Saramacca District
Saramaka is also the name of a group of Maroons who established communities along the Saramacca River having fled slavery.
History
The district was founded in 1983, but the history dates back to 1790 when the first plantation was opened. Until 1936, Saramacca could only be access by boat, but with the construction of a road to Paramaribo, which is now part of the East-West Link, Saramacca was removed for its isolation. In 1982, oil was discovered in Sarammacca which boosted its economy. On 13 December 2014, Staatsolie opened an oil refinery.
Agriculture
The district has traditionally been the site of dozens of small, family owned farming communities, and it has only been recently that large agricultural projects have begun to emerge, primarily geared to the production of bananas, rice, and peanuts. Boskamp is a fishing village.
Nature
The district is known for its birds, with ornithologists and birdwatchers coming from all over the world to study and admire Saramacca's toucans, parrots and cocks-of-the-rock.
Saramacca is home to three nature reserves: Coppename Monding Nature Reserve (12,000 hectares), Boven Coesewijne Nature Reserve (27,000 hectares) and the Noord Saramacca Special Control Area (88,400 hectares).
Resorts
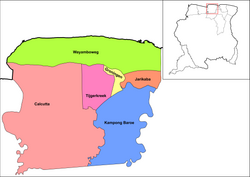
Saramacca is divided into 6 resorts (ressorten):
Villages
References
- ^ "Resorts in Suriname Census 2012" (PDF). Retrieved 27 May 2020.
- ^ "Distrikt Saramacca 1". Anda Suriname (in Dutch). Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- ^ "Distrikt Saramacca 2". Anda Suriname (in Dutch). Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- ^ "Structuur Analyse" (PDF). Planning Office Suriname (in Dutch). Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ^ "Bananenproductie Jarikaba komt op gang". GFC Nieuws (in Dutch). Retrieved 27 May 2020.
- ^ "Nickerie Bigi Pan 2 daaagse tour". Purity Tours (in Dutch). Retrieved 28 May 2020.
