Pattani Province
Geography
Pattani is on the Malay Peninsula, with the coast of the Gulf of Thailand to the north. The south is dominated by the Sankalakhiri mountain range, which includes Budo-Su-ngai Padi National Park, on the border with Yala and Narathiwat. The total forest area is 110 km (42 sq mi) or 5.6 percent of provincial area.
National parks
There are two national parks, along with three other national parks, make up region 6 (Pattani branch) of Thailand's protected areas.
- Budo–Su-ngai Padi National Park, 341 km (132 sq mi)
- Namtok Sai Khao National Park, 70 km (27 sq mi)
Toponymy
The name Pattani is the Thai adaptation of the Malay name Patani (Jawi: ڤتاني), which can mean "this beach" in Patani Malay language. (In standard Malay, this would be pantai ini.) According to legend, the founder of Patani went hunting and saw an albino mouse-deer the size of a goat, which then disappeared. He enquired where the animal had gone, and his men replied: "Pata ni lah!" ("this beach!") They searched for the mouse-deer but found instead an old man, who said his name was Che' Tani. The raja later ordered a town be built on the site where the mouse-deer had disappeared, and it is therefore believed that the town was named either after the beach or the old man. Another suggestion is that it derives from a Sanskrit word pathini, meaning "virgin nymph"; Pathini was the name of a daughter of Merong Mahawangsa, founder of the preceding Langkasuka Empire.
History
Historically, Pattani province was the centre of the Malay Sultanate of Patani Darul Makrif. For centuries a tributary state of Siam, Patani has been governed by Siam since its conquest in 1786. The provinces of Patani were turned into seven smaller provinces: Patani, Nong Chik, Raman, Ra-ngae, Saiburi, Yala and Yaring, later regrouped in 1906 into 4 larger provinces: Patani, Bangnara, Saiburi and Yala. Siamese rule was officially acknowledged by the Burney Treaty of 1826 negotiated with the British Empire which included also Kedah, Kelantan, Perlis and Terengganu. Unlike these four sultanates, Patani was not included in the Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909 and remained under Siamese rule. Both Yala (Jala) and Narathiwat (Menara) were originally part of Patani, but were made provinces in their own right during the territorial administrative reform and the creation of a united centralized Siam state in the early-20th century.
Demographics
Pattani is one of the four provinces of Thailand where the majority of the population are Muslim, the others being Yala, Narathiwat, and Satun. In the 2014 census, the Muslim population made up roughly 88 percent of the population. This is mainly due to the people of Malay ancestry, and large portion of Pattani Malay speakers (though most speak Thai as well).
Symbols
The seal of the province shows the cannon called Phraya Tani, known as Sri Pattani in Malay, which was cast in Pattani province. It was brought to Bangkok in 1785, and is now on display in front of the Ministry of Defence in Bangkok.
The provincial flower is the Chinese hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), and the provincial tree is the Ironwood (Hopea odorata). The provincial aquatic life is the snakeskin gourami (Trichopodus pectoralis).
Administrative divisions
Provincial government
Pattani is divided into 12 districts (amphoe), which are further divided into 115 subdistricts (tambon) and 629 villages (muban). The districts of Chana (Malay: Chenok), Thepha (Malay:Tiba) and Saba Yoi (Malay:Sebayu) were detached from Pattani and transferred to Songkhla in 1796 by Siam government.
| No. | Name | Thai | Jawi | Malay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mueang Pattani | เมืองปัตตานี | فطاني | Patani/Fathoni |
| 2 | Khok Pho | โคกโพธิ์ | خوكفور | Khuppur |
| 3 | Nong Chik | หนองจิก | نوڠجيك | Nongjik |
| 4 | Panare | ปะนาเระ | فناريق | Penarik |
| 5 | Mayo | มายอ | مايور | Mayu |
| 6 | Thung Yang Daeng | ทุ่งยางแดง | طوڠيڠديڠ | Thungyangdeng |
| 7 | Sai Buri | สายบุรี | سليندوڠ بايو ، تلوبن | Selindung Bayu, Teluban |
| 8 | Mai Kaen | ไม้แก่น | مايكين | Maikaen |
| 9 | Yaring | ยะหริ่ง | جمبو | Jambu |
| 10 | Yarang | ยะรัง | ياليمو | Yalimo |
| 11 | Kapho | กะพ้อ | كأفور | Kapor |
| 12 | Mae Lan | แม่ลาน | ميلان | Melan |
Local government

As of 26 November 2019 there are: one Pattani Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 17 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Pattani and Taluban have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 15 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 96 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).
Economy
Six of Pattani's districts lie on the shore of the Gulf of Thailand. The number of fisheries workers in Pattani exceeds 80,000 as of 2019. Pattani is the only province in Thailand where the agriculture ministry prohibits trawlers and destructive fishing nets within four nautical miles of the shoreline. Local fish stocks have rebounded as a result.
Despite having many interesting places, Pattani is the least visited province in the country. According to data from Ministry of Tourism and Sports in 2018, the total number of tourists who visited the province was only 20,000–30,000, and consisted of mostly Thai people.
Transportation
Roads
Highway 42 is main highway in Pattani, which is tourist attractions are nearby and connecting several districts.
Highway 43 is secondary main highway that bypassing Mueang Pattani for saving times and fuels.
Also AH18 is part of Highway 42 and Highway 43.
Highway 410 is main highway in Yala Province, connecting to Mueang Yala and Betong.
Highway 409 and Highway 418 are secondary main highway on Yala Province.
Air
The Royal Thai Air Force's Pattani Airport is used for counter-insurgency operations in the area. It does not run public flights, Pattani's nearly public airport is Narathiwat Airport
Bus
Pattani's main bus stop is Pattani Bus Terminal, Including Pattani-Yala Transit.
Railway
Pattani's main railway stop is Khok Pho Railway Station.
Human achievement index 2022
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 15 | 77 | 33 | 76 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 45 | 11 | 7 | 40 |
| Province Pattani, with an HAI 2022 value of 0.6149 is "low", occupies place 70 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 13 | "high" |
| 14 - 29 | "somewhat high" |
| 30 - 45 | "average" |
| 46 - 61 | "somewhat low" |
| 62 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2022 rankings |
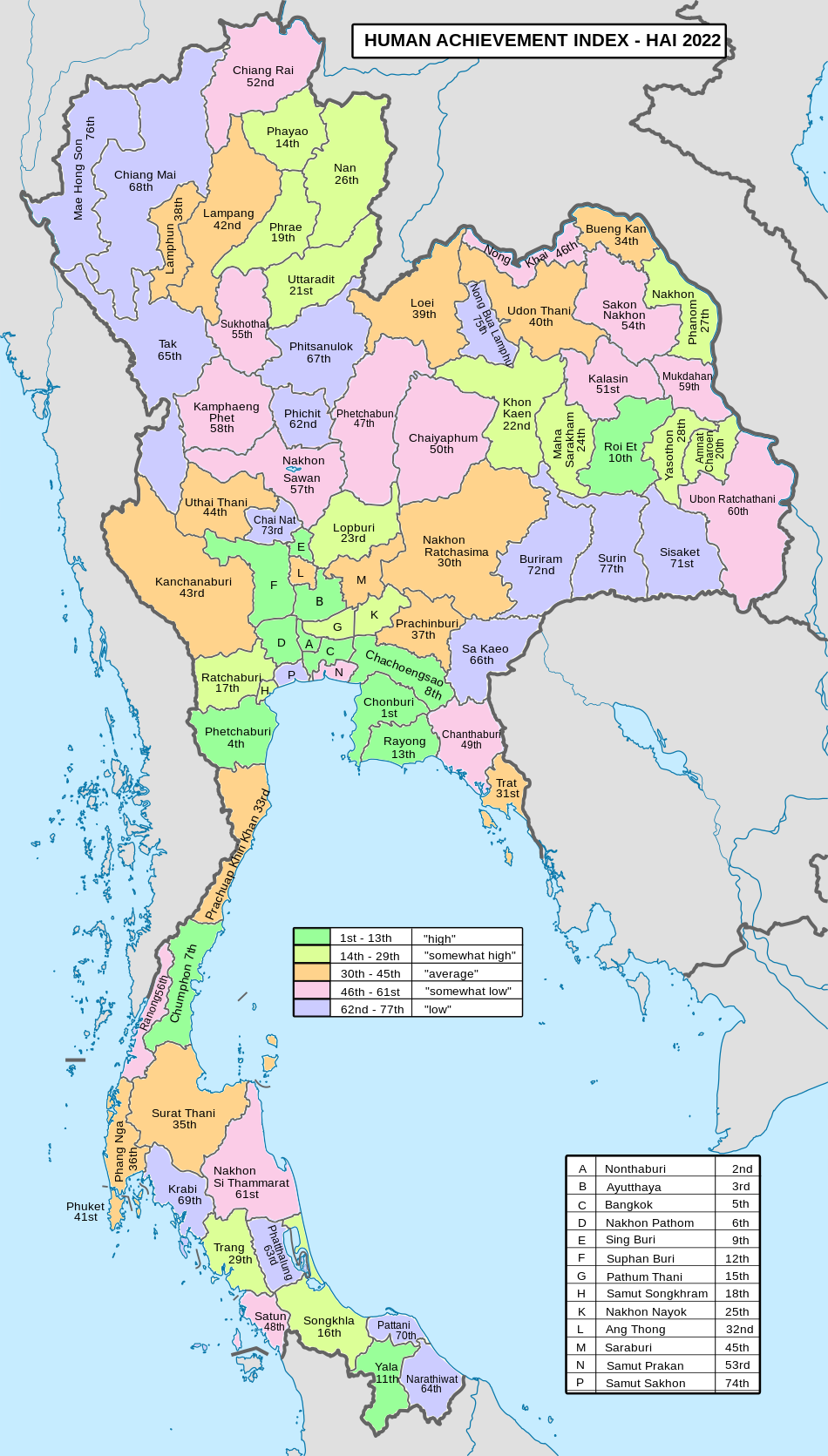
|
Military rule
As of 2018, the provisions of Thailand's Internal Security Act remain imposed on Mae Lan District. Internal security restrictions, maintained by Thailand's Internal Security Operations Command can result in curfews, prohibited entry, or prohibited transport of goods. It is considered one step below the imposition of full martial law.
Places of interest

Pattani has named as the land of three religions (Buddhism, Islam, Chinese religion). There are important places of worship for all three religions:
- Wat Rat Burana (Thai: วัดราษฎร์บูรณะ), also widely known as Wat Chang Hai (Thai: วัดช้างให้), an ancient Thai Buddhist temple older than 300 years, the legendary monk Luang Pu Thuat was once the abbot.
- Leng Chu Kiang Shrine (Thai: ศาลเจ้าเล่งจูเกียง) Chinese shrine of Lim Ko Niao (younger sister of Lin Daoqian).
- Krue Se Mosque (Thai: มัสยิดกรือเซะ) Regarded as one of the more famous mosques with the oldest history.
See also
References
- ^ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- ^ "ข้อมูลสถิติดัชนีความก้าวหน้าของคน ปี 2565 (PDF)" [Human Achievement Index Databook year 2022 (PDF)]. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC) (in Thai). Retrieved 12 March 2024, page 45
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "Gross Regional and Provincial Product, 2019 Edition". <>. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). July 2019. ISSN 1686-0799. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ^ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "ข้อมูลพื้นที่อุทยานแห่งชาติ ที่ประกาศในราชกิจจานุบกษา 133 แห่ง" [National Park Area Information published in the 133 Government Gazettes]. Department of National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation (in Thai). December 2020. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- ^ Wyatt, David K. (December 1967). "A Thai Version of Newbold's "Hikayat Patani"". Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society. 40 (2 (212)): 16–37. JSTOR 41491922.
- ^ "{ms} Sejarah Malaysia - Asal Usul nama Sungai Petani". Sejarahmalaysia.pnm.my. Archived from the original on 2013-06-03. Retrieved 2012-08-24.
- ^ "A Brief Introduction to the Malay Kingdom of Patani". Islamic Human Rights Commission. 21 December 2004.
- ^ Pattani : Selamat Datang Ke Pattani (PDF). Songkhla: IQ Media. 2018. p. 16.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
31 Pattani: 1 PAO, 2 Town mun., 15 Subdistrict mun., 96 SAO.
- ^ Kongrut, Anchalee (2 September 2019). "From Pattani seas to Bangkok plates". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 7 September 2019.
- ^ Laohavichai, Nakan (2019-01-11). "เมืองที่ไม่มีใครแล" [Town that nobody cares]. Posttoday (in Thai). Retrieved 2020-01-01.
- ^ Raksaseri, Kornchanok (8 January 2018). "Isoc power boost 'not political'". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- ^ "สุขสุดใจ 'ปัตตานี' สัมผัสของดีในแดนใต้" [Happiness "Pattani" experience the good things in the southern land]. Manager Online (in Thai). 2016-03-07. Retrieved 2019-01-15.
External links
 Pattani travel guide from Wikivoyage
Pattani travel guide from Wikivoyage- Pattani province website (Thai)
- Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT): Pattani
- Pattani Erupts Archived February 13, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Thailand Islamic Insurgency
- Muslim rebels light fuse in Thailand

