Rorschach Heiden Bergbahn
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
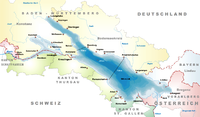
The Rorschach–Heiden railway (German: Rorschach-Heiden-Bahn, RHB) is a railway line and former railway company in Switzerland. It is a standard gauge rack railway, using the Riggenbach rack system and is part of Appenzeller Bahnen. The 7 km (4.3 mi) route links Rorschach with Heiden.
The line is popular with tourists for its scenic views over Lake Constance. During the summer months, it is operated with old open coaches.
Route
The separate RHB line starts a half a kilometre east of Rorschach station, shortly after it branches off from the Chur–Rorschach railway line belonging to the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB). The property line is exactly at kilometre 64.41483. The entry signal from Heiden into the Rorschach train station is at kilometre 64.476. This position is often incorrectly stated as the property limit, but in fact it is the operational limit. The property line between SBB and AB and the zero point of the kilometers in the direction of Heiden are behind the SBB depot, directly in front of the two points in the Appenzeller Bahnen parking facility. The rack also begins immediately after the two switches. The gradient that begins afterwards is on average 91 ‰, the maximum value is 93.6‰. Above Wienacht Tobel, the route is a little flatter and only reaches 79.6‰.
The route continues via the stations at Seebleiche, Sandbüchel, Wartensee, Wienacht-Tobel and Schwendi bei Heiden to Heiden. All intermediate stations are request-only stops. The terminal station in Heiden is at an altitude of 794 metres. The trains to Heiden start from Rorschach Hafen station, initially following a piece of the Romanshorn–Rorschach railway line operated by SBB to Rorschach station and from there the route towards St. Margrethen to the junction.
The route runs through the municipalities of Rorschacherberg (Seebleiche, Sandbüchel), Thal (Wartensee), Lutzenberg (Wienacht-Tobel), Heiden (Schwendi) and Grub (without a station) and ends in the municipality of Heiden.
Current operations
Passenger services on the route are currently operated as line S25 of the St. Gallen S-Bahn and Bodensee S-Bahn, running hourly between Rorschach Hafen and Heiden. The schedule in the early morning differs from those after 9:00 a.m.
In the summer, steam-powered services are also offered. The historic summer wagons are used in regular operation; a bicycle wagon is used to transport bicycles.
There is no longer freight traffic on the line, with the exception of AB's own construction trains, as the main customers, Starrag and Wolfhalden grain mill, have ceased to exist. During the reorganisation of Swiss freight traffic, many service points with a lower volume of goods, including all of the RHB, were discontinued.
The motor car BDeh 3/6 25 was repaired between September 2009 to May 2010 in the main workshop of the Rhaetian Railway in Landquart. It was repainted in the current colors and given the AB logo.
The Rorschach-Heiden-Bergbahn is included in the Ostwind tariff network.
Threat of closure
Due to declining frequencies and a cost recovery rate of less than 30%, the cantons of Appenzell Ausserrhoden and St. Gallen are considering whether the three rack railways operated by Appenzeller Bahnen (Rorschach Hafen to Heiden, Altstätten Stadt to Gais, and from Rheineck to Walzenhausen) should continue to operate. In particular, a switch to bus operation or fully automatic operation is up for discussion.
History

The first efforts to establish a rail connection to the village of Heiden began in 1872. Early plans for an adhesion railway were soon discarded in favour of a shorter rack-and-pinion line from Rorschach. After receiving the concession in January 1874, construction work began in May of the same year. After a year and a half of construction, the line was finished. After officially opening on 3 September 1875, regular services began on 6 September 1875. The route was built in such a way that an extension to Trogen was possible.
The entire route was 7,163 m long at the start of operations, 5,784 m of which were owned by the railway company. The construction costs of the line amounted to CHF 2,225,000, the costs for the rolling stock amounted to CHF 218,200. At the beginning, the railway company had three steam locomotives, nine passenger cars with a total capacity of 400 people and eight freight cars with a total capacity of 56 t.
In 1897 the company was issued a concession allowing the construction of a branch of its line of km. 2,666 to a quarry in the "Chrennen" (then "Krinnen") near Wienacht. For this purpose, a new track with a length of about 250 m was laid, which became an integral part of the entire railway system.
The line was electrified with the same 15 kV, 16⅔ Hz AC system as the Swiss Federal Railways network. Two new class FZeh 2/4 electric locomotives were supplied by the Swiss Locomotive and Machine Works (SLM) and numbered 21 and 22. In 1950 four-wheel electric railcar, BCFhe 2/4 number 23, was supplied by SLM, followed in 1967 by a second railcar, ABDeh 2/4 number 24, from the same supplier. A third railcar, the articulated BDeh 3/6 number 25, was built by Stadler Rail in 1998.
On 1 July 2006, the RHB merged with the Rheineck–Walzenhausen mountain railway, Trogenerbahn and the former Appenzeller Bahnen to form a new company operating under the name Appenzeller Bahnen.
References
- ^ Sonderegger, Konrad; Eggenberger, Peter (2000). Rorschach-Heiden-Bergbahn (RHB), Drahtseilbahn/Bergbahn Rheineck-Walzenhausen (RhW) (2nd ed.). Herisau: Appenzeller Verlag. ISBN 3-85882-295-7.
- ^ "Fakten und Zahlen" [Facts and Numbers] (in German). Appenzeller Bahnen. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Eisenbahnatlas Schweiz. Verlag Schweers + Wall GmbH. 2012. pp. 14–15. ISBN 978-3-89494-130-7.
- ^ Rorschach-Heiden rack railway, bodensee.eu
- ^ "S-Bahn Bodensee" (in German). Retrieved 2023-06-11.
- ^ Gafafer, Tobias (28 February 2019). "Ostschweizer Zahnradbahnen stehen auf der roten Liste" [Rack railways in eastern Switzerland stand on the red list]. Neue Zürcher Zeitung (in German). Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Ballinger, Mike (January 2024). "Systems Factfile: Appenzell/St. Gallen, Switzerland". Tramways & Urban Transit. Light Rail Transit Association. pp. 28–32. ISSN 1460-8324.
- ^ "Agglomerationsbahn ins Appenzellerland" [Conurbation railway in Appenzell]. Neue Zürcher Zeitung (in German). 3 July 2006. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ "Geschäftsbericht 2006" [Annual Report 2006] (PDF) (in German). Appenzeller Bahnen. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
External links
![]() Media related to Rorschach-Heiden-Bergbahn at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Rorschach-Heiden-Bergbahn at Wikimedia Commons
- Appenzeller Bahnen official website (in German)