- Manucci, Niccolao; tr. from French by François Catrou (1826). History of the Mogul dynasty in India, 1399–1657. London : J.M. Richardson.
- Lane-Poole, Stanley (1906). History of India: From Reign of Akbar the Great to the Fall of Moghul Empire (Vol. 4). London, Grolier society.
- Manucci, Niccolao; tr. by William Irvine (1907). Storia do Mogor; or, Mogul India 1653–1708, Vol. 1. London, J. Murray.
- Manucci, Niccolao; tr. by William Irvine (1907). Storia do Mogor; or, Mogul India 1653–1708, Vol. 2. London, J. Murray.
- Manucci, Niccolao; tr. by William Irvine (1907). Storia do Mogor; or, Mogul India 1653–1708, Vol. 3. London, J. Murray.
- Owen, Sidney J (1912). The Fall of the Mogul Empire. London, J. Murray.
External links
- Mughal India an interactive experience from the British Museum
- The Mughal Empire, BBC Radio 4 discussion with Sanjay Subrahmanyam, Susan Stronge & Chandrika Kaul (In Our Time, 26 February 2004)
- Sunil Khilnani's "Akbar", From BBC Radio 4's Incarnations: India in 50 Lives.