Montenegro Fault
Etymology
The fault is named after Montenegro, Quindío.
Description
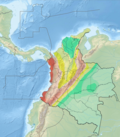
The 21.7 kilometres (13.5 mi) Montenegro Fault is part of the Romeral Fault System, running through the western slope of the Central Ranges. The fault is located to the west of the city of Armenia. The fault crosscuts and deforms the Pleistocene volcanic and volcano-sedimentary deposits of the Quindío Fan (Spanish: Abanico del Quindío), which covers about 400 square kilometres (150 sq mi).
The Montenegro Fault forms outstanding fault scarps as much as 60 metres (200 ft) in height, beheaded streams, hanging valleys, ponded alluvium, aligned and offset drainages, as well as soil and rock slides on the face of the scarps. The fault deforms Quaternary volcanic debris flows and ash deposits. The Espejo River follows the strike of the Montenegro Fault.
See also
References
Bibliography
- Paris, Gabriel; Machette, Michael N.; Dart, Richard L.; Haller, Kathleen M. (2000a), Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions (PDF), USGS, pp. 1–66, retrieved 2017-09-18
Maps
- Paris, Gabriel; Machette, Michael N.; Dart, Richard L.; Haller, Kathleen M. (2000b), Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions (PDF), USGS, p. 1, retrieved 2017-09-18
- Mosquera, D (2000), Mapa Geológico de Quindío 1:100,000, INGEOMINAS, p. 1, retrieved 2017-09-21
Further reading
- Page, W.D (1986), Seismic geology and seismicity of Northwestern Colombia, San Francisco, California, Woodward-Clyde Consultants Report for ISA and Integral Ltda., Medellín, pp. 1–200