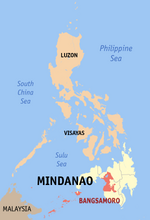
Tawi-Tawi Province
It is the southernmost province of the country, sharing sea borders with the Malaysian state of Sabah and the Indonesian North Kalimantan province, both on the island of Borneo to the west. To the northeast lies the province of Sulu. Tawi-Tawi also covers some islands in the Sulu Sea to the northwest, Cagayan de Tawi-Tawi Island and the Turtle Islands, just 20 kilometres (12 mi) away from Sabah.
The municipalities comprising the current Tawi-Tawi province were formerly under the jurisdiction of Sulu until 1973.
Etymology
The province was named after its main island, which at 580.5 km (224.1 sq mi) accounts for a little more than half the province's 1,087.40 km (419.85 sq mi) land area. Tawi-Tawi is the Sinama form of jawi-jawi, Malay for the banyan tree; the island is known for having an abundance of this tree. Early Spanish accounts give the name of the island as Tauitaui and Tavi-Tavi or Tavitavi.
History
Early history
Evidence of human presence in Tawi-tawi was carbon-dated to be 6,810 BC to 3,190 B.C., signifying one of the earliest known evidence of human presence in Southeast Asia. The bones, jars, shells, and other artifacts and fossils were found in the Bolobok Rock Shelter Cave Archaeological Site, which has been declared as an Important Cultural Treasure by the government in 2017.
Much of the Tawi-tawi area was the center of Sama culture and arts for hundreds of years. Some islands are sites of centuries-old traditional burial grounds featuring traditional Sama okil carvings of ancestors.
In 1380, the first mosque in the Philippines, the Sheik Karimol Makhdum Mosque, was established by an Arab trader and missionary, Makhdum Karim. The area was heavily converted to Islam, especially when the Sultanate of Sulu in nearby Sulu province was founded. Although unlike the Tausug people, many Sama retained at least part of their ancient animist religions.
Spanish colonial era
As early as January 28, 1761, Sultan Muizz ud-Din entered into an agreement with Alexander Dalrymple of the British East India Company for commercial and economic concessions. The subsequent treaties with Muizz ud-Din on September 12, 1762, and with Sultan Azim ud-Din, claimant to the Sultanate and a prisoner of the British in Manila, on February 23, 1763, confirmed these British claims. However, on March 5, 1775, Datu Teteng annihilated the British troops in Balambangan. Since then, the Muslims not only fought the British soldiers but also the Spanish troops. After the brother of Sultan Aliyud-Din I captured the Spanish ship San Jose in Tawi-Tawi, the British forces withdrew from Balambangan in 1805.
On January 22, 1878, Baron von Overbeck, representing the British North Borneo Company, signed a treaty with Sultan Jamalul Alam for the lease of the Sultan's land in Borneo at an annual rent of 5,000 Mexican dollars. The Germans also asked for commercial concessions. Due to foreign encroachments, the Spaniards constructed a naval base at Tata'an and built garrisons in Bongao and Siasi.
On March 7, 1885, Spain, Britain and Germany signed a protocol in Madrid whereby Spain relinquished all her claims to the offshore lands in Borneo, granted freedom of trade and navigation in Sulu, and Britain and Germany recognized Spanish sovereignty over Balabac and Cagayan de Sulu. However, the British diplomatically continued to pay the annual rents for Sabah (Sultan's land in Borneo) to Harun ar-Rashid.
During the Philippine Revolution of 1896, the mutiny of the 68th Regiment at Busbus, Jolo implicated Tagalog soldiers. The Muslims, however, retained their own views on independence and freedom.
American invasion era
When the American forces occupied Jolo on May 19, 1899, they established garrisons at Bongao and Siasi after the Muslims wiped out the Spanish garrison in Tata'an, Tawi-Tawi. In 1900, the United States entered into a treaty with Spain whereby Sibutu and Cagayan de Sulu were ceded to the former for $100,000. The Sultanate continued to receive the rentals for Sabah until 1946 when the British North Borneo Company sold its rights to the British Crown.
Japanese occupation era
During World War II, the calm but exposed waters around the islands were used by the Imperial Japanese Navy as a major fleet anchorage due to its proximity to the oilfields of Borneo. Japanese forces, however, did not develop any facilities on the islands leaving the anchorage without an airfield, which allowed American submarines to track the movements of the Japanese fleet at the exposed anchorage. After the Japanese Imperial Forces occupied Tawi-Tawi, guerilla forces were organized under Lts. Konglamtio and Alejandro Tresperes in Siasi and Tawi-Tawi. These units were under the Sulu Command led by Lt. Col. Alejandro Suarez. The Command aided the American Liberation Forces at Sanga-Sanga Island on April 2, 1945.
On October 16, 1947, the offshore lands of Borneo—Taganak, Bakkungan, Bayaua, Sibauang and Lihiman Islands—were turned over to the Philippines by the British North Borneo government. The unveiling ceremonies of the marker in Taganak Island on June 26, 1948, were attended by M.G. Combe, representing Great Britain, former President Diosdado Macapagal for the Philippines, Princess Tarhata Kiram for the Sultanate, and Governor Kalingalan Caluang for Sulu.
Philippine Independence
Foundation
Previously part of the province of Sulu, Tawi-Tawi was converted into a province on September 11, 1973, pursuant to Presidential Decree No. 302 and erstwhile Commodore Romulo Espaldon was appointed as its first governor until the first provincial elections were held.
Prior to issuing the decree, President Marcos had asked Espaldon, “Why are the young boys of Tawi-Tawi easily wooed by the Moro National Liberation Front?” Espaldon replied, “The Sama boys, like their elders and leaders, are tired and weary of their union with the Province of Sulu. They want to have their own leaders and manage their own affairs. If His Excellency wants to solve the problem, I recommend that he create them into a separate province and allow them to exercise their own local prerogatives.” Hence, Espaldon earned the moniker "Father of Tawi-Tawi."
During the first 730 days of Tawi-Tawi as a province, Espaldon spearheaded over 100 civilian infrastructure projects, including the construction of the provincial capitol, provincial hospital, public market, 50 mosques, school houses, radio station, airstrips, piers, houses, bridges, roads and water system.
The seat of the provincial government was initially designated as Bato-Bato in the municipality of Balimbing (now Panglima Sugala), but was moved to Bongao on April 4, 1979, by virtue of Batas Pambansa Blg. 24.
Contemporary
Tawi-Tawi is currently being groomed as the location of a special economic zone and transhipment point, a future center of commerce as the Tawi-Tawi freeport is being built in the area.
Geography

The province lies at the southwestern tip of the country, situated between the Sulu Sea in the north and the Celebes Sea in the south. The province is part of the Sulu Archipelago, and consists of Tawitawi Island and 106 surrounding islands and islets with a combined land area of 1,087.4 square kilometres (419.8 square miles). Tawitawi Island itself has an area of 580.5 square kilometres (224.1 square miles). The last island of the province at the edge of the Philippine-Malaysia border is Panguan Island.
The province has two seasons: dry and wet. The climate is generally moderate. The wettest months are from August to November. The other months of the year are generally dry with occasional rain showers.
Biogeography
The main island of Tawi-Tawi supports many endemic species and subspecies of vertebrates, invertebrates and plants unique to this island, plus some that are only shared with Sulu Province. These include the Tawitawi brown dove, the Sulu hornbill and the Sulu bleeding-heart, although this latter species may already be extinct.
The rapid expansion of human settlements into forested areas together with clearance for agriculture in the last few decades has dramatically reduced the available habitat for most of the endemic species, many of which are now considered 'Critically Endangered' by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Administrative divisions
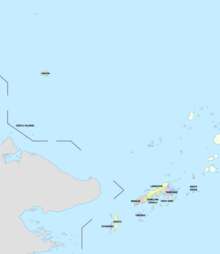
Tawi-Tawi comprises 11 municipalities, all encompassed by two legislative districts and further subdivided into 203 barangays.
- Bongao — the capital of the province
- Languyan — created by President Marcos for rebel leader Hadjiril Matba who joined the government in the 1970s
- Mapun — Tawi-Tawi's northernmost municipality, formerly Cagayan de Tawi-Tawi or Cagayan de Sulu
- Panglima Sugala — formerly known as Balimbing. However, in the EDSA Revolution, the word "balimbing" acquired a derogatory meaning associated with turncoatism due to the fruit's many sides. It is the former capital of the province.
- Sapa-Sapa
- Sibutu — home to the descendants of Malay royalty in Borneo and not necessarily associated with the Sulu royalty and home to Saluag Island (Sikulan), the southernmost island in the country
- Simunul — site of oldest mosque in the Philippines and home of Sheikh Makdum, one of the early pioneers spreading Islam in the country
- Sitangkai — southernmost municipality in the country.
- South Ubian
- Tandubas
- Turtle Islands — a turtle sanctuary and protected area
Most of the municipalities are located on the islands in the Sulu Archipelago. Two of them, Mapun (which is closer to Palawan) and Turtle Islands, lie within the Sulu Sea.
|
† Provincial capital
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 16,675 | — |
| 1918 | 44,799 | +6.81% |
| 1939 | 45,769 | +0.10% |
| 1948 | 58,531 | +2.77% |
| 1960 | 78,594 | +2.49% |
| 1970 | 110,196 | +3.43% |
| 1975 | 143,487 | +5.44% |
| 1980 | 194,651 | +6.29% |
| 1990 | 228,204 | +1.60% |
| 1995 | 250,718 | +1.78% |
| 2000 | 322,317 | +5.53% |
| 2007 | 450,346 | +4.72% |
| 2010 | 366,550 | −7.22% |
| 2015 | 390,715 | +1.22% |
| 2020 | 440,276 | +2.38% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority | ||
The population of Tawi-Tawi in the 2020 census was 440,276 people, with a density of 400 inhabitants per square kilometre or 1,000 inhabitants per square mile.
Inhabitants
This article needs attention from an expert in Philippines. See the talk page for details. (June 2014) |
Most of the people in Tawi-Tawi belong to the Sama cultural group. Within this group are subgroups and named based on the location of the speaker. Sama Sibutu are those from the Sibutu-Sitangkai Island Group, Sama Simunul are those from Simunul-Manuk Mangkaw Island Group, and so on.
The Jama Mapun are largely found in the Cagayan Mapun and Turtle Island Group. Many of the people from the Turtle Islands and Cagayan Mapun maintain daily commerce with Sabah, since it is only 14 kilometers away.
The Badjao (also called "Sama Dilaut") are widely dispersed across the province, though their population is diminishing due to diseases and migration to other areas in the Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia.
The Tausog or Tau Sug, Orang Suluk or Aa Suk are a Moro ethnic group constituting a significant minority in Tawi-Tawi.
Language
The Tausug language is the lingua franca of Tawi-Tawi, as in the case of the rest of the provinces in the Sulu Archipelago. Another prevailing local language, Sama, is spoken in varied tones and accents with the major ones being Sinama Sibutu (spoken mainly in the Sibutu-Sitangkai Region), Sinama Simunul (concentrated in Simunul-Manuk-Mangkaw Islands), Sinama Kapoan (spoken in the South Ubian-Tandubas and Sapa-Sapa Regions) and Sinama Banguingui (concentrated in Buan Island and spoken by Banguingui people).
Chavacano, Cebuano, and Yakan are also spoken, as are the official languages of Filipino and English. Many locals and barter traders can also speak Sabah Malay. Many can also speak Cebuano because of the mass influx of Visayan settlers to Mindanao, since Tausug is a related Visayan language.
Religion
Almost all (99%) of the population of Tawi-Tawi is Muslim, with a minority of Christians (0.7%).
A majority of Tawi-Tawi's Muslim population practice Sunni Islam of the Shafi'i tradition, as taught by Arab, Persian, Indian Muslim, Chinese Muslim and Malaccan missionaries from the 14th century onwards. The oldest mosque in the Philippines, the Sheik Karimol Makdum Mosque, can be found in Simunul, Tawi-Tawi.
Relatively newer Islamic sects, mostly brought by returning veterans of the Afghan wars and missionaries from Pakistan's stricter Sufi traditions, referred to as the Tableegh, have been active in propagating what they believe to be a "purer" Islamic way of life and worship. A very small number who have since married into Iranian or Iraqi families have converted to Shiite Islam.
Majority of Tawi-Tawi Christians are Roman Catholic, they are under the jurisdiction of Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zamboanga through its suffragan Apostolic Vicariate of Jolo/Diocese of Jolo. Non-Catholic Christians include Evangelicals, Jesus Miracle Crusade, Episcopalian, and Iglesia ni Cristo (INC), Mormons, Seventh-day Adventists, Jehovah's Witnesses, and a number of other Protestant denominations. Only the most recent Chinese immigrants adhere to Buddhism or Taoism, while most of the older Chinese families have acculturated and have either converted to Islam while retaining most of their Chinese beliefs.
Economy
Poverty incidence of Tawi-Tawi
10
20
30
40
50
60
2006
52.41 2009
35.28 2012
28.61 2015
17.86 2018
22.20 2021
28.10 Source: Philippine Statistics Authority |
Agriculture, fishing, and agar-agar (seaweeds) farming are the leading source of livelihood of the people of Tawi-Tawi, with quite a number engaged in the barter trade business. Copra is the top agricultural product, followed by root crops, fruits, and vegetables.
Transportation
Sanga-Sanga Airport, the main airport of the province, is located in the municipality of Bongao.
Recently, Philippine Airlines and Bangsamoro Government launches the inaugural flight of the first ever regional air connectivity on June 9, 2022, from Cotabato City, the regions seat and capital. Meanwhile, Cebu Pacific began operating a daily flight from Zamboanga City to Tawi-Tawi Province on October 14, 2011, utilizing its 150-seater Airbus A319 aircraft. Philippine Airlines (operated by PAL Express) also started operating flights to and from Zamboanga City on December 15, 2019.
A sea connection to other parts of the Philippine archipelago as well as an international route to Semporna, Malaysia is available from Bongao.
See also
References
- ^ Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, Department of Agriculture: Tawi-Tawi Archived 2012-09-06 at the Wayback Machine (There seems to be major discrepancies among authoritative sources: 362,655 ha (NSCB 2007), 120,876 ha (NAMRIA), 1,197 square kilometres (462 square miles) (Department of Tourism), 999 square kilometres (386 square miles) (Mapcentral))
- ^ Malicdem, Ervin (7 June 2017). "Bud Bongao, Tawi-Tawi's Overwatch and Sacred Peak". Schadow1 Expeditions. Retrieved 15 August 2017.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ Batasang Pambansa ng Pilipinas (4 April 1979). "Batas Pambansa Bilang 24 - AN ACT TRANSFERRING THE PROVINCIAL CAPITAL OF TAWI-TAWI FROM BATO-BATO TO BONGAO, AMENDING SECTION TWO OF PRESIDENTIAL DECREE NUMBERED THREE HUNDRED TWO". Chan Robles Law Library. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ^ Crawfurd, John (1852). A Grammar and Dictionary of the Malay Language: With a Preliminary Dissertation, Volume 2. Smith, Elder & Co. p. 59.
- ^ United States Congress (1907). Congressional edition, Volume 5113. United States Government Printing Office.
- ^ Combes, Francisco (1667). Historia de las islas de Mindanao, Jolo y sus adyacentes. Herederos de Pablo de Val.
- ^ Pio A. De Pazos y Vela-Hidalgo, ed. (1879). Jolo, Relato Historico-Militar: Desde Su Descubrimiento Por Los Espanoles en 1578 A Nuestros Dias (1879). Imprenta y Estereotipia de Polo.
- ^ "Tawi-tawi: Glimpse of pre-historic life at Balobok Rock Shelter". 18 March 2009.
- ^ Peralta, Jesus T. (1980). "Southwestern Philippine Art". Anthropological Papers (National Museum (Philippines)) (7): 32–34.
- ^ Baradas, David B. (1968). "Some Implications of the Okir Motif in Lanao and Sulu Art" (PDF). Asian Studies. 6 (2): 129–168. S2CID 27892222. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-01-29.
- ^ Clifford Sather (2006). "Sea Nomads and Rainforest Hunter-Gatherers: Foraging Adaptations in the Indo-Malaysian Archipelago - The Sama-Bajau". In Peter Bellwood; James J. Fox; Darrell Tryon (eds.). The Austronesians: Historical and Comparative Perspectives. ANU E Press. pp. 257–264. ISBN 9781920942854.
- ^ Philippine Bureau of Local Government (1975). The Symbols of the State. pp. 258–259.
- ^ "The Pacific War Online Encyclopedia: Tawi Tawi". Retrieved 2020-06-03.
- ^ "Presidential Decree No. 302; Creating the Province of Tawi-Tawi". The LawPhil Project. 27 September 1973. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "Letter of Instruction No. 116; Designation of ROMULO ESPALDON as Governor of Tawi-Tawi". Official Gazette. 18 August 1973. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ Tahang, Nash (March 2005). "Espaldon: The Unifying Leader". Tawi-Tawi Mirror Magazine. 1 (2): 9–10.
- ^ Tawi Tawi After 730 Days: A Report To The People. 1975-09-11.
- ^ Tawi-Tawi eyed as world-class economic zone By Patrick Garcia (Manila Bulletin)
- ^ "Islands of Philippines". Island Directory. United Nations Environment Programme. Archived from the original on 28 April 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ^ "Tawi Tawi". www.britannica.com. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- ^ "Province: Tawi-Tawi". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ "PSGC Interactive; List of Provinces". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
- ^ "DA-Tawi-Tawi". Department of Agriculture and Fisheries - Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao. Archived from the original on 6 September 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
Total Land Area; 108, 740 has.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "ARMM – Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). "Bangsamoro (BARMM)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ Rosaldo, Renato, ed. (2003). Citizenship in Island Southeast Asia: Nation and Belonging in the Hinterlands. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520227484. Retrieved 15 March 2013.
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- ^ "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 29 November 2005.
- ^ "2009 Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 8 February 2011.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 27 August 2016.
- ^ "Updated Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population with Measures of Precision, by Region and Province: 2015 and 2018". Philippine Statistics Authority. 4 June 2020.
- ^ "2021 Full Year Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 August 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ Arayata, Ma. Cristina. "PAL to introduce Zamboanga-Tawi-Tawi route Dec. 15". Philippine News Agency. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
External links
 Media related to Tawi-Tawi at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tawi-Tawi at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Tawi-Tawi at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Tawi-Tawi at OpenStreetMap- Wilfredo L. Campos (June 2005). "Baseline Assessment of Existing or Potential MPA's in FISH Project Focal Areas: Tawi-tawi" (PDF). UP in the Visayas Foundation Inc. (Alternative format)
- Telling Our Story: A compilation of success stories from FISH Project-assisted communities (PDF). USAID. 2010.
- Provincial Fatwa on Marine Environmental Protection and Conservation, May 16, 2006