Fujiyoshida
Geography
Fujiyoshida lies at the northern base of Mount Fuji, and is built upon old lava flows. It is considered a high-elevation city in Japan, at 650 to 850 metres (2,140 to 2,800 feet) above sea level. The city is also located between two of the Fuji Five Lakes. The Katsura River flows through the eastern part of the city.
Neighboring municipalities
- Shizuoka Prefecture
- Yamanashi Prefecture
Climate
The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification Cfa). The average annual temperature in Fujiyoshida is 9.1 °C (48.4 °F). The average annual rainfall is 1,845 millimetres (72.6 in) with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 21 °C (70 °F), and lowest in January, at around −2.3 °C (27.9 °F).
Demographics
Per Japanese census data, the population of Fujiyoshida has declined in recent decades.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1940 | 49,960 | — |
| 1950 | 61,882 | +23.9% |
| 1960 | 42,607 | −31.1% |
| 1970 | 50,046 | +17.5% |
| 1980 | 53,569 | +7.0% |
| 1990 | 54,804 | +2.3% |
| 2000 | 54,090 | −1.3% |
| 2010 | 50,619 | −6.4% |
| 2020 | 46,530 | −8.1% |
History
Following the Meiji restoration, the area around Fujiyoshida was organized into Minamitsuru District, Yamanashi per the cadastral reforms of July 22, 1878. With the establishment of the modern municipalities system on July 1, 1889, the villages of Mizuho, Akemi and Fukuchi were established. In 1939, Mizuho was raised to town status and renamed Shimoyoshida. Likewise, in 1947, Fukuchi was raised to town status and renamed Fujikamiyoshida and Akemi was raised to town status in 1948, retaining its original name. These three towns merged on March 20, 1951, to form the city of Fujiyoshida.
Government
Fujiyoshida has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 20 members.
Economy
For several centuries, artisans around the Fujiyoshida area have produced high quality textiles, and now the city is the center of commerce and high technology in southern Yamanashi Prefecture.
Education
- Showa University
- Fujiyoshida has seven public elementary schools and four public middle schools operated by the city government, and three public private high schools operated by the Yamanashi Prefectural Board of Education. The city also has one private middle school and one private high school.
Senior high schools
In Japan the public Senior High Schools are operated by the prefecture, which in this case in the Yamanashi prefecture. While not compulsory, 94% of all junior high school graduates entered high schools. These high schools are the equivalent of grades 10 – 12 in the United States or the Fifth and Sixth form in the English system.
Prefectural public high schools
- Fuji Hokuryo High School
- Hibarigaoka High School
- Yoshida High School
Private high schools
- Fuji Gakuen High School
Junior high schools
The public Junior High Schools are operated by the City of Fujiyoshida. These schools are the equivalent of grades 6 – 9 in the United States or the First to Fourth form in the English system.
Municipal junior high schools
- Akemi Junior High School
- Fujimidai Junior High School
- Shimoyoshida Junior High School
- Yoshida Junior High School
Private junior high schools
- Fuji Gakuen Junior High School
Primary schools
The public Primary Schools are operated by the City of Fujiyoshida. Municipal Primary Schools
- Akemi Elementary School
- Fuji Elementary School
- Shimoyoshida 2nd Elementary School
- Shimoyoshida Daiichi Elementary School
- Shimoyoshida Higashi Elementary School
- Yoshida Elementary School
- Yoshida Nishi Elementary School
Transportation
Railway
Highway
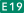 Chūō Expressway
Chūō Expressway Higashifuji-goko Road
Higashifuji-goko Road National Route 137
National Route 137 National Route 138
National Route 138 National Route 139
National Route 139 National Route 300
National Route 300 National Route 413
National Route 413
Sister cities
 Colorado Springs, Colorado, United States, since 1962
Colorado Springs, Colorado, United States, since 1962 Chamonix-Mont Blanc, France, since 1978
Chamonix-Mont Blanc, France, since 1978
Local attractions

- Arakurayama Sengen Park and the Chūrei-tō pagoda, built on a hilltop facing Mount Fuji.
- Fuji-Q Highland an amusement park with a variety of attractions suitable for adults and children.
- Kitaguchi Hongū Fuji Sengen Jinja, a Shinto shrine dedicated to the kami of Mount Fuji, the Kitaguchi Hongū Fuji Sengen Jinja is the historical starting point for pilgrims climbing the mountain. The main structure was originally built in 788 and underwent reconstruction in the 17th century. Additional buildings include a shrine dedicated to Takeda Shingen (1521–1573), and a red torii which is taken down and rebuilt every "Fuji Year" (60 years). The shrine has a local history museum which displays items from Fujiyoshida's past including household items, farm implements, clothing and samples of the cities' famous textiles.
- Mt. Fuji Radar Dome Museum. A tribute to the meteorologists who built a radar research facility at the summit of Mount Fuji, which features a room which simulates the conditions at the summit of the mountain.
- Mt. Fuji Visitors Center. It is home to interactive displays, videos, books and guides about Mount Fuji.
Notable people from Fujiyoshida
- Keiji Mutoh, professional wrestler
- Shun Sugata, actor
References
- ^ Fujiyoshida City official statistics(in Japanese)
- ^ "Fujiyoshida climate: Temperature Fujiyoshida & Weather By Month". en.climate-data.org. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ^ "Yamanashi (Japan): Cities, Towns and Villages in Prefecture - Population Statistics, Charts and Map". www.citypopulation.de. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ^ "Fujiyoshida Welcomes You". Fujiyoshida City International Affairs Desk. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- ^ "MEXT : Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology". Archived from the original on 2008-06-17. Retrieved 2021-02-24.
- ^ "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- ^ "Player - Keiji Muto". Wrestle-1 Official Web Site (in Japanese). 2013. Archived from the original on 1 November 2014. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- ^ 日本映画人名事典』男優編. Kinema-Junpo. 1996. p. 832. ISBN 978-4873761886.
External links
![]() Media related to Fujiyoshida, Yamanashi at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Fujiyoshida, Yamanashi at Wikimedia Commons
 Fuji Yoshida travel guide from Wikivoyage
Fuji Yoshida travel guide from Wikivoyage- Official Website (in Japanese)