State Route 92 (California)
Route description

Between Half Moon Bay and Interstate 280, Route 92 winds through the Coast Range as a narrow, mainly undivided two and three lane highway with a switchback turn. The east-bound uphill portion was upgraded with a long passing lane. Between Interstate 280 and Interstate 880 it is entirely a divided multilane highway, including the toll San Mateo-Hayward Bridge, the longest span across the San Francisco Bay; west of that bridge, Route 92 is carried on twin girder bridges across Seal Slough, which forms the border between the cities of San Mateo and Foster City. East of Interstate 880 the route becomes a divided surface street in Hayward, locally known as Jackson Street.
State Route 92 traverses through significant habitat areas including wetland, California oak woodland, chaparral and grassland. In one serpentine soil location near Crystal Springs Reservoir, it passes near one of the only known colonies of the endangered wildflower Pentachaeta bellidiflora and near one of the limited number of colonies of the endangered Eriophyllum latilobum.
SR 92 is part of the California Freeway and Expressway System, and a small portion near SR 1 as well as the entire portion east of I-280 are part of the National Highway System, a network of highways that are considered essential to the country's economy, defense, and mobility by the Federal Highway Administration. SR 92 is eligible for the State Scenic Highway System, but it is not officially designated as a scenic highway by the California Department of Transportation.
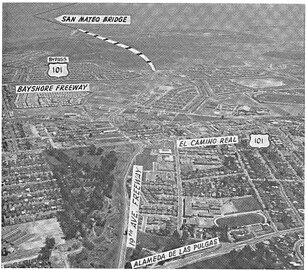
- Aerial views of SR 92
-
View directed west near interchange with I-280, showing Crystal Springs Reservoir and route from San Mateo to Half Moon Bay
-
View directed east c. 1962, showing 19th Avenue Freeway segment under construction; the Antoine Borel family estate is the wooded area north (left) of the new freeway
-
View directed west as-completed c. 1963, showing full cloverleaf interchange with SR 82, center, and bridges over SP's Peninsula Corridor
-
View directed north over Hayward; SR 92 runs along bottom right corner
History
The alignment was designated as Legislative Route Number 105 by Caltrans in 1933.
The San Mateo section also was referred to as the 19th Avenue Freeway which was the street name where the freeway now exists. Parts of the street remain. This section is also known as the J. Arthur Younger Freeway; J. Arthur Younger was a United States representative who served during the 1950s and 60s. On August 29, 1963, the 19th Avenue segment was completed and by 1964, the present name had been adopted; planning began for the segments in Alameda County, east of the San Mateo–Hayward Bridge, and the remainder in San Mateo County, west of Interstate 280.
Updates
An upgrade of the intersection with Main Street in Half Moon Bay, near the western terminus, was scheduled to be completed by fall 2008.
The old cloverleaf interchange with Interstate 880 was converted into a three-level combination interchange with direct ramp replacements for two of the tight "cloverleaf" ramps, and a new wider and taller overpass to carry Route 92 over Interstate 880. The project took four years and was completed in October 2011.
A similar cloverleaf interchange at SR 82 (El Camino Real) was rebuilt in 2018 into a partial cloverleaf interchange. Two of the loop off-ramps from SR 92 were eliminated: from westbound SR 92 to northbound El Camino Real, and from eastbound SR 92 to southbound El Camino Real. The remaining off-ramps were widened and signalized to allow left and right turns onto El Camino Real.
Planning for improvements to the interchange with the Bayshore Freeway (U.S. 101) began in 2018; construction is scheduled to begin in 2024. In addition, a separated bikeway will be built on Fashion Island Boulevard, which largely follows the former alignment of 19th Avenue, connecting the cities of Foster City and San Mateo. This project is scheduled to be completed by the end of 2026.
Major intersections
Except where prefixed with a letter, postmiles were measured on the road as it was in 1964, based on the alignment that existed at the time, and do not necessarily reflect current mileage. R reflects a realignment in the route since then, M indicates a second realignment, L refers to an overlap due to a correction or change, and T indicates postmiles classified as temporary (). Segments that remain unconstructed or have been relinquished to local control may be omitted. The numbers reset at county lines; the start and end postmiles in each county are given in the county column.
| County | Location | Postmile | Exit | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Mateo SM 0.00-R18.80 | Half Moon Bay | 0.00 | Western terminus | ||
| 0.20 | Main Street – Downtown Half Moon Bay | Former SR 1 | |||
| | 5.19 | West end of SR 35 overlap | |||
| | 7.19 | East end of SR 35 overlap | |||
| | Western end of freeway | ||||
| | R7.31 | 8 | Access from I-280 south to SR 92 west is via SR 35; signed as exits 8A (south) and 8B (north) eastbound; I-280 exit 33 | ||
| San Mateo | R7.93 | 9A | Ralston Avenue – Belmont | Former Legislative Route 214 | |
| R8.67 | 9B | De Anza Boulevard, Polhemus Road | |||
| R9.38 | 10 | West Hillsdale Boulevard | |||
| R10.56 | 11 | Alameda de las Pulgas | |||
| R11.21 | 12A | Formerly signed as exits 12A (south) and 12B (north) | |||
| R11.61 | 12B | Delaware Street | Formerly signed as exit 12C | ||
| R12.14 | 13A | US 101 exit 414B | |||
| R12.14 | 13B | ||||
| Foster City | R12.78 | 14A | Mariners Island Boulevard, Edgewater Boulevard | ||
| R13.61 | 14B | Foster City Boulevard, East Hillsdale Boulevard | |||
| San Francisco Bay | R14.44– R0.00 | San Mateo–Hayward Bridge (westbound toll only) | |||
| Alameda ALA R0.00-8.22 | Hayward | R4.48 | 24 | Clawiter Road, Eden Landing Road | |
| R5.12 | 25A | Industrial Boulevard | |||
| R5.76 | 25B | Hesperian Boulevard – San Lorenzo | |||
| 6.39 | 26A | I-880 exit 27; former SR 17 | |||
| 6.39 | 26B | ||||
| Eastern end of freeway | |||||
| 6.78 | Santa Clara Street | Serves CSU East Bay | |||
| 8.22 | Eastern terminus; access to SR 185 is via a left turn on A Street from SR 238 north | ||||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also
References
- ^ California Department of Transportation. "State Truck Route List". Sacramento: California Department of Transportation. Archived from the original (XLS file) on September 5, 2015. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ^ Faigin, Daniel P. "County Highways - State Route 92". www.cahighways.org. Retrieved July 21, 2008.
- ^ "Article 2 of Chapter 2 of Division 1". California Streets and Highways Code. Sacramento: California Office of Legislative Counsel. Retrieved February 6, 2019.
- ^ Federal Highway Administration (March 25, 2015). National Highway System: San Francisco–Oakland, CA (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Washington, DC: Federal Highway Administration. Retrieved October 8, 2017.
- ^ Natzke, Stefan; Neathery, Mike & Adderly, Kevin (June 20, 2012). "What is the National Highway System?". National Highway System. Washington, DC: Federal Highway Administration. Retrieved July 1, 2012.
- ^ "Article 2.5 of Chapter 2 of Division 1". California Streets & Highways Code. Sacramento: California Office of Legislative Counsel. Retrieved February 6, 2019.
- ^ California Department of Transportation (August 2019). "Officially Designated State Scenic Highways and Historic Parkways" (XLSX). Sacramento: California Department of Transportation. Retrieved October 8, 2017.
- ^ "Chronology of California Highways, Phase III: A Significant System is Created (1933-1946)". California Highways. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ Sinclair, J. P. (May–June 1961). "Bay Area Freeways" (PDF). California Highways and Public Works. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ Sinclair, J. P. (May–June 1962). "Bay Area Report" (PDF). California Highways and Public Works. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ "III. Circulation". City of San Mateo. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 8, 2007.
- ^ Sinclair, J. P. (May–June 1964). "Bay Area Report" (PDF). California Highways and Public Works. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ "Half Moon Bay Highway Improvements". San Mateo County Transportation Authority. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ Kurhi, Eric (October 7, 2011). "At long last, improved connectors open at Hayward traffic trouble spot". San Jose Mercury News.
- ^ Weigel, Samantha (March 6, 2017). "Interchange revamp in gear: State Route 92, El Camino Real project underway". San Mateo Daily Journal. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ Project Report: In San Mateo County in the City of San Mateo at the SR 92/SR 82 Interchange 04-SM -92-PM 11.0/11.5, 04-SM -82-PM 10.3/10.7 (Report). City of San Mateo. May 2014. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ "US 101/ SR 92 Short-Term Interchange Improvements Projects". District 4, California Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ "Fact Sheet: US 101/SR 92 Area Improvements & Multimodal Project" (PDF). California Transportation Commission. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ California Department of Transportation (July 2007). "Log of Bridges on State Highways". Sacramento: California Department of Transportation.
- ^ California Department of Transportation, All Traffic Volumes on CSHS, 2005 and 2006
- ^ California Department of Transportation, California Numbered Exit Uniform System, State Route 92 Freeway Interchanges, Retrieved on 2009-02-07.
External links
- Caltrans: State Route 92 highway conditions
- Caltrans Traffic Conditions Map
- California Highway Patrol Traffic Incidents
- Bay Area FasTrak – includes toll information on the San Mateo–Hayward Bridge and the other Bay Area toll facilities
- California @ AARoads.com - State Route 92
- California Highways: SR 92