Tropical Storm Olaf (1997)
Meteorological history

Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
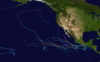
The origins of Olaf were from a tropical wave first noted over Central America on September 22. It moved slowly through the eastern Pacific Ocean, and gradually developed an area of convection. Concurrently, an upper-level low-pressure area moved from the Gulf of Mexico across Mexico into the Pacific, which produced wind shear across the region; wind shear is the difference in wind speed and direction in the atmosphere, and is usually harmful to tropical cyclogenesis. The disturbance associated with the tropical wave persisted and developed outflow. This caused the upper-level low to move away from the system. On September 26, it was sufficiently organized to be classified Tropical Depression Seventeen-E, while located about 345 miles (555 km) south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec.
A few hours after developing, the depression attained tropical storm status, or winds of at least 40 mph (64 km/h). Upon doing so, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) gave it the name "Olaf". The upper-level low, which was moving away from the region, caused the storm to move northward toward the Mexican coast. Olaf quickly intensified, as evidenced by reports from a nearby ship, and the winds reached 70 mph (110 km/h) by late on September 27; the NHC anticipated further intensification to hurricane status, or winds of at least 75 mph (121 km/h). Instead, interaction with the rough terrain of Mexico caused weakening. Olaf made landfall on Salina Cruz, Oaxaca early on September 29 as a 35 mph (56 km/h) tropical depression. Within a few hours, the circulation was not evident on satellite imagery, and the NHC discontinued advisories.
Despite being considered dissipated, a re-analysis of satellite imagery indicated the circulation of Olaf persisted as turned to the west toward open waters. Early on September 30, the system reached the Pacific, and it continued westward for about a week, during which it retained some convective activity. On October 5, Olaf turned toward the east, as it interacted with the large circulation of developing Hurricane Pauline. Later that day, the NHC resumed issuing advisories, while it was located about 560 miles (900 km) southwest of the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. The system turned to the southeast, and, failing to organize, the NHC discontinued advisories on October 8. Three days later, after the remnants of Olaf turned toward the north, the NHC again resumed advisories, when it was just 70 miles (110 km) south-southwest of Tecomán, Colima. Late on October 12, the circulation of Olaf made its final landfall near Manzanillo, Colima, and it quickly dissipated. An associated area of thunderstorms moved over open waters again, but failed to redevelop.
Impact and preparations

Prior to moving ashore, a tropical storm warning was issued from Punta Maldonado, Guerrero, to Tapachula, Chiapas, and the Port of Chiapas, near the Mexico–Guatemala border. When Olaf was strengthening faster than anticipated, the advisory was upgraded to a hurricane warning, although it was downgraded to a tropical storm after the intensification did not occur. Upon making its first landfall, Tropical Depression Olaf produced gusty winds and heavy rains along the southeastern coast of Mexico. The peak 24‑hour rainfall total was 6.71 inches (17.0 cm) in Juchitán de Zaragoza in Oaxaca; the highest rainfall total throughout Olaf's duration was 27.73 inches (70.4 cm) at a station called Soyalapa/Comaltepec in Oaxaca. Heavy rainfall was also reported in Guatemala and El Salvador.
Across the affected region, the heavy rainfall caused flooding, which resulted in 18 deaths. In Mexico, the flooding damaged 50,000 acres (200 km) of coffee, corn, and other crops; in Chiapas, the coffee crop damage represented a severe cut into the yearly total. The precipitation flooded many buildings across the region, including 30 houses in the Chiapas capital of Tuxtla Gutiérrez, when a river exceeded its banks. In mountainous regions, mudslides left dozens of small villages isolated from the outside world. Along the coast, high waves of up to 16 feet (4.9 m) forced the closure of all ports in three Mexican states, which affected thousands of fishermen. Further west, three fishing vessels were reported missing near Acapulco, prompting rescue parties. The storm also forced the closure of several airports. In its final landfall, there was no damage reported; precipitation in that region peaked at 2.96 inches (7.5 cm) in Coquimatlán, Colima.
Following the storm, the Mexican government sent food, water, and housing supplies to affected families in Oaxaca. Less than a week after Olaf moved through southern Mexico, Hurricane Pauline struck the same region with much stronger winds. Pauline caused heavier rainfall and more damage, killing at least 250 people. Some regions received 10 days of heavy rainfall.
See also
References
- ^ Lixion A. Avila (1997). "Tropical Storm Olaf Tropical Cyclone Report". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on 2005-09-25. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Alberto Hernández Unzón y Geog. Cirilo Bravo Lujan (2009). "Tormenta Tropical Olaf" (PDF). Servicio Meteorológico Nacional. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 27, 2011. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ David Roth (1997). "Tropical Storm Olaf - September 27-October 2 and October 10-16, 1997". NOAA. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Niko Price (1997). "Hurricane Bears Down on Mexico". Associated Press. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Dow Jones Newswires (1998). "Coffee Crop in Mexico Suffers Blow From Heavy Rainstorms". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Lawrence, Miles B (November 7, 1997). Preliminary Report: Hurricane Pauline October 5 – 10, 1997 (PDF) (Report). United States National Hurricane Center.
- ^ Lawrence-Journal World (1997). "Pauline becomes hurricane in Pacific". Retrieved 2010-03-19.