Museum De Toulouse
History
The museum was founded in 1796 by the naturalist Philippe-Isidore Picot de Lapeyrouse, with his collections being able to be housed (after the revolution) in the former Carmelite monastery in Toulouse. In 1808, the emperor Napoleon formally gifted all the Carmelite buildings and land to the city of Toulouse, and in 1865, the museum was opened to the public in its present location and under the directorship of Édouard Filhol. Toulouse museum was the first museum in the world to open a gallery of prehistory thanks to the collection of the malacologist Alfred de Candie de Saint-Simon (1731–1851), and the collaboration of Émile Cartailhac, Jean-Baptiste Noulet, and Eugène Trutat.
In 1887 (on the occasion of a world exposition in Toulouse), the botanical gardens of the University of Toulouse became part of the museum. In 2008, the museum reopened in its present form (as of May 2018) with the renovations and extensions of the museum, designed by the architectural firm of Jean-Paul Viguier, having been completed.
Permanent exhibitions
The permanent exhibition has five linked themes:
- Sequence 1: Feeling the Earth's power.
Nature of the Solar System and its formation. Nature of the Earth – plate tectonics, seismic and volcanic activity and erosion, petrology and mineralogy.
- Sequence 2: Doing away with our notions of hierarchy.
The nature of life – biodiversity, classification, and organization.
- Sequence 3: Getting to grips with the huge scale.
Earth history from 3.8 billion years ago. Introduces time, palaeontology and the evolution of life
- Sequence 4: Admitting the obvious.
The main functions of living beings – feeding, respiration, locomotion, reproduction, protection and communication.
- Sequence 5: Inventing the future.
The impact of human activity – demographic pressure on ecosystems and natural resources
Collections
This section presents examples to illustrate the content of each different collection of the Museum de Toulouse.
Prehistory
The prehistoric collection includes mostly artefacts excavated in France. They also contain comparative material from other parts of Europe and other continents. Notable collectors include Édouard Harlé (1850–1922), Antoine Meillet (1866–1936), Alexis Damour (1808–1902), Félix Regnault (1847–1908), Louis Péringuey (1855–1924), Émile Cartailhac (1845–1921), Daniel Bugnicourt, Edward John Dunn (1844–1937), Henri Breuil (1877–1961), and Louis Lartet (1840–1899), as well as the curators Jean-Baptiste Noulet (1802–1890), Eugène Trutat (1840–1910), and Édouard Filhol (1814–1883).
-
Mesolithic tomb from Téviec, Brittany
-
-
-
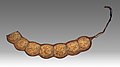
Bronze bead necklace Holocene Bronze Age Jean-Baptiste Noulet collection
Botany
- The herbarium contains historic specimens collected by Benjamin Balansa (1825–1891).
-
Entada phaseoloides – fruit
-
Luffa aegyptiaca – fibrous skeleton
-
Cassia fistula – ripe fruit
Entomology
-
Cerapterus pilipennis - Zambia
-
Chrysochroa rajah thailandica - Chiang Mai, Thailand
-
Hiperantha testacea
Bupestrid from Colombia -
Metaxymorpha gloriosa Bupestrid from North Queensland, Australia
Lepidoptera
-
Charaxes varanes vologeses - Malawi
-
Morpho didius - Peru
-
Archaeoprepona licomedes - Brazil
Orthoptera
-
Oedipoda caerulescens - Etang de la Maourine Toulouse
-
Titanacris albipes- French Guiana
-
Porphyromma speciosa-French Guiana
Mineralogy
-
Celestine - Turkmenistan
-
Fluorite - France
-
Nepouite - New Caledonia
-
Scheelite - China
-
Sphalerite - Roumania
Ornithology
- The bird collection of MHNT contains more than 30,000 specimens, of which 20,000 are eggs. About 8,500 bird mounts and 1,500 scientific bird skins are included. Other bird items are around 2,000 skeletons and skulls and 5,300 eggs. The collection focuses on Europe (especially France), but the collection also has exotic species . Most are documented on card or computer systems.
- The bird mount collection of Victor Besaucèle, with 5,000 specimens, is one of the most important historic collections in Europe.
- Other collectors represented are R. Bourret, G. Cossaune, M. Gourdon, Hammonville, A. Lacroix, and Reboussin.
-
Snowy owl: The oldest mount in the museum, collected by Mr Dode in 1807
- The egg collection of Jacques Perrin de Brichambaut (1920–2007) was acquired in 2010. It contains his personal collections, supplemented by those of other ornithologists, notably Georges Guichard, Henri Heim de Balsac, and Rene de Naurois. It includes all the Palearctic species (Europe, North Africa, and Asia), about 1,000 species and nearly 15,000 eggs, and is one of the most complete and best-documented palearctic egg collections in Europe.
-
Egg of wedge-tailed eagle
-
Egg of little egret
-
Egg of helmeted guineafowl
-
Egg of southern giant petrel
-
Nest of common house martin
-
Egg of passenger pigeon
Osteology
Paleontology
The specimens of the collection of paleontology amount to tens of thousands. They date from the Paleoarchean to the Eocene.
Invertebrates
The invertebrates room was named Saint-Simon in honor to the collection of the malacologist Alfred de Candie de Saint-Simon, presented during the museum opening exhibit in 1865, under the directorship of Édouard Filhol.
-
One of the oldest life forms, a Stromatolite of Paleoarchean age – 3, 600 to 3, 200 million years ago (Mya)
-
Trilobite of Middle Ordovician – 468 to 460 Mya
Vertebrates
-
Woolly rhinoceros complete skeleton of Pleistocene age – 370, 000 to 10, 000 years ago
-
Woolly rhinoceros, complete skull
-
Cave bear mandible of Pleistocene age

Henri Gaussen Botanical Garden
Henri Gaussen was a Toulouse-based phytogeographer and botanist. The botanic garden which honours his name is attached to the museum and is part of the Earth and Life Science Research and Training Paul Sabatier University. A second botanical area, The Museum Gardens, extends over 3 hectares. It is notable for "potagers du monde" (vegetable gardens of the world) and a "shade house" which recreates the conditions required by shade plants.
References
- ^ Le Muséum de Toulouse on the official site of the tourism office of Toulouse
- ^ "NYBG Steere Herbarium, Index Herbariorum: Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle de Toulouse". Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- ^ "Quelques dates de l'histoire du Muséum..." (in French). Muséum de Toulouse. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- ^ Camboulives, Roger (October 1977). "Excursion à Saint Simon au site de Candie". L'Auta (in French). No. 431. Toulouse, France. pp. 218–227. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
- ^ Le Muséum de Toulouse et l'invention de la préhistoire, 2010 ISBN 978-2-906702-18-9.
- ^ "" Toulouse (Haute-Garonne), Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle : rapport de fouilles "".
- ^ "Jean-Paul Viguier et Associés: Muséum de Toulouse". Archived from the original on 2018-08-23. Retrieved 2018-05-30.
External links
- Official website
 (in French)
(in French) - François Bon, Sébastien Dubois, Marie-Dominique Labails, 2010. Le Muséum de Toulouse et l'invention de la préhistoire Toulouse Editions Muséum de Toulouse ISBN 978-2-906702-18-9
- Part of this article is a translation of (or greatly inspired by) the French Wikipedia's article (see the list of title=Mus%C3%A9um_de_Toulouse&action=history authors)