Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. A large share of its claims are pseudoscientific, with the majority of treatments having no robust evidence of effectiveness or logical mechanism of action.
Medicine in traditional China encompassed a range of sometimes competing health and healing practices, folk beliefs, literati theory and Confucian philosophy, herbal remedies, food, diet, exercise, medical specializations, and schools of thought. TCM as it exists today has been described as a largely 20th century invention. In the early twentieth century, Chinese cultural and political modernizers worked to eliminate traditional practices as backward and unscientific. Traditional practitioners then selected elements of philosophy and practice and organized them into what they called "Chinese medicine" (Chinese: 中医 Zhongyi). In the 1950s, the Chinese government sought to revive traditional medicine (including legalizing previously banned practices) and sponsored the integration of TCM and Western medicine, and in the Cultural Revolution of the 1960s, promoted TCM as inexpensive and popular. The creation of modern TCM was largely spearheaded by Mao Zedong, despite the fact that, according to The Private Life of Chairman Mao, he did not believe in its effectiveness. After the opening of relations between the United States and China after 1972, there was great interest in the West for what is now called traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
TCM is said to be based on such texts as Huangdi Neijing (The Inner Canon of the Yellow Emperor), and Compendium of Materia Medica, a sixteenth-century encyclopedic work, and includes various forms of herbal medicine, acupuncture, cupping therapy, gua sha, massage (tui na), bonesetter (die-da), exercise (qigong), and dietary therapy. TCM is widely used in the Sinosphere. One of the basic tenets is that the body's qi is circulating through channels called meridians having branches connected to bodily organs and functions. There is no evidence that meridians or vital energy exist. Concepts of the body and of disease used in TCM reflect its ancient origins and its emphasis on dynamic processes over material structure, similar to the humoral theory of ancient Greece and ancient Rome.
The demand for traditional medicines in China is a major generator of illegal wildlife smuggling, linked to the killing and smuggling of endangered animals. The Chinese authorities have engaged in attempts to crack down on illegal TCM-related wildlife smuggling.
Ancient history

Scholars in the history of medicine in China distinguish its doctrines and practice from those of present-day TCM. J. A. Jewell and S. M. Hillier state that the term "Traditional Chinese Medicine" became an established term due to the work of Dr. Kan-Wen Ma, a Western-trained medical doctor who was persecuted during the Cultural Revolution and immigrated to Britain, joining the University of London's Wellcome Institute for the History of Medicine. Ian Johnson says, on the other hand, that the English-language term "traditional Chinese medicine" was coined by "party propagandists" in 1955.
Nathan Sivin criticizes attempts to treat medicine and medical practices in traditional China as if they were a single system. Instead, he says, there were 2,000 years of "medical system in turmoil" and speaks of a "myth of an unchanging medical tradition". He urges that "Traditional medicine translated purely into terms of modern medicine becomes partly nonsensical, partly irrelevant, and partly mistaken; that is also true the other way around, a point easily overlooked." TJ Hinrichs observes that people in modern Western societies divide healing practices into biomedicine for the body, psychology for the mind, and religion for the spirit, but these distinctions are inadequate to describe medical concepts among Chinese historically and to a considerable degree today.
The medical anthropologist Charles Leslie writes that Chinese, Greco-Arabic, and Indian traditional medicines were all grounded in systems of correspondence that aligned the organization of society, the universe, and the human body and other forms of life into an "all-embracing order of things". Each of these traditional systems was organized with such qualities as heat and cold, wet and dry, light and darkness, qualities that also align the seasons, compass directions, and the human cycle of birth, growth, and death. They provided, Leslie continued, a "comprehensive way of conceiving patterns that ran through all of nature," and they "served as a classificatory and mnemonic device to observe health problems and to reflect upon, store, and recover empirical knowledge," but they were also "subject to stultifying theoretical elaboration, self-deception, and dogmatism."
The doctrines of Chinese medicine are rooted in books such as the Yellow Emperor's Inner Canon and the Treatise on Cold Damage, as well as in cosmological notions such as yin–yang and the five phases. The Compendium of Materia Medica dates back to around 1,100 BCE when only a few dozen drugs were described. By the end of the 16th century, the number of drugs documented had reached close to 1,900. And by the end of the last century, published records of CMM had reached 12,800 drugs." Starting in the 1950s, these precepts were standardized in the People's Republic of China, including attempts to integrate them with modern notions of anatomy and pathology. In the 1950s, the Chinese government promoted a systematized form of TCM.
Shang dynasty
Traces of therapeutic activities in China date from the Shang dynasty (14th–11th centuries BCE). Though the Shang did not have a concept of "medicine" as distinct from other health practices, their oracular inscriptions on bones and tortoise shells refer to illnesses that affected the Shang royal family: eye disorders, toothaches, bloated abdomen, and such. Shang elites usually attributed them to curses sent by their ancestors. There is currently no evidence that the Shang nobility used herbal remedies.
Stone and bone needles found in ancient tombs led Joseph Needham to speculate that acupuncture might have been carried out in the Shang dynasty. This being said, most historians now make a distinction between medical lancing (or bloodletting) and acupuncture in the narrower sense of using metal needles to attempt to treat illnesses by stimulating points along circulation channels ("meridians") in accordance with beliefs related to the circulation of "Qi". The earliest evidence for acupuncture in this sense dates to the second or first century BCE.
Han dynasty
The Yellow Emperor's Inner Canon (Huangdi Neijing), the oldest received work of Chinese medical theory, was compiled during the Han dynasty around the first century BCE on the basis of shorter texts from different medical lineages. Written in the form of dialogues between the legendary Yellow Emperor and his ministers, it offers explanations on the relation between humans, their environment, and the cosmos, on the contents of the body, on human vitality and pathology, on the symptoms of illness, and on how to make diagnostic and therapeutic decisions in light of all these factors. Unlike earlier texts like Recipes for Fifty-Two Ailments, which was excavated in the 1970s from the Mawangdui tomb that had been sealed in 168 BCE, the Inner Canon rejected the influence of spirits and the use of magic. It was also one of the first books in which the cosmological doctrines of Yinyang and the Five Phases were brought to a mature synthesis.
The Treatise on Cold Damage Disorders and Miscellaneous Illnesses (Shang Han Lun) was collated by Zhang Zhongjing sometime between 196 and 220 CE; at the end of the Han dynasty. Focusing on drug prescriptions rather than acupuncture, it was the first medical work to combine Yinyang and the Five Phases with drug therapy. This formulary was also the earliest public Chinese medical text to group symptoms into clinically useful "patterns" (zheng 證) that could serve as targets for therapy. Having gone through numerous changes over time, the formulary now circulates as two distinct books: the Treatise on Cold Damage Disorders and the Essential Prescriptions of the Golden Casket, which were edited separately in the eleventh century, under the Song dynasty.
Nanjing or "Classic of Difficult Issues", originally called "The Yellow Emperor Eighty-one Nan Jing", ascribed to Bian Que in the eastern Han dynasty. This book was compiled in the form of question-and-answer explanations. A total of 81 questions have been discussed. Therefore, it is also called "Eighty-One Nan". The book is based on basic theory and has also analyzed some disease certificates. Questions one to twenty-two is about pulse study, questions twenty-three to twenty-nine is about meridian study, questions thirty to forty-seven is related to urgent illnesses, questions forty-eight to sixty-one is related to serious diseases, questions sixty-two to sixty-eight is related to acupuncture points, and questions sixty-nine to eighty-one is related to the needlepoint methods.
The book is credited as developing its own path, while also inheriting the theories from Huangdi Neijing. The content includes physiology, pathology, diagnosis, treatment contents, and a more essential and specific discussion of pulse diagnosis. It has become one of the four classics for Chinese medicine practitioners to learn from and has impacted the medical development in China.
Shennong Ben Cao Jing is one of the earliest written medical books in China. Written during the Eastern Han dynasty between 200 and 250 CE, it was the combined effort of practitioners in the Qin and Han dynasties who summarized, collected and compiled the results of pharmacological experience during their time periods. It was the first systematic summary of Chinese herbal medicine. Most of the pharmacological theories and compatibility rules and the proposed "seven emotions and harmony" principle have played a role in the practice of medicine for thousands of years. Therefore, it has been a textbook for medical workers in modern China. The full text of Shennong Ben Cao Jing in English can be found online.
Post-Han dynasty
In the centuries that followed, several shorter books tried to summarize or systematize the contents of the Yellow Emperor's Inner Canon. The Canon of Problems (probably second century CE) tried to reconcile divergent doctrines from the Inner Canon and developed a complete medical system centered on needling therapy. The AB Canon of Acupuncture and Moxibustion (Zhenjiu jiayi jing 針灸甲乙經, compiled by Huangfu Mi sometime between 256 and 282 CE) assembled a consistent body of doctrines concerning acupuncture; whereas the Canon of the Pulse (Maijing 脈經; c. 280) presented itself as a "comprehensive handbook of diagnostics and therapy."
Around 900–1000 AD, Chinese were the first to develop a form of vaccination, known as variolation or inoculation, to prevent smallpox. Chinese physicians had realised that when healthy people were exposed to smallpox scab tissue, they had a smaller chance of being infected by the disease later on. The common methods of inoculation at the time was through crushing smallpox scabs into powder and breathing it through the nose.
Prominent medical scholars of the post-Han period included Tao Hongjing (456–536), Sun Simiao of the Sui and Tang dynasties, Zhang Jiegu (c. 1151–1234), and Li Shizhen (1518–1593).
Modern history
Chinese communities under Colonial rule
Chinese communities living in colonial port cities were influenced by the diverse cultures they encountered, which also led to evolving understandings of medical practices where Chinese forms of medicine were combined with Western medical knowledge. For example, the Tung Wah Hospital was established in Hong Kong in 1869 based on the widespread rejection of Western medicine for pre-existing medical practices, although Western medicine would still be practiced in the hospital alongside Chinese medicinal practices. The Tung Wah Hospital was likely connected to another Chinese medical institution, the Kwong Wai Shiu Hospital of Singapore, which had previous community links to Tung Wah, was established for similar reasons and also provided both Western and Chinese medical care. By 1935, English-language newspapers in Colonial Singapore already used the term "Traditional Chinese Medicine" to label Chinese ethnic medical practices.
People's Republic
In 1950, Chinese Communist Party (CCP) chairman Mao Zedong announced support of traditional Chinese medicine; this was despite the fact that Mao did not personally believe in and did not use TCM, according to his personal physician Li Zhisui. In 1952, the president of the Chinese Medical Association said that, "This One Medicine, will possess a basis in modern natural sciences, will have absorbed the ancient and the new, the Chinese and the foreign, all medical achievements – and will be China's New Medicine!"
During the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) the CCP and the government emphasized modernity, cultural identity and China's social and economic reconstruction and contrasted them to the colonial and feudal past. The government established a grassroots health care system as a step in the search for a new national identity and tried to revitalize traditional medicine and made large investments in traditional medicine to try to develop affordable medical care and public health facilities. The Ministry of Health directed health care throughout China and established primary care units. Chinese physicians trained in Western medicine were required to learn traditional medicine, while traditional healers received training in modern methods. This strategy aimed to integrate modern medical concepts and methods and revitalize appropriate aspects of traditional medicine. Therefore, traditional Chinese medicine was re-created in response to Western medicine.

In 1968, the CCP supported a new system of health care delivery for rural areas. Villages were assigned a barefoot doctor (a medical staff with basic medical skills and knowledge to deal with minor illnesses) responsible for basic medical care. The medical staff combined the values of traditional China with modern methods to provide health and medical care to poor farmers in remote rural areas. The barefoot doctors became a symbol of the Cultural Revolution, for the introduction of modern medicine into villages where traditional Chinese medicine services were used.
The State Intellectual Property Office (now known as CNIPA) established a database of patents granted for traditional Chinese medicine.
In the second decade of the twenty-first century, Chinese Communist Party general secretary Xi Jinping strongly supported TCM, calling it a "gem". As of May 2011, in order to promote TCM worldwide, China had signed TCM partnership agreements with over 70 countries. His government pushed to increase its use and the number of TCM-trained doctors and announced that students of TCM would no longer be required to pass examinations in Western medicine. Chinese scientists and researchers, however, expressed concern that TCM training and therapies would receive equal support with Western medicine. They also criticized a reduction in government testing and regulation of the production of TCMs, some of which were toxic. Government censors have removed Internet posts that question TCM. In 2020 Beijing drafted a local regulation outlawing criticism of TCM. According to Caixin, the regulation was later passed with the provision outlawing criticism of TCM removed.
Hong Kong
This section needs to be updated. The reason given is: Development after the enactment of Chinese Medicine Ordinance (Cap. 549) needed.. (January 2024) |
At the beginning of Hong Kong's opening up, Western medicine was not yet popular, and Western medicine doctors were mostly foreigners; local residents mostly relied on Chinese medicine practitioners. In 1841, the British government of Hong Kong issued an announcement pledging to govern Hong Kong residents in accordance with all the original rituals, customs and private legal property rights. As traditional Chinese medicine had always been used in China, the use of traditional Chinese medicine was not regulated.
The establishment in 1870 of the Tung Wah Hospital was the first use of Chinese medicine for the treatment in Chinese hospitals providing free medical services. As the promotion of Western medicine by the British government started from 1940, Western medicine started being popular among Hong Kong population. In 1959, Hong Kong had researched the use of traditional Chinese medicine to replace Western medicine.
Historiography of Chinese medicine
Historians have noted two key aspects of Chinese medical history: understanding conceptual differences when translating the term 身, and observing the history from the perspective of cosmology rather than biology.
In Chinese classical texts, the term 身 is the closest historical translation to the English word "body" because it sometimes refers to the physical human body in terms of being weighed or measured, but the term is to be understood as an "ensemble of functions" encompassing both the human psyche and emotions. This concept of the human body is opposed to the European duality of a separate mind and body. It is critical for scholars to understand the fundamental differences in concepts of the body in order to connect the medical theory of the classics to the "human organism" it is explaining.
Chinese scholars established a correlation between the cosmos and the "human organism". The basic components of cosmology, qi, yin yang and the Five Phase theory, were used to explain health and disease in texts such as Huangdi neijing. Yin and yang are the changing factors in cosmology, with qi as the vital force or energy of life. The Five Phase theory (Wuxing) of the Han dynasty contains the elements wood, fire, earth, metal, and water. By understanding medicine from a cosmology perspective, historians better understand Chinese medical and social classifications such as gender, which was defined by a domination or remission of yang in terms of yin.
These two distinctions are imperative when analyzing the history of traditional Chinese medical science.
A majority of Chinese medical history written after the classical canons comes in the form of primary source case studies where academic physicians record the illness of a particular person and the healing techniques used, as well as their effectiveness. Historians have noted that Chinese scholars wrote these studies instead of "books of prescriptions or advice manuals;" in their historical and environmental understanding, no two illnesses were alike so the healing strategies of the practitioner was unique every time to the specific diagnosis of the patient. Medical case studies existed throughout Chinese history, but "individually authored and published case history" was a prominent creation of the Ming dynasty. An example such case studies would be the literati physician, Cheng Congzhou, collection of 93 cases published in 1644.
Critique
Historians of science have developed the study of medicine in traditional China into a field with its own scholarly associations, journals, graduate programs, and debates with each other. Many distinguish "medicine in traditional China" from the recent traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), which took elements from traditional texts and practices to construct a systematic body. Paul Unschuld, for instance, sees a "departure of TCM from its historical origins." What is called "Traditional Chinese Medicine" and practiced today in China and the West is not thousands of years old, but recently constructed using selected traditional terms, some of which have been taken out of context, some badly misunderstood. He has criticized Chinese and Western popular books for selective use of evidence, choosing only those works or parts of historical works that seem to lead to modern medicine, ignoring those elements that do not now seem to be effective.
Critics say that TCM theory and practice have no basis in modern science, and TCM practitioners do not agree on what diagnosis and treatments should be used for any given person. A 2007 editorial in the journal Nature wrote that TCM "remains poorly researched and supported, and most of its treatments have no logical mechanism of action." It also described TCM as "fraught with pseudoscience". A review of the literature in 2008 found that scientists are "still unable to find a shred of evidence" according to standards of science-based medicine for traditional Chinese concepts such as qi, meridians, and acupuncture points, and that the traditional principles of acupuncture are deeply flawed. "Acupuncture points and meridians are not a reality", the review continued, but "merely the product of an ancient Chinese philosophy". In June 2019, the World Health Organization included traditional Chinese medicine in a global diagnostic compendium, but a spokesman said this was "not an endorsement of the scientific validity of any Traditional Medicine practice or the efficacy of any Traditional Medicine intervention."
A 2012 review of cost-effectiveness research for TCM found that studies had low levels of evidence, with no beneficial outcomes. Pharmaceutical research on the potential for creating new drugs from traditional remedies has few successful results. Proponents suggest that research has so far missed key features of the art of TCM, such as unknown interactions between various ingredients and complex interactive biological systems. One of the basic tenets of TCM is that the body's qi (sometimes translated as vital energy) is circulating through channels called meridians having branches connected to bodily organs and functions. The concept of vital energy is pseudoscientific. Concepts of the body and of disease used in TCM reflect its ancient origins and its emphasis on dynamic processes over material structure, similar to Classical humoral theory.
TCM has also been controversial within China. In 2006, the Chinese philosopher Zhang Gongyao triggered a national debate with an article entitled "Farewell to Traditional Chinese Medicine", arguing that TCM was a pseudoscience that should be abolished in public healthcare and academia. The Chinese government took the stance that TCM is a science and continued to encourage its development.
There are concerns over a number of potentially toxic plants, animal parts, and mineral Chinese compounds, as well as the facilitation of disease. Trafficked and farm-raised animals used in TCM are a source of several fatal zoonotic diseases. There are additional concerns over the illegal trade and transport of endangered species including rhinoceroses and tigers, and the welfare of specially farmed animals, including bears.
Philosophical background
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is a broad range of medicine practices sharing common concepts which have been developed in China and are based on a tradition of more than 2,000 years, including various forms of herbal medicine, acupuncture, massage (tui na), exercise (qigong), and dietary therapy. It is primarily used as a complementary alternative medicine approach. TCM is widely used in China and it is also used in the West. Its philosophy is based on Yinyangism (i.e., the combination of Five Phases theory with Yin–Yang theory), which was later absorbed by Daoism. Philosophical texts influenced TCM, mostly by being grounded in the same theories of qi, yin-yang and wuxing and microcosm-macrocosm analogies.

Yin and yang
Yin and yang are ancient Chinese deductive reasoning concepts used within Chinese medical diagnosis which can be traced back to the Shang dynasty (1600–1100 BCE). They represent two abstract and complementary aspects that every phenomenon in the universe can be divided into. Primordial analogies for these aspects are the sun-facing (yang) and the shady (yin) side of a hill. Two other commonly used representational allegories of yin and yang are water and fire. In the yin–yang theory, detailed attributions are made regarding the yin or yang character of things:
| Phenomenon | Yin | Yang |
|---|---|---|
| Celestial bodies | moon | sun |
| Gender | female | male |
| Location | inside | outside |
| Temperature | cold | hot |
| Direction | downward | upward |
| Degree of humidity | damp/moist | dry |
The concept of yin and yang is also applicable to the human body; for example, the upper part of the body and the back are assigned to yang, while the lower part of the body is believed to have the yin character. Yin and yang characterization also extends to the various body functions, and – more importantly – to disease symptoms (e.g., cold and heat sensations are assumed to be yin and yang symptoms, respectively). Thus, yin and yang of the body are seen as phenomena whose lack (or over-abundance) comes with characteristic symptom combinations:
- Yin vacuity (also termed "vacuity-heat"): heat sensations, possible sweating at night, insomnia, dry pharynx, dry mouth, dark urine, and a "fine" and rapid pulse.
- Yang vacuity ("vacuity-cold"): aversion to cold, cold limbs, bright white complexion, long voidings of clear urine, diarrhea, pale and enlarged tongue, and a slightly weak, slow and fine pulse.
TCM also identifies drugs believed to treat these specific symptom combinations, i.e., to reinforce yin and yang.
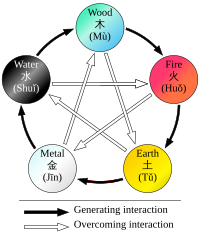
| Phenomenon | Wood | Fire | Earth | Metal | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | East | South | Centre | West | North |
| Colour | green/violet | red/purple | yellow/pink | white | black |
| Climate | wind | heat | damp | dryness | cold |
| Taste | sour | bitter | sweet | acrid | salty |
| Zang Organ | Liver | Heart | Spleen | Lung | Kidney |
| Fu Organ | Gallbladder | Small intestine | Stomach | Large intestine | Bladder |
| Sense organ | eye | tongue | mouth | nose | ears |
| Facial part | above bridge of nose | between eyes, lower part | bridge of nose | between eyes, middle part | cheeks (below cheekbone) |
| Eye part | iris | inner/outer corner of the eye | upper and lower lid | sclera | pupil |
Strict rules are identified to apply to the relationships between the Five Phases in terms of sequence, of acting on each other, of counteraction, etc. All these aspects of Five Phases theory constitute the basis of the zàng-fǔ concept, and thus have great influence regarding the TCM model of the body. Five Phase theory is also applied in diagnosis and therapy.
Correspondences between the body and the universe have historically not only been seen in terms of the Five Elements, but also of the "Great Numbers" (大數; dà shū) For example, the number of acu-points has at times been seen to be 365, corresponding with the number of days in a year; and the number of main meridians–12–has been seen as corresponding with the number of rivers flowing through the ancient Chinese empire.
Model of the body

TCM "holds that the body's vital energy (chi or qi) circulates through channels, called meridians, that have branches connected to bodily organs and functions." Its view of the human body is only marginally concerned with anatomical structures, but focuses primarily on the body's functions (such as digestion, breathing, temperature maintenance, etc.):
These functions are aggregated and then associated with a primary functional entity – for instance, nourishment of the tissues and maintenance of their moisture are seen as connected functions, and the entity postulated to be responsible for these functions is xiě (blood). These functional entities thus constitute concepts rather than something with biochemical or anatomical properties.
The primary functional entities used by traditional Chinese medicine are qì, xuě, the five zàng organs, the six fǔ organs, and the meridians which extend through the organ systems. These are all theoretically interconnected: each zàng organ is paired with a fǔ organ, which are nourished by the blood and concentrate qi for a particular function, with meridians being extensions of those functional systems throughout the body.
Concepts of the body and of disease used in TCM are pseudoscientific, similar to Mediterranean humoral theory. TCM's model of the body is characterized as full of pseudoscience. Some practitioners no longer consider yin and yang and the idea of an energy flow to apply. Scientific investigation has not found any histological or physiological evidence for traditional Chinese concepts such as qi, meridians, and acupuncture points. It is a generally held belief within the acupuncture community that acupuncture points and meridians structures are special conduits for electrical signals but no research has established any consistent anatomical structure or function for either acupuncture points or meridians. The scientific evidence for the anatomical existence of either meridians or acupuncture points is not compelling. Stephen Barrett of Quackwatch writes that, "TCM theory and practice are not based upon the body of knowledge related to health, disease, and health care that has been widely accepted by the scientific community. TCM practitioners disagree among themselves about how to diagnose patients and which treatments should go with which diagnoses. Even if they could agree, the TCM theories are so nebulous that no amount of scientific study will enable TCM to offer rational care."
Qi
Qi is a polysemous word that traditional Chinese medicine distinguishes as being able to transform into many different qualities of qi (气; 氣; qì). In a general sense, qi is something that is defined by five "cardinal functions":
- Actuation (推动; 推動; tuīdòng) – of all physical processes in the body, especially the circulation of all body fluids such as blood in their vessels. This includes actuation of the functions of the zang-fu organs and meridians.
- Warming (温煦; 溫煦; wēnxù) – the body, especially the limbs.
- Defense (防御; fángyù) – against Exogenous Pathogenic Factors
- Containment (固摄; 固攝; gùshè) – of body fluids, i.e., keeping blood, sweat, urine, semen, etc. from leakage or excessive emission.
- Inter-transformationel (气化; 氣化; qìhuà) – of food, drink, and breath into qi, xue (blood), and jinye ("fluids"), and/or transformation of all of the latter into each other.
A lack of qi will be characterized especially by pale complexion, lassitude of spirit, lack of strength, spontaneous sweating, laziness to speak, non-digestion of food, shortness of breath (especially on exertion), and a pale and enlarged tongue.
Qi is believed to be partially generated from food and drink, and partially from air (by breathing). Another considerable part of it is inherited from the parents and will be consumed in the course of life.
TCM uses special terms for qi running inside of the blood vessels and for qi that is distributed in the skin, muscles, and tissues between them. The former is called yingqi (营气; 營氣; yíngqì); its function is to complement xuè and its nature has a strong yin aspect (although qi in general is considered to be yang). The latter is called weiqi (卫气; 衛氣; weìqì); its main function is defence and it has pronounced yang nature.
Qi is said to circulate in the meridians. Just as the qi held by each of the zang-fu organs, this is considered to be part of the 'principal' qi of the body.
Xie
In contrast to the majority of other functional entities, xuè or xiě (血, "blood") is correlated with a physical form – the red liquid running in the blood vessels. Its concept is, nevertheless, defined by its functions: nourishing all parts and tissues of the body, safeguarding an adequate degree of moisture, and sustaining and soothing both consciousness and sleep.
Typical symptoms of a lack of xiě (usually termed "blood vacuity" [血虚; xiě xū]) are described as: Pale-white or withered-yellow complexion, dizziness, flowery vision, palpitations, insomnia, numbness of the extremities; pale tongue; "fine" pulse.
Jinye
Closely related to xuě are the jinye (津液; jīnyè, usually translated as "body fluids"), and just like xuě they are considered to be yin in nature, and defined first and foremost by the functions of nurturing and moisturizing the different structures of the body. Their other functions are to harmonize yin and yang, and to help with the secretion of waste products.
Jinye are ultimately extracted from food and drink, and constitute the raw material for the production of xuě; conversely, xuě can also be transformed into jinye. Their palpable manifestations are all bodily fluids: tears, sputum, saliva, gastric acid, joint fluid, sweat, urine, etc.
Zangfu
The zangfu (脏腑; 臟腑; zàngfǔ) are the collective name of eleven entities (similar to organs) that constitute the centre piece of TCM's systematization of bodily functions. The term zang refers to the five considered to be yin in nature – Heart, Liver, Spleen, Lung, Kidney – while fu refers to the six associated with yang – Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Gallbladder, Urinary Bladder, Stomach and San Jiao. Despite having the names of organs, they are only loosely tied to (rudimentary) anatomical assumptions. Instead, they are primarily understood to be certain "functions" of the body. To highlight the fact that they are not equivalent to anatomical organs, their names are usually capitalized.
The zang's essential functions consist in production and storage of qi and xuě; they are said to regulate digestion, breathing, water metabolism, the musculoskeletal system, the skin, the sense organs, aging, emotional processes, and mental activity, among other structures and processes. The fǔ organs' main purpose is merely to transmit and digest (傳化; chuán-huà) substances such as waste and food.
Since their concept was developed on the basis of Wǔ Xíng philosophy, each zàng is paired with a fǔ, and each zàng-fǔ pair is assigned to one of five elemental qualities (i.e., the Five Elements or Five Phases). These correspondences are stipulated as:
- Fire (火) = Heart (心; xīn) and Small Intestine (小腸; xiaǒcháng) (and, secondarily, Sānjiaō [三焦, "Triple Burner"] and Pericardium [心包; xīnbaò])
- Earth (土) = Spleen (脾; pí) and Stomach (胃; weì)
- Metal (金) = Lung (肺; feì) and Large Intestine (大腸; dàcháng)
- Water (水) = Kidney (腎; shèn) and Bladder (膀胱; pángguāng)
- Wood (木) = Liver (肝; gān) and Gallbladder (膽; dān)
The zàng-fǔ are also connected to the twelve standard meridians – each yang meridian is attached to a fǔ organ, and five of the yin meridians are attached to a zàng. As there are only five zàng but six yin meridians, the sixth is assigned to the Pericardium, a peculiar entity almost similar to the Heart zàng.
Jing-luo

The meridians (经络, jīng-luò) are believed to be channels running from the zàng-fǔ in the interior (里, lǐ) of the body to the limbs and joints ("the surface" [表, biaǒ]), transporting qi and xuĕ. TCM identifies 12 "regular" and 8 "extraordinary" meridians; the Chinese terms being 十二经脉 (shí-èr jīngmài, lit. "the Twelve Vessels") and 奇经八脉 (qí jīng bā mài) respectively. There's also a number of less customary channels branching from the "regular" meridians.
Gender in traditional medicine
Fuke (妇科; 婦科; Fùkē) is the traditional Chinese term for women's medicine (it means gynecology and obstetrics in modern medicine). However, there are few or no ancient works on it except for Fu Qingzhu's Fu Qingzhu Nu Ke (Fu Qingzhu's Gynecology). In traditional China, as in many other cultures, the health and medicine of female bodies was less understood than that of male bodies. Women's bodies were often secondary to male bodies, since women were thought of as the weaker, sicklier sex.
In clinical encounters, women and men were treated differently. Diagnosing women was not as simple as diagnosing men. First, when a woman fell ill, an appropriate adult man was to call the doctor and remain present during the examination, for the woman could not be left alone with the doctor. The physician would discuss the female's problems and diagnosis only through the male. However, in certain cases, when a woman dealt with complications of pregnancy or birth, older women assumed the role of the formal authority. Men in these situations would not have much power to interfere. Second, women were often silent about their issues with doctors due to the societal expectation of female modesty when a male figure was in the room. Third, patriarchal society also caused doctors to call women and children patients "the anonymous category of family members (Jia Ren) or household (Ju Jia)" in their journals. This anonymity and lack of conversation between the doctor and woman patient led to the inquiry diagnosis of the Four Diagnostic Methods being the most challenging. Doctors used a medical doll known as a Doctor's lady, on which female patients could indicate the location of their symptoms.
Cheng Maoxian (b. 1581), who practiced medicine in Yangzhou, described the difficulties doctors had with the norm of female modesty. One of his case studies was that of Fan Jisuo's teenage daughter, who could not be diagnosed because she was unwilling to speak about her symptoms, since the illness involved discharge from her intimate areas. As Cheng describes, there were four standard methods of diagnosis – looking, asking, listening and smelling and touching (for pulse-taking). To maintain some form of modesty, women would often stay hidden behind curtains and screens. The doctor was allowed to touch enough of her body to complete his examination, often just the pulse taking. This would lead to situations where the symptoms and the doctor's diagnosis did not agree and the doctor would have to ask to view more of the patient.
These social and cultural beliefs were often barriers to learning more about female health, with women themselves often being the most formidable barrier. Women were often uncomfortable talking about their illnesses, especially in front of the male chaperones that attended medical examinations. Women would choose to omit certain symptoms as a means of upholding their chastity and honor. One such example is the case in which a teenage girl was unable to be diagnosed because she failed to mention her symptom of vaginal discharge. Silence was their way of maintaining control in these situations, but it often came at the expense of their health and the advancement of female health and medicine. This silence and control were most obviously seen when the health problem was related to the core of Ming fuke, or the sexual body. It was often in these diagnostic settings that women would choose silence. In addition, there would be a conflict between patient and doctor on the probability of her diagnosis. For example, a woman who thought herself to be past the point of child-bearing age, might not believe a doctor who diagnoses her as pregnant. This only resulted in more conflict.
Yin yang and gender
Yin and yang were critical to the understanding of women's bodies, but understood only in conjunction with male bodies. Yin and yang ruled the body, the body being a microcosm of the universe and the earth. In addition, gender in the body was understood as homologous, the two genders operating in synchronization. Gender was presumed to influence the movement of energy and a well-trained physician would be expected to read the pulse and be able to identify two dozen or more energy flows. Yin and yang concepts were applied to the feminine and masculine aspects of all bodies, implying that the differences between men and women begin at the level of this energy flow. According to Bequeathed Writings of Master Chu the male's yang pulse movement follows an ascending path in "compliance [with cosmic direction] so that the cycle of circulation in the body and the Vital Gate are felt...The female's yin pulse movement follows a defending path against the direction of cosmic influences, so that the nadir and the Gate of Life are felt at the inch position of the left hand". In sum, classical medicine marked yin and yang as high and low on bodies which in turn would be labeled normal or abnormal and gendered either male or female.
Bodily functions could be categorized through systems, not organs. In many drawings and diagrams, the twelve channels and their visceral systems were organized by yin and yang, an organization that was identical in female and male bodies. Female and male bodies were no different on the plane of yin and yang. Their gendered differences were not acknowledged in diagrams of the human body. Medical texts such as the Yuzuan yizong jinjian were filled with illustrations of male bodies or androgynous bodies that did not display gendered characteristics.
As in other cultures, fertility and menstruation dominate female health concerns. Since male and female bodies were governed by the same forces, traditional Chinese medicine did not recognize the womb as the place of reproduction. The abdominal cavity presented pathologies that were similar in both men and women, which included tumors, growths, hernias, and swellings of the genitals. The "master system", as Charlotte Furth calls it, is the kidney visceral system, which governed reproductive functions. Therefore, it was not the anatomical structures that allowed for pregnancy, but the difference in processes that allowed for the condition of pregnancy to occur.
Pregnancy
Traditional Chinese medicine's dealings with pregnancy are documented from at least the seventeenth century. According to Charlotte Furth, "a pregnancy (in the seventeenth century) as a known bodily experience emerged [...] out of the liminality of menstrual irregularity, as uneasy digestion, and a sense of fullness". These symptoms were common among other illness as well, so the diagnosis of pregnancy often came late in the term. The Canon of the Pulse, which described the use of pulse in diagnosis, stated that pregnancy was "a condition marked by symptoms of the disorder in one whose pulse is normal" or "where the pulse and symptoms do not agree". Women were often silent about suspected pregnancy, which led to many men not knowing that their wife or daughter was pregnant until complications arrived. Complications through the misdiagnosis and the woman's reluctance to speak often led to medically induced abortions. Cheng, Furth wrote, "was unapologetic about endangering a fetus when pregnancy risked a mother's well being". The method of abortion was the ingestion of certain herbs and foods. Disappointment at the loss of the fetus often led to family discord.
Postpartum
If the baby and mother survived the term of the pregnancy, childbirth was then the next step. The tools provided for birth were: towels to catch the blood, a container for the placenta, a pregnancy sash to support the belly, and an infant swaddling wrap. With these tools, the baby was born, cleaned, and swaddled; however, the mother was then immediately the focus of the doctor to replenish her qi. In his writings, Cheng places a large amount of emphasis on the Four Diagnostic methods to deal with postpartum issues and instructs all physicians to "not neglect any [of the four methods]". The process of birthing was thought to deplete a woman's blood level and qi so the most common treatments for postpartum were food (commonly garlic and ginseng), medicine, and rest. This process was followed up by a month check-in with the physician, a practice known as zuo yuezi.
Infertility
Infertility, not very well understood, posed serious social and cultural repercussions. The seventh-century scholar Sun Simiao is often quoted: "those who have prescriptions for women's distinctiveness take their differences of pregnancy, childbirth and [internal] bursting injuries as their basis." Even in contemporary fuke placing emphasis on reproductive functions, rather than the entire health of the woman, suggests that the main function of fuke is to produce children.
Once again, the kidney visceral system governs the "source Qi", which governs the reproductive systems in both sexes. This source Qi was thought to "be slowly depleted through sexual activity, menstruation and childbirth." It was also understood that the depletion of source Qi could result from the movement of an external pathology that moved through the outer visceral systems before causing more permanent damage to the home of source Qi, the kidney system. In addition, the view that only very serious ailments ended in the damage of this system means that those who had trouble with their reproductive systems or fertility were seriously ill.
According to traditional Chinese medical texts, infertility can be summarized into different syndrome types. These were spleen and kidney depletion (yang depletion), liver and kidney depletion (yin depletion), blood depletion, phlegm damp, liver oppression, and damp heat. This is important because, while most other issues were complex in Chinese medical physiology, women's fertility issues were simple. Most syndrome types revolved around menstruation, or lack thereof. The patient was entrusted with recording not only the frequency, but also the "volume, color, consistency, and odor of menstrual flow." This placed responsibility of symptom recording on the patient, and was compounded by the earlier discussed issue of female chastity and honor. This meant that diagnosing female infertility was difficult, because the only symptoms that were recorded and monitored by the physician were the pulse and color of the tongue.
Concept of disease
In general, disease is perceived as a disharmony (or imbalance) in the functions or interactions of yin, yang, qi, xuĕ, zàng-fǔ, meridians etc. and/or of the interaction between the human body and the environment. Therapy is based on which "pattern of disharmony" can be identified. Thus, "pattern discrimination" is the most important step in TCM diagnosis. It is also known to be the most difficult aspect of practicing TCM.
To determine which pattern is at hand, practitioners will examine things like the color and shape of the tongue, the relative strength of pulse-points, the smell of the breath, the quality of breathing or the sound of the voice. For example, depending on tongue and pulse conditions, a TCM practitioner might diagnose bleeding from the mouth and nose as: "Liver fire rushes upwards and scorches the Lung, injuring the blood vessels and giving rise to reckless pouring of blood from the mouth and nose." He might then go on to prescribe treatments designed to clear heat or supplement the Lung.
Disease entities
In TCM, a disease has two aspects: "bìng" and "zhèng". The former is often translated as "disease entity", "disease category", "illness", or simply "diagnosis". The latter, and more important one, is usually translated as "pattern" (or sometimes also as "syndrome"). For example, the disease entity of a common cold might present with a pattern of wind-cold in one person, and with the pattern of wind-heat in another.
From a scientific point of view, most of the disease entities (病; bìng) listed by TCM constitute symptoms. Examples include headache, cough, abdominal pain, constipation etc.
Since therapy will not be chosen according to the disease entity but according to the pattern, two people with the same disease entity but different patterns will receive different therapy. Vice versa, people with similar patterns might receive similar therapy even if their disease entities are different. This is called yì bìng tóng zhì, tóng bìng yì zhì (异病同治,同病异治; 'different diseases', 'same treatment', 'same disease', 'different treatments').
Patterns
In TCM, "pattern" (证; zhèng) refers to a "pattern of disharmony" or "functional disturbance" within the functional entities of which the TCM model of the body is composed. There are disharmony patterns of qi, xuě, the body fluids, the zàng-fǔ, and the meridians. They are ultimately defined by their symptoms and signs (i.e., for example, pulse and tongue findings).
In clinical practice, the identified pattern usually involves a combination of affected entities (compare with typical examples of patterns). The concrete pattern identified should account for all the symptoms a person has.
Six Excesses
The Six Excesses (六淫; liù yín, sometimes also translated as "Pathogenic Factors", or "Six Pernicious Influences"; with the alternative term of 六邪; liù xié, – "Six Evils" or "Six Devils") are allegorical terms used to describe disharmony patterns displaying certain typical symptoms. These symptoms resemble the effects of six climatic factors. In the allegory, these symptoms can occur because one or more of those climatic factors (called 六气; liù qì, "the six qi") were able to invade the body surface and to proceed to the interior. This is sometimes used to draw causal relationships (i.e., prior exposure to wind/cold/etc. is identified as the cause of a disease), while other authors explicitly deny a direct cause-effect relationship between weather conditions and disease, pointing out that the Six Excesses are primarily descriptions of a certain combination of symptoms translated into a pattern of disharmony. It is undisputed, though, that the Six Excesses can manifest inside the body without an external cause. In this case, they might be denoted "internal", e.g., "internal wind" or "internal fire (or heat)".
The Six Excesses and their characteristic clinical signs are:
- Wind (风; fēng): rapid onset of symptoms, wandering location of symptoms, itching, nasal congestion, "floating" pulse; tremor, paralysis, convulsion.
- Cold (寒; hán): cold sensations, aversion to cold, relief of symptoms by warmth, watery/clear excreta, severe pain, abdominal pain, contracture/hypertonicity of muscles, (slimy) white tongue fur, "deep"/"hidden" or "string-like" pulse, or slow pulse.
- Fire/Heat (火; huǒ): aversion to heat, high fever, thirst, concentrated urine, red face, red tongue, yellow tongue fur, rapid pulse. (Fire and heat are basically seen to be the same)
- Dampness (湿; shī): sensation of heaviness, sensation of fullness, symptoms of Spleen dysfunction, greasy tongue fur, "slippery" pulse.
- Dryness (燥; zào): dry cough, dry mouth, dry throat, dry lips, nosebleeds, dry skin, dry stools.
- Summerheat (暑; shǔ): either heat or mixed damp-heat symptoms.
Six-Excesses-patterns can consist of only one or a combination of Excesses (e.g., wind-cold, wind-damp-heat). They can also transform from one into another.
Typical examples of patterns
For each of the functional entities (qi, xuĕ, zàng-fǔ, meridians etc.), typical disharmony patterns are recognized; for example: qi vacuity and qi stagnation in the case of qi; blood vacuity, blood stasis, and blood heat in the case of xuĕ; Spleen qi vacuity, Spleen yang vacuity, Spleen qi vacuity with down-bearing qi, Spleen qi vacuity with lack of blood containment, cold-damp invasion of the Spleen, damp-heat invasion of Spleen and Stomach in case of the Spleen zàng; wind/cold/damp invasion in the case of the meridians.
TCM gives detailed prescriptions of these patterns regarding their typical symptoms, mostly including characteristic tongue and/or pulse findings. For example:
- "Upflaming Liver fire" (肝火上炎; gānhuǒ shàng yán): Headache, red face, reddened eyes, dry mouth, nosebleeds, constipation, dry or hard stools, profuse menstruation, sudden tinnitus or deafness, vomiting of sour or bitter fluids, expectoration of blood, irascibility, impatience; red tongue with dry yellow fur; slippery and string-like pulse.
Eight principles of diagnosis
The process of determining which actual pattern is on hand is called 辩证 (biàn zhèng, usually translated as "pattern diagnosis", "pattern identification" or "pattern discrimination"). Generally, the first and most important step in pattern diagnosis is an evaluation of the present signs and symptoms on the basis of the "Eight Principles" (八纲; bā gāng). These eight principles refer to four pairs of fundamental qualities of a disease: exterior/interior, heat/cold, vacuity/repletion, and yin/yang. Out of these, heat/cold and vacuity/repletion have the biggest clinical importance. The yin/yang quality, on the other side, has the smallest importance and is somewhat seen aside from the other three pairs, since it merely presents a general and vague conclusion regarding what other qualities are found. In detail, the Eight Principles refer to the following:
- Yin and yang are universal aspects all things can be classified under, this includes diseases in general as well as the Eight Principles' first three couples. For example, cold is identified to be a yin aspect, while heat is attributed to yang. Since descriptions of patterns in terms of yin and yang lack complexity and clinical practicality, though, patterns are usually not labeled this way anymore. Exceptions are vacuity-cold and repletion-heat patterns, who are sometimes referred to as "yin patterns" and "yang patterns" respectively.
- Exterior (表; biǎo) refers to a disease manifesting in the superficial layers of the body – skin, hair, flesh, and meridians. It is characterized by aversion to cold and/or wind, headache, muscle ache, mild fever, a "floating" pulse, and a normal tongue appearance.
- Interior (里; lǐ) refers to disease manifestation in the zàng-fǔ, or (in a wider sense) to any disease that can not be counted as exterior. There are no generalized characteristic symptoms of interior patterns, since they'll be determined by the affected zàng or fǔ entity.
- Cold (寒; hán) is generally characterized by aversion to cold, absence of thirst, and a white tongue fur. More detailed characterization depends on whether cold is coupled with vacuity or repletion.
- Heat (热; rè) is characterized by an absence of aversion to cold, a red and painful throat, a dry tongue fur and a rapid and floating pulse if it falls together with an exterior pattern. In all other cases, symptoms depend on whether heat is coupled with vacuity or repletion.
- Deficiency (虚; xū), can be further differentiated into deficiency of qi, xuě, yin and yang, with all their respective characteristic symptoms. Yin deficiency can also cause "empty-heat".
- Excess (实; shí) generally refers to any disease that cannot be identified as a deficient pattern, and usually indicates the presence of one of the Six Excesses, or a pattern of stagnation (of qi, xuě, etc.). In a concurrent exterior pattern, excess is characterized by the absence of sweating.
After the fundamental nature of a disease in terms of the Eight Principles is determined, the investigation focuses on more specific aspects. By evaluating the present signs and symptoms against the background of typical disharmony patterns of the various entities, evidence is collected whether or how specific entities are affected. This evaluation can be done
- in respect of the meridians (经络辩证; jīngluò biàn zhèng)
- in respect of qi (气血辩证,; qì xuè biàn zhèng)
- in respect of xuè (气血辩证; qì xuè biàn zhèng)
- in respect of the body fluids (津液辩证; jīnyè biàn zhèng)
- in respect of the zàng-fǔ (脏腑辩证; zàngfǔ biàn zhèng) – very similar to this, though less specific, is disharmony pattern description in terms of the Five Elements [五行辩证; wǔ xíng biàn zhèng])
There are also three special pattern diagnosis systems used in case of febrile and infectious diseases only ("Six Channel system" or "six division pattern" [六经辩证; liù jīng biàn zhèng]; "Wei Qi Ying Xue system" or "four division pattern" [卫气营血辩证; weì qì yíng xuè biàn zhèng]; "San Jiao system" or "three burners pattern" [三焦辩证; sānjiaō biàn zhèng]).
Considerations of disease causes
Although TCM and its concept of disease do not strongly differentiate between cause and effect, pattern discrimination can include considerations regarding the disease cause; this is called 病因辩证 (bìngyīn biàn zhèng, "disease-cause pattern discrimination").
There are three fundamental categories of disease causes (三因; sān yīn) recognized:
- external causes: these include the Six Excesses and "Pestilential Qi".
- internal causes: the "Seven Affects" (七情; qī qíng, sometimes also translated as "Seven Emotions") – joy, anger, brooding, sorrow, fear, fright and grief. These are believed to be able to cause damage to the functions of the zàng-fú, especially of the Liver.
- non-external-non-internal causes: dietary irregularities (especially: too much raw, cold, spicy, fatty or sweet food; voracious eating; too much alcohol), fatigue, sexual intemperance, trauma, and parasites (虫; chóng).
Diagnostics
In TCM, there are five major diagnostic methods: inspection, auscultation, olfaction, inquiry, and palpation. These are grouped into what is known as the "Four pillars" of diagnosis, which are Inspection, Auscultation/ Olfaction, Inquiry, and Palpation (望,聞,問,切).
- Inspection focuses on the face and particularly on the tongue, including analysis of the tongue size, shape, tension, color and coating, and the absence or presence of teeth marks around the edge.
- Auscultation refers to listening for particular sounds (such as wheezing).
- Olfaction refers to attending to body odor.
- Inquiry focuses on the "seven inquiries", which involve asking the person about the regularity, severity, or other characteristics of: chills, fever, perspiration, appetite, thirst, taste, defecation, urination, pain, sleep, menses, leukorrhea.
- Palpation which includes feeling the body for tender A-shi points, and the palpation of the wrist pulses as well as various other pulses, and palpation of the abdomen.
Tongue and pulse
Examination of the tongue and the pulse are among the principal diagnostic methods in TCM. Details of the tongue, including shape, size, color, texture, cracks, teeth marks, as well as tongue coating are all considered as part of tongue diagnosis. Various regions of the tongue's surface are believed to correspond to the zàng-fŭ organs. For example, redness on the tip of the tongue might indicate heat in the Heart, while redness on the sides of the tongue might indicate heat in the Liver.
Pulse palpation involves measuring the pulse both at a superficial and at a deep level at three different locations on the radial artery (Cun, Guan, Chi, located two fingerbreadths from the wrist crease, one fingerbreadth from the wrist crease, and right at the wrist crease, respectively, usually palpated with the index, middle and ring finger) of each arm, for a total of twelve pulses, all of which are thought to correspond with certain zàng-fŭ. The pulse is examined for several characteristics including rhythm, strength and volume, and described with qualities like "floating, slippery, bolstering-like, feeble, thready and quick"; each of these qualities indicates certain disease patterns. Learning TCM pulse diagnosis can take several years.
Herbal medicine
This section needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (June 2020) |  |




The term "herbal medicine" is somewhat misleading in that, while plant elements are by far the most commonly used substances in TCM, other, non-botanic substances are used as well: animal, human, fungi, and mineral products are also used. Thus, the term "medicinal" (instead of herb) may be used. A 2019 review of traditional herbal treatments found they are widely used but lacking in scientific evidence, and urged a more rigorous approach by which genuinely useful medicinals might be identified.
Raw materials
There are roughly 13,000 compounds used in China and over 100,000 TCM recipes recorded in the ancient literature. Plant elements and extracts are by far the most common elements used. In the classic Handbook of Traditional Drugs from 1941, 517 drugs were listed – out of these, 45 were animal parts, and 30 were minerals.
Animal substances
Some animal parts used include cow gallstones, hornet nests, leeches, and scorpion. Other examples of animal parts include horn of the antelope or buffalo, deer antlers, testicles and penis bone of the dog, and snake bile. Some TCM textbooks still recommend preparations containing animal tissues, but there has been little research to justify the claimed clinical efficacy of many TCM animal products.
Some compounds can include the parts of endangered species, including tiger bones and rhinoceros horn which is used for many ailments (though not as an aphrodisiac as is commonly misunderstood in the West). The black market in rhinoceros horns (driven not just by TCM but also unrelated status-seeking) has reduced the world's rhino population by more than 90 percent over the past 40 years. Concerns have also arisen over the use of pangolin scales, turtle plastron, seahorses, and the gill plates of mobula and manta rays.
Poachers hunt restricted or endangered species to supply the black market with TCM products. There is no scientific evidence of efficacy for tiger medicines. Concern over China considering to legalize the trade in tiger parts prompted the 171-nation Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) to endorse a decision opposing the resurgence of trade in tigers. Fewer than 30,000 saiga antelopes remain, which are exported to China for use in traditional fever therapies. Organized gangs illegally export the horn of the antelopes to China. The pressures on seahorses (Hippocampus spp.) used in traditional medicine is enormous; tens of millions of animals are unsustainably caught annually. Many species of syngnathid are currently part of the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species or national equivalents.
Since TCM recognizes bear bile as a treatment compound, more than 12,000 asiatic black bears are held in bear farms. The bile is extracted through a permanent hole in the abdomen leading to the gall bladder, which can cause severe pain. This can lead to bears trying to kill themselves. As of 2012, approximately 10,000 bears are farmed in China for their bile. This practice has spurred public outcry across the country. The bile is collected from live bears via a surgical procedure. As of March 2020 bear bile as ingredient of Tan Re Qing injection remains on the list of remedies recommended for treatment of "severe cases" of COVID-19 by National Health Commission of China and the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
The deer penis is believed to have therapeutic benefits according to traditional Chinese medicine. Tiger parts from poached animals include tiger penis, believed to improve virility, and tiger eyes. The illegal trade for tiger parts in China has driven the species to near-extinction because of its popularity in traditional medicine. Laws protecting even critically endangered species such as the Sumatran tiger fail to stop the display and sale of these items in open markets. Shark fin soup is traditionally regarded in Chinese medicine as beneficial for health in East Asia, and its status as an elite dish has led to huge demand with the increase of affluence in China, devastating shark populations. The shark fins have been a part of traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. Shark finning is banned in many countries, but the trade is thriving in Hong Kong and China, where the fins are part of shark fin soup, a dish considered a delicacy, and used in some types of traditional Chinese medicine.
The tortoise (freshwater turtle, guiban) and turtle (Chinese softshell turtle, biejia) species used in traditional Chinese medicine are raised on farms, while restrictions are made on the accumulation and export of other endangered species. However, issues concerning the overexploitation of Asian turtles in China have not been completely solved. Australian scientists have developed methods to identify medicines containing DNA traces of endangered species. Finally, although not an endangered species, sharp rises in exports of donkeys and donkey hide from Africa to China to make the traditional remedy ejiao have prompted export restrictions by some African countries.
Human body parts

Traditional Chinese medicine also includes some human parts: the classic Materia medica (Bencao Gangmu) describes (also criticizes) the use of 35 human body parts and excreta in medicines, including bones, fingernail, hairs, dandruff, earwax, impurities on the teeth, feces, urine, sweat, organs, but most are no longer in use.
Human placenta has been used an ingredient in certain traditional Chinese medicines, including using dried human placenta, known as "Ziheche", to treat infertility, impotence and other conditions. The consumption of the human placenta is a potential source of infection.
Traditional categorization
The traditional categorizations and classifications that can still be found today are:
- The classification according to the Four Natures (四气; sì qì): hot, warm, cool, or cold (or, neutral in terms of temperature) and hot and warm herbs are used to treat cold diseases, while cool and cold herbs are used to treat heat diseases.
- The classification according to the Five Flavors, (五味; wǔ wèi, sometimes also translated as Five Tastes): acrid, sweet, bitter, sour, and salty. Substances may also have more than one flavor, or none (i.e., a "bland" flavor). Each of the Five Flavors corresponds to one of zàng organs, which in turn corresponds to one of the Five Phases. A flavor implies certain properties and therapeutic actions of a substance; e.g., saltiness drains downward and softens hard masses, while sweetness is supplementing, harmonizing, and moistening.
- The classification according to the meridian – more precisely, the zàng-fu organ including its associated meridian – which can be expected to be primarily affected by a given compound.
- The categorization according to the specific function mainly include: exterior-releasing or exterior-resolving, heat-clearing, downward-draining, or precipitating wind-damp-dispelling, dampness-transforming, promoting the movement of water and percolating dampness or dampness-percolating, interior-warming, qi-regulating or qi-rectifying, dispersing food accumulation or food-dispersing, worm-expelling, stopping bleeding or blood-stanching, quickening the Blood and dispelling stasis or blood-quickening, transforming phlegm, stopping coughing and calming wheezing or phlegm-transforming and cough- and panting-suppressing, Spirit-quieting, calming the liver and expelling wind or liver-calming and wind-extinguishing orifice-opening supplementing which includes qi-supplementing, blood-nourishing, yin-enriching, and yang-fortifying, astriction-promoting or securing and astringing, vomiting-inducing, and substances for external application.
Efficacy
This section needs to be updated. The reason given is: In recent years, there have been many updated systematic reviews and meta-analyses about the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine, including herbal medicine. (April 2024) |
As of 2007 there were not enough good-quality trials of herbal therapies to allow their effectiveness to be determined. A high percentage of relevant studies on traditional Chinese medicine are in Chinese databases. Fifty percent of systematic reviews on TCM did not search Chinese databases, which could lead to a bias in the results. Many systematic reviews of TCM interventions published in Chinese journals are incomplete, some contained errors or were misleading. The herbs recommended by traditional Chinese practitioners in the US are unregulated.
- A 2013 review found the data too weak to support use of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- A 2013 review found the research on the benefit and safety of CHM for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is of poor quality and cannot be relied upon to support their use.
- A 2013 Cochrane review found inconclusive evidence that CHM reduces the severity of eczema.
- The traditional medicine ginger, which has shown anti-inflammatory properties in laboratory experiments, has been used to treat rheumatism, headache and digestive and respiratory issues, though there is no firm evidence supporting these uses.
- A 2012 Cochrane review found no difference in mortality rate among 640 SARS patients when Chinese herbs were used alongside Western medicine versus Western medicine exclusively, although they concluded some herbs may have improved symptoms and decreased corticosteroid doses.
- A 2012 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to support the use of TCM for people with adhesive small bowel obstruction.
- A 2011 review found low quality evidence that suggests CHM improves the symptoms of Sjögren's syndrome.
- A 2011 Cochrane review found inconclusive evidence to support the use of TCM herbal medicines for treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
- A 2011 Cochrane review did not find improvement in fasting C-peptide when compared to insulin treatment for latent autoimmune diabetes in adults after 3 months. It is important to highlight that the studies available to be included in this review presented considerable flaws in quality and design.
- A 2010 review found TCM seems to be effective for the treatment of fibromyalgia but the findings were of insufficient methodological rigor.
- A 2008 Cochrane review found promising evidence for the use of Chinese herbal medicine in relieving painful menstruation, but the trials assessed were of such low methodological quality that no conclusion could be drawn about the remedies' suitability as a recommendable treatment option.
- Turmeric has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries to treat various conditions. This includes jaundice and hepatic disorders, rheumatism, anorexia, diabetic wounds, and menstrual complications. Most of its effects have been attributed to curcumin. Research that curcumin shows strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities have instigated mechanism of action studies on the possibility for cancer and inflammatory diseases prevention and treatment. It also exhibits immunomodulatory effects.
- A 2005 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence for the use of CHM in HIV-infected people and people with AIDS.
- A 2010 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to support the use of Traditional Chinese Herbal Products (THCP) in the treatment of angina.
- A 2010 Cochrane review found no evidence supporting the use of TCHM for stopping bleeding from haemorrhoids. There was some weak evidence of pain relief.
Drug research

With an eye to the enormous Chinese market, pharmaceutical companies have explored creating new drugs from traditional remedies. The journal Nature commented that "claims made on behalf of an uncharted body of knowledge should be treated with the customary skepticism that is the bedrock of both science and medicine."
There had been success in the 1970s, however, with the development of the antimalarial drug artemisinin, which is a processed extract of Artemisia annua, a herb traditionally used as a fever treatment. Artemisia annua has been used by Chinese herbalists in traditional Chinese medicines for 2,000 years. In 1596, Li Shizhen recommended tea made from qinghao specifically to treat malaria symptoms in his Compendium of Materia Medica. Researcher Tu Youyou discovered that a low-temperature extraction process could isolate an effective antimalarial substance from the plant. Tu says she was influenced by a traditional Chinese herbal medicine source, The Handbook of Prescriptions for Emergency Treatments, written in 340 by Ge Hong, which states that this herb should be steeped in cold water. The extracted substance, once subject to detoxification and purification processes, is a usable antimalarial drug – a 2012 review found that artemisinin-based remedies were the most effective drugs for the treatment of malaria. For her work on malaria, Tu received the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Despite global efforts in combating malaria, it remains a large burden for the population. Although WHO recommends artemisinin-based remedies for treating uncomplicated malaria, resistance to the drug can no longer be ignored.
Also in the 1970s Chinese researcher Zhang TingDong and colleagues investigated the potential use of the traditionally used substance arsenic trioxide to treat acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Building on his work, research both in China and the West eventually led to the development of the drug Trisenox, which was approved for leukemia treatment by the FDA in 2000.
Huperzine A, an extract from the herb, Huperzia serrata, is under preliminary research as a possible therapeutic for Alzheimer's disease, but poor methodological quality of the research restricts conclusions about its effectiveness.
Ephedrine in its natural form, known as má huáng (麻黄) in TCM, has been documented in China since the Han dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE) as an antiasthmatic and stimulant. In 1885, the chemical synthesis of ephedrine was first accomplished by Japanese organic chemist Nagai Nagayoshi based on his research on Japanese and Chinese traditional herbal medicines
Pien tze huang was first documented in the Ming dynasty.
Cost-effectiveness
A 2012 systematic review found there is a lack of available cost-effectiveness evidence in TCM.
Safety

From the earliest records regarding the use of compounds to today, the toxicity of certain substances has been described in all Chinese materiae medicae. Since TCM has become more popular in the Western world, there are increasing concerns about the potential toxicity of many traditional Chinese plants, animal parts and minerals. Traditional Chinese herbal remedies are conveniently available from grocery stores in most Chinese neighborhoods; some of these items may contain toxic ingredients, are imported into the U.S. illegally, and are associated with claims of therapeutic benefit without evidence. For most compounds, efficacy and toxicity testing are based on traditional knowledge rather than laboratory analysis. The toxicity in some cases could be confirmed by modern research (i.e., in scorpion); in some cases it could not (i.e., in Curculigo). Traditional herbal medicines can contain extremely toxic chemicals and heavy metals, and naturally occurring toxins, which can cause illness, exacerbate pre-existing poor health or result in death. Botanical misidentification of plants can cause toxic reactions in humans. The description of some plants used in TCM has changed, leading to unintended poisoning by using the wrong plants. A concern is also contaminated herbal medicines with microorganisms and fungal toxins, including aflatoxin. Traditional herbal medicines are sometimes contaminated with toxic heavy metals, including lead, arsenic, mercury and cadmium, which inflict serious health risks to consumers. Also, adulteration of some herbal medicine preparations with conventional drugs which may cause serious adverse effects, such as corticosteroids, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, and glibenclamide, has been reported.
Substances known to be potentially dangerous include Aconitum, secretions from the Asiatic toad, powdered centipede, the Chinese beetle (Mylabris phalerata), certain fungi, Aristolochia, arsenic sulfide (realgar), mercury sulfide, and cinnabar. Asbestos ore (Actinolite, Yang Qi Shi, 阳起石) is used to treat impotence in TCM. Due to galena's (litharge, lead(II) oxide) high lead content, it is known to be toxic. Lead, mercury, arsenic, copper, cadmium, and thallium have been detected in TCM products sold in the U.S. and China.
To avoid its toxic adverse effects Xanthium sibiricum must be processed. Hepatotoxicity has been reported with products containing Reynoutria multiflora (synonym Polygonum multiflorum), glycyrrhizin, Senecio and Symphytum. The herbs indicated as being hepatotoxic included Dictamnus dasycarpus, Astragalus membranaceus, and Paeonia lactiflora. Contrary to popular belief, Ganoderma lucidum mushroom extract, as an adjuvant for cancer immunotherapy, appears to have the potential for toxicity. A 2013 review suggested that although the antimalarial herb Artemisia annua may not cause hepatotoxicity, haematotoxicity, or hyperlipidemia, it should be used cautiously during pregnancy due to a potential risk of embryotoxicity at a high dose.
However, many adverse reactions are due to misuse or abuse of Chinese medicine. For example, the misuse of the dietary supplement Ephedra (containing ephedrine) can lead to adverse events including gastrointestinal problems as well as sudden death from cardiomyopathy. Products adulterated with pharmaceuticals for weight loss or erectile dysfunction are one of the main concerns. Chinese herbal medicine has been a major cause of acute liver failure in China.
The harvesting of guano from bat caves (yemingsha) brings workers into close contact with these animals, increasing the risk of zoonosis. The Chinese virologist Shi Zhengli has identified dozens of SARS-like coronaviruses in samples of bat droppings.
Acupuncture and moxibustion


Acupuncture is the insertion of needles into superficial structures of the body (skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles) – usually at acupuncture points (acupoints) – and their subsequent manipulation; this aims at influencing the flow of qi. According to TCM it relieves pain and treats (and prevents) various diseases. The US FDA classifies single-use acupuncture needles as Class II medical devices, under CFR 21.
Acupuncture is often accompanied by moxibustion – the Chinese characters for acupuncture (针灸; 針灸; zhēnjiǔ) literally meaning "acupuncture-moxibustion" – which involves burning mugwort on or near the skin at an acupuncture point. According to the American Cancer Society, "available scientific evidence does not support claims that moxibustion is effective in preventing or treating cancer or any other disease".
In electroacupuncture, an electric current is applied to the needles once they are inserted, to further stimulate the respective acupuncture points.
A recent historian of Chinese medicine remarked that it is "nicely ironic that the specialty of acupuncture – arguably the most questionable part of their medical heritage for most Chinese at the start of the twentieth century – has become the most marketable aspect of Chinese medicine." She found that acupuncture as we know it today has hardly been in existence for sixty years. Moreover, the fine, filiform needle we think of as the acupuncture needle today was not widely used a century ago. Present day acupuncture was developed in the 1930s and put into wide practice only as late as the 1960s.
Efficacy
A 2013 editorial in the American journal Anesthesia and Analgesia stated that acupuncture studies produced inconsistent results, (i.e. acupuncture relieved pain in some conditions but had no effect in other very similar conditions) which suggests the presence of false positive results. These may be caused by factors like biased study design, poor blinding, and the classification of electrified needles (a type of TENS) as a form of acupuncture. The inability to find consistent results despite more than 3,000 studies, the editorial continued, suggests that the treatment seems to be a placebo effect and the existing equivocal positive results are the type of noise one expects to see after a large number of studies are performed on an inert therapy. The editorial concluded that the best controlled studies showed a clear pattern, in which the outcome does not rely upon needle location or even needle insertion, and since "these variables are those that define acupuncture, the only sensible conclusion is that acupuncture does not work."
According to the US NIH National Cancer Institute, a review of 17,922 patients reported that real acupuncture relieved muscle and joint pain, caused by aromatase inhibitors, much better than sham acupuncture. Regarding cancer patients, the review hypothesized that acupuncture may cause physical responses in nerve cells, the pituitary gland, and the brain – releasing proteins, hormones, and chemicals that are proposed to affect blood pressure, body temperature, immune activity, and endorphin release.
A 2012 meta-analysis concluded that the mechanisms of acupuncture "are clinically relevant, but that an important part of these total effects is not due to issues considered to be crucial by most acupuncturists, such as the correct location of points and depth of needling ... [but is] ... associated with more potent placebo or context effects". Commenting on this meta-analysis, both Edzard Ernst and David Colquhoun said the results were of negligible clinical significance.
A 2011 overview of Cochrane reviews found evidence that suggests acupuncture is effective for some but not all kinds of pain. A 2010 systematic review found that there is evidence "that acupuncture provides a short-term clinically relevant effect when compared with a waiting list control or when acupuncture is added to another intervention" in the treatment of chronic low back pain. Two review articles discussing the effectiveness of acupuncture, from 2008 and 2009, have concluded that there is not enough evidence to conclude that it is effective beyond the placebo effect.
Acupuncture is generally safe when administered using Clean Needle Technique (CNT). Although serious adverse effects are rare, acupuncture is not without risk. Severe adverse effects, including very rarely death (five case reports), have been reported.
Tui na

Tui na (推拿) is a form of massage, based on the assumptions of TCM, from which shiatsu is thought to have evolved. Techniques employed may include thumb presses, rubbing, percussion, and assisted stretching.
Qigong
Qìgōng (气功; 氣功) is a TCM system of exercise and meditation that combines regulated breathing, slow movement, and focused awareness, purportedly to cultivate and balance qi. One branch of qigong is qigong massage, in which the practitioner combines massage techniques with awareness of the acupuncture channels and points.
Qi is air, breath, energy, or primordial life source that is neither matter or spirit. While Gong is a skillful movement, work, or exercise of the qi.
Forms
- Neigong: introspective and meditative
- Waigong: external energy and motion
- Donggong: dynamic or active
- Jinggong: tranquil or passive
Other therapies
Cupping
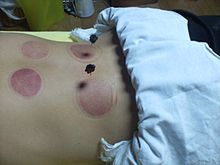
Cupping (拔罐; báguàn) is a type of Chinese massage, consisting of placing several glass "cups" (open spheres) on the body. A match is lit and placed inside the cup and then removed before placing the cup against the skin. As the air in the cup is heated, it expands, and after placing in the skin, cools, creating lower pressure inside the cup that allows the cup to stick to the skin via suction. When combined with massage oil, the cups can be slid around the back, offering "reverse-pressure massage".
Gua sha

Gua sha (刮痧; guāshā) is abrading the skin with pieces of smooth jade, bone, animal tusks or horns or smooth stones; until red spots then bruising cover the area to which it is done. It is believed that this treatment is for almost any ailment. The red spots and bruising take three to ten days to heal, there is often some soreness in the area that has been treated.
Die-da
Diē-dǎ (跌打) or Dit Da, is a traditional Chinese bone-setting technique, usually practiced by martial artists who know aspects of Chinese medicine that apply to the treatment of trauma and injuries such as bone fractures, sprains, and bruises. Some of these specialists may also use or recommend other disciplines of Chinese medical therapies if serious injury is involved. Such practice of bone-setting (正骨; 整骨) is not common in the West.
Chinese food therapy
This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2021) |
The concepts yin and yang are associated with different classes of foods, and tradition considers it important to consume them in a balanced fashion. However, there is no scientific evidence supporting such claims, nor their implied notions.
Regulations
Many governments have enacted laws to regulate TCM practice.
Australia
From 1 July 2012 Chinese medicine practitioners must be registered under the national registration and accreditation scheme with the Chinese Medicine Board of Australia and meet the Board's Registration Standards, to practice in Australia.
Canada
TCM is regulated in five provinces in Canada: Alberta, British Columbia, Ontario, Quebec, and Newfoundland & Labrador.
China (mainland)
The National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine was created in 1949, which then absorbed existing TCM management in 1986 with major changes in 1998.
China's National People's Congress Standing Committee passed the country's first law on TCM in 2016, which came into effect on 1 July 2017. The new law standardized TCM certifications by requiring TCM practitioners to (i) pass exams administered by provincial-level TCM authorities, and (ii) obtain recommendations from two certified practitioners. TCM products and services can be advertised only with approval from the local TCM authority.
Hong Kong
During British rule, Chinese medicine practitioners in Hong Kong were not recognized as "medical doctors", which means they could not issue prescription drugs, give injections, etc. However, TCM practitioners could register and operate TCM as "herbalists". The Chinese Medicine Council of Hong Kong was established in 1999. It regulates the compounds and professional standards for TCM practitioners. All TCM practitioners in Hong Kong are required to register with the council. The eligibility for registration includes a recognised 5-year university degree of TCM, a 30-week minimum supervised clinical internship, and passing the licensing exam.
Currently, the approved Chinese medicine institutions are HKU, CUHK and HKBU.
Macau
The Portuguese Macau government seldom interfered in the affairs of Chinese society, including with regard to regulations on the practice of TCM. There were a few TCM pharmacies in Macau during the colonial period. In 1994, the Portuguese Macau government published Decree-Law no. 53/94/M that officially started to regulate the TCM market. After the sovereign handover, the Macau S.A.R. government also published regulations on the practice of TCM. In 2000, Macau University of Science and Technology and Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine established the Macau College of Traditional Chinese Medicine to offer a degree course in Chinese medicine.
In 2022, a new law regulating TCM, Law no. 11/2021, came into effect. The same law also repealed Decree-Law no. 53/94/M.
Indonesia

All traditional medicines, including TCM, are regulated by Indonesian Minister of Health Regulation of 2013 on traditional medicine. Traditional medicine license (Surat Izin Pengobatan Tradisional – SIPT) is granted to the practitioners whose methods are recognized as safe and may benefit health. The TCM clinics are registered but there is no explicit regulation for it. The only TCM method which is accepted by medical logic and is empirically proofed is acupuncture. The acupuncturists can get SIPT and participate in health care facilities.
Japan

Under modern Japanese medical law, it is possible for doctors to perform acupuncture and massage, but because there is a separate law regarding acupuncture and massage, these treatments are mainly performed by massage therapists, acupuncturists, and moxibustion practitioners.
Korea

Under the Medical Service Act (의료법/醫療法), an oriental medical doctor, whose obligation is to administer oriental medical treatment and provide guidance for health based on oriental medicine, shall be treated in the same manner as a medical doctor or dentist.
The Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine is the top research center of TCM in Korea.
Malaysia
The Traditional and Complementary Medicine Bill was passed by parliament in 2012 establishing the Traditional and Complementary Medicine Council to register and regulate traditional and complementary medicine practitioners, including TCM practitioners as well as other traditional and complementary medicine practitioners such as those in traditional Malay medicine and traditional Indian medicine.
Netherlands

There are no specific regulations in the Netherlands on TCM; TCM is neither prohibited nor recognised by the government of the Netherlands. Chinese herbs as well as Chinese herbal products that are used in TCM are classified as foods and food supplements, and these Chinese herbs can be imported into the Netherlands as well as marketed as such without any type registration or notification to the government.
Despite its status, some private health insurance companies reimburse a certain amount of annual costs for acupuncture treatments, this depends on one's insurance policy, as not all insurance policies cover it, and if the acupuncture practitioner is or is not a member of one of the professional organisations that are recognised by private health insurance companies. The recognized professional organizations include the Nederlandse Vereniging voor Acupunctuur (NVA), Nederlandse Artsen Acupunctuur Vereniging (NAAV), ZHONG, (Nederlandse Vereniging voor Traditionele Chinese Geneeskunde), Nederlandse Beroepsvereniging Chinese Geneeswijzen Yi (NBCG Yi), and Wetenschappelijke Artsen Vereniging voor Acupunctuur in Nederland (WAVAN).
New Zealand
Although there are no regulatory standards for the practice of TCM in New Zealand, in the year 1990, acupuncture was included in the Governmental Accident Compensation Corporation (ACC) Act. This inclusion granted qualified and professionally registered acupuncturists to provide subsidised care and treatment to citizens, residents, and temporary visitors for work or sports related injuries that occurred within and upon the land of New Zealand. The two bodies for the regulation of acupuncture and attainment of ACC treatment provider status in New Zealand are Acupuncture NZ and The New Zealand Acupuncture Standards Authority.
Singapore
The TCM Practitioners Act was passed by Parliament in 2000 and the TCM Practitioners Board was established in 2001 as a statutory board under the Ministry of Health, to register and regulate TCM practitioners. The requirements for registration include possession of a diploma or degree from a TCM educational institution/university on a gazetted list, either structured TCM clinical training at an approved local TCM educational institution or foreign TCM registration together with supervised TCM clinical attachment/practice at an approved local TCM clinic, and upon meeting these requirements, passing the Singapore TCM Physicians Registration Examination (STRE) conducted by the TCM Practitioners Board.
In 2024, Nanyang Technological University will offer the four-year Bachelor of Chinese Medicine programme, which is the first local programme accredited by the Ministry of Health.
Taiwan

In Taiwan, TCM practitioners are physicians and are regulated by the Physicians Act. They possess the authority to independently diagnose medical conditions, issue prescriptions, dispense Traditional Chinese Medicine, and prescribe a variety of diagnostic tests including X-rays, ECG, and blood and urine test.
Under current law, those who wish to qualify for the Chinese medicine exam must have obtained a 7-year university degree in TCM.
The National Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, established in 1963, is the largest Chinese herbal medicine research center in Taiwan.
United States
As of July 2012, only six states lack legislation to regulate the professional practice of TCM: Alabama, Kansas, North Dakota, South Dakota, Oklahoma, and Wyoming. In 1976, California established an Acupuncture Board and became the first state licensing professional acupuncturists.
See also
- Compendium of Materia Medica
- Huangdi Neijing
- American Journal of Chinese Medicine
- The body in traditional Chinese medicine
- Capsicum plaster
- Chinese classic herbal formula
- Chinese food therapy
- Chinese herbology
- Chinese Ophthalmology
- Chinese patent medicine
- Guizhentang Pharmaceutical company
- Hallucinogenic plants in Chinese herbals
- HIV/AIDS and traditional Chinese medicine
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Hua Tuo
- Li Shizhen
- List of branches of alternative medicine
- List of topics characterized as pseudoscience
- List of traditional Chinese medicines
- Medicinal mushrooms
- Pharmacognosy
- Public health in the People's Republic of China
- Qingdai
- Qiu Li Gao
- Snake farm
- Sun Simiao
- Tao Hongjing
- Taoist diet
- Traditional Korean medicine
- Traditional Mongolian medicine
- Traditional Vietnamese medicine
- Traditional Tibetan medicine
- Traditional Indian medicine
- Turtle farming
- Xingqi (circulating breath)
- Zhang Jiegu
Notes
- ^ Singh & Ernst (2008) stated, "Scientists are still unable to find a shred of evidence to support the existence of meridians or Ch'i", "The traditional principles of acupuncture are deeply flawed, as there is no evidence at all to demonstrate the existence of Ch'i or meridians" and "Acupuncture points and meridians are not a reality, but merely the product of an ancient Chinese philosophy".
- ^ 元气; 元氣; yuánqì, also known as "true" qi (真气; 真氣; zhēnqì) or "original" qi (原气; 原氣; yuánqì).
References
Citations
- ^ Eigenschink, Michael; Dearing, Lukas; Dablander, Tom E.; Maier, Julian; Sitte, Harald H. (May 2020). "A critical examination of the main premises of Traditional Chinese Medicine". Wiener klinische Wochenschrift. 132 (9–10): 260–273. doi:10.1007/s00508-020-01625-w. PMC 7253514. PMID 32198544.
- ^ "Hard to swallow". Nature. 448 (7150): 105–6. July 2007. Bibcode:2007Natur.448S.105.. doi:10.1038/448106a. PMID 17625521.
Constructive approaches to divining the potential usefulness of traditional therapies are to be welcomed. But it seems problematic to apply a brand new technique, largely untested in the clinic, to test the veracity of traditional Chinese medicine, when the field is so fraught with pseudoscience. In the meantime, claims made on behalf of an uncharted body of knowledge should be treated with the customary skepticism that is the bedrock of both science and medicine.
- ^ Andrews (2013b), pp. 10–17.
- ^ "No, Traditional Chinese Medicine Has Not Been Vindicated by Science". Office for Science and Society. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ Lei (2014), pp. 97–120.
- ^ Taylor (2005), pp. 30–36.
- ^ "The World Health Organization Has a Pseudoscience Problem". Office for Science and Society. Retrieved 28 June 2024.
- ^ "中醫的發明和國族認同有關係?文化大革命對「傳統中醫學」的影響". 故事 StoryStudio. 7 April 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ Levinovitz A (22 October 2013). "Chairman Mao Invented Traditional Chinese Medicine". Slate. Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ Taylor (2005), pp. 138–141.
- ^ Huangdi Neijing: A Synopsis with Commentaries. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Press. 3 November 2010. ISBN 978-962-996-927-1. Archived from the original on 11 November 2023. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- ^ Barrett S (12 January 2011). "Be Wary of Acupuncture, Qigong, and 'Chinese Medicine'". Archived from the original on 2 June 2018. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ^ Novella S (25 January 2012). "What Is Traditional Chinese Medicine?". Science-based Medicine. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 14 April 2014.
- ^ "As China pushes traditional medicine globally, illegal wildlife trade flourishes". Reuters. 28 March 2019. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021.
- ^ Xiaoyu, Wang (10 February 2023). "Campaign cracks down on illegal wildlife trade". China Daily.
- ^ "Chinese authorities cracked down on nearly 12,000 wildlife crime cases in three months". Traffic. 10 August 2022.
- ^ J A Jewell and Sheila Hillier (2017). "Kan-Wen Ma". British Medical Journal. 356.
- ^ Johnson (2021).
- ^ Sivin (1987), p. 198.
- ^ Hinrichs (2005), p. 3859.
- ^ Leslie, Charles. "Medicine". In Embry, Ainslee (ed.). Encyclopedia of Asian History. Vol. 2. pp. 521–522.
- ^ Leung AY (2006). "Traditional toxicity documentation of Chinese Materia Medica--an overview". Toxicologic Pathology. 34 (4): 319–26. doi:10.1080/01926230600773958. PMID 16787890. S2CID 8301501.
- ^ Unschuld PU (1985). Medicine in China: A History of Ideas. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-05023-5.
- ^ Peng B, 彭邦炯, eds. (2008). Jiaguwen yixue ziliao: shiwen kaobian yu yanjiu 甲骨文医学资料: 释文考辨与研究 [Medical data in the oracle bones: translations, philological analysis, and research]. Beijing: Renmin weisheng chubanshe. ISBN 978-7-117-09270-8.
- ^ Lu GD, Needham J (2002). Celestial Lancets: A History and Rationale of Acupuncture and Moxa. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-700-71458-2.
- ^ Harper D (1998). Early Chinese Medical Literature: The Mawangdui Medical Manuscripts. London and New York: Kegan Paul International. ISBN 978-0-7103-0582-4.
- ^ Epler DC (1980). "Bloodletting in early Chinese medicine and its relation to the origin of acupuncture". Bulletin of the History of Medicine. 54 (3): 337–67. PMID 6998524.
- ^ Liao Y, 廖育群 (1991). "Qin Han zhi ji zhenjiu liaofa lilun de jianli" 秦漢之際鍼灸療法理論的建立 [The formation of the theory of acumoxa therapy in the Qin and Han periods]. Ziran Kexue Yanjiu 自然科學研究 (Research in the Natural Sciences). 10: 272–79.
- ^ Sivin N (1993). "Huang-ti nei-ching" 黃帝內經. In Loewe M (ed.). Early Chinese Texts: A Bibliographical Guide. Los Angeles and Berkeley: Institute for East Asian Studies, University of California, Berkeley. pp. 196–215. ISBN 978-1-55729-043-4.
- ^ Liu (2019).
- ^ Sivin N (1987). Traditional Medicine in Contemporary China. Ann Arbor: Center for Chinese Studies, University of Michigan. ISBN 978-0-89264-074-4.
- ^ Ergil MC, Ergil KV (2009). Pocket Atlas of Chinese Medicine. Stuttgart: Thieme. ISBN 978-3-13-141611-7. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ Goldschmidt A (2009). The Evolution of Chinese Medicine: Song Dynasty, 960–1200. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-42655-8.
- ^ 《难经》在线阅读_【中医宝典】. zhongyibaodian.com. Archived from the original on 14 July 2019. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ^ 顾观光 (August 2007). 神农本草经. 哈尔滨出版社. ISBN 9787806999752. Archived from the original on 14 July 2019. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ^ Shen Nong Ben Cao Ling (The Divine Farmers Materia Medica) archive.org
- ^ Bushak, Lecia (21 March 2016). "A Brief History Of Vaccines: From Medieval Chinese 'Variolation' To Modern Vaccination". Medical Daily. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 16 April 2021.
- ^ Elizabeth Sinn (2011). Power and Charity: A Chinese Merchant Elite in Colonial Hong Kong. Hong Kong Univ. Press. pp. x, 141.
- ^ "POWDER WITH ARSENIC". The Straits Times. 9 November 1935. p. 13.
- ^ Tan, Jamie Y. L. (2023). The founding of Kwong Wai Shiu free hospital: reconciling modernity and tradition in healthcare in Singapore between the 1890s to 1911 (Master's thesis ed.). Nanyang Technological University, Singapore. doi:10.32657/10356/179855. hdl:10356/179855.
- ^ "Gushi.tw" 中醫的發明和國族認同有關係?文化大革命對「傳統中醫學」的影響 | 故事. gushi.tw (in Chinese (Taiwan)). 7 April 2019. Archived from the original on 13 June 2019.
- ^ Cheng, Wenting (2023). China in Global Governance of Intellectual Property: Implications for Global Distributive Justice. Palgrave Socio-Legal Studies series. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 214. ISBN 978-3-031-24369-1.
- ^ Cheung, Felix (December 2011). "TCM: Made in China". Nature. 480 (7378): S82 – S83. Bibcode:2011Natur.480S..82C. doi:10.1038/480S82a. PMID 22190085. S2CID 600909.
- ^ Cyranoski, David (November 2017). "China to roll back regulations for traditional medicine despite safety concerns". Nature. 551 (7682): 552–553. Bibcode:2017Natur.551..552C. doi:10.1038/nature.2017.23038. PMID 29189784. S2CID 4464138.
- ^ Dyer, Owen (9 June 2020). "Beijing proposes law to ban criticism of traditional Chinese medicine". BMJ. 369: m2285. doi:10.1136/bmj.m2285. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 32518070.
- ^ Liangzi, Sun (2 December 2020). "北京中医药条例通过 禁止诋毁中医药条款被删除 (Beijing Regulation on Traditional Chinese Medicine passed, provision prohibiting smearing of TCM removed)". Caixin. Archived from the original on 20 June 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2024.
- ^ 香港與中國: 歷史文獻資料彙編, 第1集. Hong Kong: 廣角鏡出版社. 1981. p. 164. ISBN 978-9622260160.
- ^ Ho, Polly L H (December 2002). "Agenda-Setting for the Regulation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Hong Kong". Asian Journal of Public Administration. 24 (2): 257–286. doi:10.1080/02598272.2002.10800403. S2CID 155221420.
- ^ "About Us". Tung Wah Group of Hospitals. Archived from the original on 4 March 2019. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ^ Dudovskiy J (24 March 2014). "Historical evolution of Chinese Healthcare System". Business Research Methodology. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ "Coverpage - MMIS" 粵共研究中藥替代西藥用途. Wah Kiu Yat Po (in Chinese). 13 May 1959. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ^ Furth C (1999). A Flourishing Yin: Gender in China's Medical History, 960–1665. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- ^ Sivin (1988).
- ^ Unschuld (2018), p. xi.
- ^ Unschuld (1988), p. 647.
- ^ Shang A, Huwiler K, Nartey L, Jüni P, Egger M (October 2007). "Placebo-controlled trials of Chinese herbal medicine and conventional medicine comparative study" (PDF). International Journal of Epidemiology. 36 (5): 1086–92. doi:10.1093/ije/dym119. PMID 17602184.
- ^ Singh & Ernst 2008, p. 72
- ^ Singh & Ernst 2008, p. 107
- ^ Singh & Ernst 2008, p. 387
- ^ "The World Health Organization's decision about traditional Chinese medicine could backfire". Nature. 570 (7759): 5. 5 June 2019. Bibcode:2019Natur.570Q...5.. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-01726-1. PMID 31165792. S2CID 174809790.
- ^ "The World Health Organization Gives the Nod to Traditional Chinese Medicine. Bad Idea - Scientific American". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 9 January 2022.
- ^ Hunt, Katie (26 May 2019). "Chinese medicine gains WHO acceptance but it has many critics". CNN. Archived from the original on 26 March 2022. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ Zhang F, Kong LL, Zhang YY, Li SC (December 2012). "Evaluation of impact on health-related quality of life and cost effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials". Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 18 (12): 1108–20. doi:10.1089/acm.2011.0315. PMID 22924383.
- ^ Qiu J (April 2007). "China plans to modernize traditional medicine". Nature. 446 (7136): 590–1. Bibcode:2007Natur.446..590Q. doi:10.1038/446590a. PMID 17410143.
Zhang argued that TCM is a pseudoscience and should not be part of public healthcare and research
- ^ Shaw D (December 2010). "Toxicological risks of Chinese herbs". Planta Medica. 76 (17): 2012–8. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1250533. PMID 21077025.
- ^ Liu Q, Cao L, Zhu XQ (August 2014). "Major emerging and re-emerging zoonoses in China: a matter of global health and socioeconomic development for 1.3 billion". International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 25: 65–72. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2014.04.003. PMC 7110807. PMID 24858904.
- ^ "Traditional Chinese Medicine and Endangered Animals". Encyclopædia Britannica. 22 October 2007. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ Traditional Chinese Medicine, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, Traditional Chinese Medicine: An Introduction Archived 26 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bannon D (1994). "Balancing the Yang and Yin: Development and Contributions of Chinese Medicine". Asian Pacific Quarterly. 26 (2): 22–37.
- ^ "Zou Yan". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ^ Liu, Zheng-Cai (1999): "A Study of Daoist Acupuncture & Moxibustion" Archived 15 July 2022 at the Wayback Machine Blue Poppy Press, first edition. ISBN 978-1-891845-08-6
- ^ Raphals L (2017), "Chinese Philosophy and Chinese Medicine", in Zalta EN (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2017 ed.), Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University, archived from the original on 18 March 2019, retrieved 17 January 2020
- ^ Men, J. & Guo, L. (2010) "A General Introduction to Traditional Chinese Medicine" Archived 20 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine Science Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9173-1
- ^ Wiseman & Ellis (1996)
- ^ Kaptchuck, Ted J. (2000): "The Web That Has No Weaver" Archived 20 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine 2nd edition. Contemporary Books. ISBN 978-0-8092-2840-9
- ^ Aung & Chen (2007)
- ^ Deng, T. (1999): "Practical diagnosis in traditional Chinese medicine". Elsevier. 5th reprint, 2005. ISBN 978-0-443-04582-0
- ^ Maciocia, Giovanni, (1989): The Foundations of Chinese Medicine: A Comprehensive Text for Acupuncturists and Herbalists; Churchill Livingstone; ISBN 978-0-443-03980-5, p. 26
- ^ Matuk, Camillia (2006). "Seeing the Body: The Divergence of Ancient Chinese and Western Medical Illustration" (PDF). The Journal of Biocommunication. 32 (1). CiteSeerX 10.1.1.592.1410. S2CID 6336033. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 June 2010.
- ^ "There are 365 days in the year, while humans have 365 joints [or acu-points]... There are 12 channel rivers across the land, while humans have 12 channel", A Study of Daoist Acupuncture & Moxibustion, Cheng-Tsai Liu, Liu Zheng-Cai, Ka Hua, p. 40, [1] Archived 30 September 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Ross, Jeremy (1984) "Zang Fu, the organ systems of traditional Chinese medicine" Elsevier. First edition 1984. ISBN 978-0-443-03482-4
- ^ Ross, Jeremy (1984). "Zang Fu, the organ systems of traditional Chinese medicine" Elsevier. First edition 1984. ISBN 978-0-443-03482-4 pp. 12–13. "For example, [the term] Xue is used rather than Blood, since the latter implies the blood of Western medicine, with its precise parameters of biochemistry and histology. Although Xue and blood share some common attributes, fundamentally, Xue is a different concept."
- ^ Aung & Chen (2007), p. 19
- ^ Jin Z (2005). Global Technological Change: From Hard Technology to Soft Technology. Intellect Books. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-84150-124-6. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
The vacuum created by China's failure to adequately support a disciplined scientific approach to traditional Chinese medicine has been filled by pseudoscience
- ^ Williams WF (2013). "Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience: From Alien Abductions to Zone Therapy". Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience. Routledge. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-1135955229. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ Ahn, Andrew C.; Colbert, Agatha P.; Anderson, Belinda J.; Martinsen, Ørjan G.; Hammerschlag, Richard; Cina, Steve; Wayne, Peter M.; Langevin, Helene M. (May 2008). "Electrical properties of acupuncture points and meridians: A systematic review". Bioelectromagnetics. 29 (4): 245–256. doi:10.1002/bem.20403. PMID 18240287. S2CID 7001749.
- ^ Ernst E (February 2006). "Acupuncture--a critical analysis". Journal of Internal Medicine. 259 (2): 125–37. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2005.01584.x. PMID 16420542. S2CID 22052509.
- ^ Aung & Chen (2007), pp. 11–12. "氣的生理功能...(一)推動作用...(二)溫煦作用...(三)防御作用...(四)固攝作用...(五)氣化作用" [Physiological functions of qi: 1.) Function of actuation ... 2.) Function of warming ... 3.) Function of defense ... 4.) Function of containment ... 5.) Function of transformation ...]
- ^ Reninger E. "Qi (Chi): Various Forms Used in Qigong & Chinese Medicine – How Are The Major Forms Of Qi Created Within The Body?". Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2010.
- ^ "Blood from a TCM Perspective". Shen-Nong Limited. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Wiseman & Ellis (1996), p. 147
- ^ "Body Fluids (Yin Ye)". 2001–2010 by Sacred Lotus Arts. Archived from the original on 27 November 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ^ "三、津液的功能 ...(三)调节阴阳 ...(四)排泄废物 ..." [3.) Functions of the Jinye: ... 3.3.)Harmonizing yin and yang ... 3.4.)Secretion of waste products ...] As seen at: 《中医基础理论》第四章 精、气、血、津液. 第四节 津液 [Basics of TCM theory. Chapter 4: Essence, qi, blood, jinye. Section 4: jinye] (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 13 November 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ^ "津液包括各脏腑组织的正常体液和正常的分泌物,胃液、肠液、唾液、关节液等。习惯上也包括代谢产物中的尿、汗、泪等。" [The (term) jinye comprises all physiological bodily fluids of the zang-fu and tissues, and physiological secretions, gastric juice, intestinal juice, saliva, joint fluid, etc. Customarily, this also includes metabolic products like urine, sweat, tears, etc.] As seen at: 《中医基础理论》第四章 精、气、血、津液. 第四节 津液 [Basics of TCM theory. Chapter 4: Essence, qi, blood, jinye. Section 4: jinye] (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 13 November 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ^ by citation from the Huangdi Neijing's Suwen: "言人身臟腑中陰陽,則臟者為陰,腑者為陽。" [Within the human body's zang-fu, there's yin and yang; the zang are yin, the fu are yang]. As seen at: 略論臟腑表裏關係 [outline on the relationships between the zang-fu] (in Chinese). 22 January 2010. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 13 December 2010.
- ^ "Cultural China–Chinese Medicine–Basic Zang Fu Theory". Archived from the original on 14 March 2011. Retrieved 8 January 2011.
- ^ "Cultural China–Chinese Medicine–Basic Zang Fu Theory". Archived from the original on 14 March 2011. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ^ "六腑:膽、胃、小腸、大腸、膀胱、三焦;"傳化物質"。 [The Six Fu: gallbladder, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, bladder, sanjiao; "transmit and digest"] as seen at 中醫基礎理論-髒腑學說 [Basics of TCM theory–The zangfu concept] (in Chinese). 11 June 2010. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ Aung & Chen (2007), pp. 15–16
- ^ Aung & Chen (2007), p. 16
- ^ Aung & Chen (2007), p. 20
- ^ "(三)十二经脉 ...(四)奇经八脉 ..." [(3.) The Twelve Vessels ... (4.) The Extraordinary Eight Vessels ...] as seen at 经络学 [meridian theory] (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- ^ Fu S (1995). Fu Qingzhu's gynecology. Blue Poppy Press. ISBN 093618535X. OCLC 46812372.
- ^ Furth, Charlotte. A Flourishing Yin: Gender in China's Medical History, 960–1665. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999. hdl.handle.net Archived 15 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Furth C (1999). A flourishing yin: gender in Chinaʼs medical history. University of California Press. pp. 245, 250, 255. ISBN 0520208293. OCLC 955120174.
- ^ Furth C (March 1999). A Flourishing Yin: Gender in China's Medical History. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520208292.
- ^ Wang LF (2002). Diagnostic of Traditional Chinese Medicine – A newly compiled practical English-Chinese library of Traditional Chinese medicine. Shanghai university of TCM press. ISBN 7810106805.
- ^ Heller T (2012). You and Your Doctor: A Guide to a Healing Relationship, with Physicians' Insights. McFarland & Company. p. 66. ISBN 9780786462933.
- ^ Furth C (March 1999). A Flourishing Yin: Gender in China's Medical History: 960–1665. University of California Press. p. 248. ISBN 9780520208292.
- ^ Farquhar, Judith (1991). "Objects, Processes, and Female Infertility in Chinese Medicine". Medical Anthropology Quarterly. 5 (4): 370–399. doi:10.1525/maq.1991.5.4.02a00040. JSTOR 649292.
- ^ Canon of the Pulse (Maijing).
- ^ Bequeathed Writings of Master Chu.
- ^ Wu, Yi-Li, and 吳一立. "The Gendered Medical Iconography of the Golden Mirror, Yuzuan Yizong Jinjian 御纂醫宗金鑑, 1742." In Imagining Chinese Medicine, edited by Lo Vivienne, 羅維前, Barrett Penelope, Dear David, Di Lu, 蘆笛, Reynolds Lois, Yang Dolly, and 楊德秀, 111–32. Leiden; Boston: Brill, 2018. JSTOR 10.1163/j.ctvbqs6ph.12.
- ^ "Diagnosis for Pulse-Taking and Pulse Subtlety", The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Medicine – Essential Questions, WORLD SCIENTIFIC, March 2019, pp. 69–77, doi:10.1142/9789813273580_0017, ISBN 9789813273573, S2CID 241372790
- ^ Nakagawa T, Sun B, Muramatsu K (1966). Shinzoku kibun. Tōkyō: Heibonsha.
- ^ Cheng Maoxian. Yi'an (casebook). Dated 1633, but Xue Qinghu (1991) states that the original was printed in 1644
- ^ Pillsbury, Barbara L.K. (January 1978). "'Doing the month': Confinement and convalescence of Chinese women after childbirth". Social Science & Medicine. Part B: Medical Anthropology. 12 (1B): 11–22. doi:10.1016/0160-7987(78)90003-0. PMID 565536. S2CID 13414474.
- ^ Flaws, B. & Finney, D. (1996): "A handbook of TCM patterns & their treatments" Archived 20 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine Blue Poppy Press. 6th Printing 2007. ISBN 978-0-936185-70-5
- ^ Flaws, Bob (1990): "Sticking to the Point" Archived 20 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine Blue Poppy Press. 10th Printing, 2007. ISBN 978-0-936185-17-0
- ^ "Tongue Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine", Giovanni Maciocia, Eastland Press; Revised edition (June 1995)
- ^ Maciocia G (1989). The Foundations of Chinese Medicine. Churchill Livingstone.
- ^ Deadman, Peter; Al-Khafaji, Mazin (September 1994). "Some Acupuncture Points Which Treat Disorders of Blood". Journal of Chinese Medicine (46): 21–29. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ Clavey, Steven (1995): "Fluid physiology and pathology in traditional Chinese medicine". Elsevier. 2nd edition, 2003. ISBN 978-0-443-07194-2
- ^ Vickers AJ, Linde K (March 2014). "Acupuncture for chronic pain". JAMA. 311 (9): 955–6. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.285478. PMC 4036643. PMID 24595780.
- ^ Marcus & Kuchera (2004). Foundations for integrative musculoskeletal medicine: an east-west approach. North Atlantic Books. ISBN 978-1-55643-540-9. Archived from the original on 31 January 2021. Retrieved 22 March 2011. p. 159
- ^ Wiseman & Ellis (1996), pp. 80, 142
- ^ Tierra & Tierra 1998, p. 108
- ^ Cheng X (1987). Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion (1st ed.). Foreign Languages Press. ISBN 978-7-119-00378-8.
- ^ Maciocia G (2001). Tongue Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine.
- ^ Wright T, Eisenberg D (1995). Encounters with Qi: exploring Chinese medicine. New York: Norton. pp. 53–54. ISBN 978-0-393-31213-3.
- ^ "ENDANGERED AND ABUSED WILD ANIMALS & The USE OF HERBAL ALTERNATIVES TO REPLACE ANIMAL DERIVATIVES". Asian Animal Protection Network. 26 July 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Vincent AC, Foster SJ, Koldewey HJ (June 2011). "Conservation and management of seahorses and other Syngnathidae". Journal of Fish Biology. 78 (6): 1681–724. Bibcode:2011JFBio..78.1681V. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2011.03003.x. PMID 21651523. S2CID 37920910.
- ^ "The Essentials of Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine". china.org.cn. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ^ Lu, D. (2023). The Global Circulation of Chinese Materia Medica, 1700-1949: A Microhistory of the Caterpillar Fungus. Medicine and Biomedical Sciences in Modern History. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 1–294. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-24723-1. ISBN 978-3-031-24722-4. S2CID 256618310. Archived from the original on 20 November 2023. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
- ^ Wiseman N, Feng Y (2002). Introduction to English Terminology of Chinese Medicine. Paradigm Publications. ISBN 978-0912111643. Archived from the original on 31 January 2021. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- ^ Chen, K; Yu, B (1999). "Certain progress of clinical research on Chinese integrative medicine". Chinese Medical Journal. 112 (10): 934–937. PMID 11717980.
- ^ Foster, S. & Yue, C. (1992): "Herbal emissaries: bringing Chinese herbs to the West" Archived 20 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Healing Arts Press. ISBN 978-0-89281-349-0
- ^ Hesketh T, Zhu WX (July 1997). "Health in China. Traditional Chinese medicine: one country, two systems". BMJ. 315 (7100): 115–7. doi:10.1136/bmj.315.7100.115. PMC 2127090. PMID 9240055.
- ^ "Lu Feng Fang, Materia Metrica". Archived from the original on 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Leech, Acupuncture Today". Archived from the original on 5 January 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ "Scorpion, Acupuncture Todady". Archived from the original on 4 January 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ^ Still J (June 2003). "Use of animal products in traditional Chinese medicine: environmental impact and health hazards". Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 11 (2): 118–22. doi:10.1016/S0965-2299(03)00055-4. PMID 12801499.
- ^ Wiseman N, Feng Y (1998). A Practical Dictionary of Chinese Medicine (2 ed.). Paradigm Publications. p. 904. ISBN 978-0912111544. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ Facts about traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): rhinoceros horn, Encyclopædia Britannica, Facts about traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): rhinoceros horn, as discussed in rhinoceros (mammal): – Britannica Online Encyclopedia Archived 29 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Poaching for rhino horn". Save The Rhino. 20 August 2010. Archived from the original on 21 March 2016. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- ^ Larson, Rhishja (July 2010). "Rhino horn: All myth, no medicine". Archived from the original on 11 April 2015.
- ^ Davies E (13 March 2014). "'Shocking' scale of pangolin smuggling revealed". Nature News. BBC. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ Chen TH, Chang HC, Lue KY (2009). "Unregulated Trade in Turtle Shells for Chinese Traditional Medicine in East and Southeast Asia: The Case of Taiwan". Chelonian Conservation and Biology. 8 (1): 11–18. doi:10.2744/CCB-0747.1. S2CID 86821249.
- ^ "NOVA Online | Amanda Vincent". PBS. Archived from the original on 9 December 2009. Retrieved 7 December 2009.
- ^ Chou CT (2 April 2013). "Diminishing ray of hope". 101 East. Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2013.
- ^ Weirum BK (11 November 2007). "Will traditional Chinese medicine mean the end of the wild tiger?". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on 1 February 2009. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ "Rhino rescue plan decimates Asian antelopes". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- ^ Sheng X, Zhang H, Weng Q (April 2012). "Traditional Chinese medicine: China's bear farms prompt public outcry". Nature. 484 (7395): 455. Bibcode:2012Natur.484R.455S. doi:10.1038/484455c. PMID 22538598.
- ^ "We've been accused of peddling 'fake news' – so here are the facts about China's recommended use of bear bile - EIA". eia-international.org. 25 March 2020. Archived from the original on 16 May 2020. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ^ Harding A (23 September 2006). "Beijing's penis emporium". BBC News. Archived from the original on 20 April 2009. Retrieved 16 March 2009.
- ^ van Uhm DP (2016). The Illegal Wildlife Trade: Inside the World of Poachers, Smugglers and Traders (Studies of Organized Crime). Vol. 15. New York: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-42129-2. ISBN 978-3-319-42128-5. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ "2008 report from TRAFFIC". Archived from the original on 22 January 2009. Retrieved 16 March 2009.
- ^ "Shark Fin Soup: An Eco-Catastrophe?". San Francisco Chronicle. 20 January 2003. Archived from the original on 14 June 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ Radford B (9 July 2011). "Sharks Fin Soup Bans Don't Stop Strong Demand". livescience.com. Archived from the original on 14 August 2020. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ "China bans shark fin dishes at official banquets". CNN. 9 December 2013. Archived from the original on 1 May 2014. Retrieved 27 March 2014.
- ^ Dharmananda S. "Endangered Species Issues Affecting Turtles And Tortoises Used in Chinese Medicine". Archived from the original on 4 October 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2013.
- ^ DNA may weed out toxic Chinese medicine Archived 13 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine – By Carolyn Herbert – Australian Broadcasting Corporation – Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ "China's quest to buy up global supply of donkeys halted by African nations". The Independent. 30 September 2016. Archived from the original on 3 October 2017. Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- ^ Tierra L, Tierra M (1998). Chinese traditional herbal medicine. Twin Lakes, WI: Lotus Light Pub. pp. 225. ISBN 978-0-914955-32-0.
- ^ Nie, Jing-Bao (1999). "'Human Drugs' in Chinese Medicine and the Confucian View: An Interpretive Study". Confucian Bioethics. pp. 167–206. doi:10.1007/0-306-46867-0_7. ISBN 978-0-7923-5723-0.
- ^ THE HUMAN BODY AS A NEW COMMODITY, Tsuyoshi Awaya, The Review of Tokuyama, June 1999
- ^ Commodifying bodies, Nancy Scheper-Hughes, Loïc J. D. Wacquant, 2002
- ^ "Traditional Chinese medicine contains human placenta". News-Medical.Net. 8 May 2004. Archived from the original on 16 January 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Xu, L. & Wang, W. (2002) "Chinese materia medica: combinations and applications" Archived 15 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine Donica Publishing Ltd. 1st edition. ISBN 978-1-901149-02-9
- ^ Wu XY, Tang JL, Mao C, Yuan JQ, Qin Y, Chung VC (2013). "Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of traditional chinese medicine must search chinese databases to reduce language bias". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013: 812179. doi:10.1155/2013/812179. PMC 3816048. PMID 24223063.
- ^ Ma B, Guo J, Qi G, Li H, Peng J, Zhang Y, et al. (2011). Hartling L (ed.). "Epidemiology, quality and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews of traditional Chinese medicine interventions published in Chinese journals". PLOS ONE. 6 (5): e20185. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...620185M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020185. PMC 3102106. PMID 21633698.
- ^ Humber JM, Almeder RF (9 March 2013). Alternative Medicine and Ethics. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 10–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2774-6. Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ Ma CH, Lin WL, Lui SL, Cai XY, Wong VT, Ziea E, Zhang ZJ (July 2013). "Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine for benign prostatic hyperplasia: systematic review of randomized controlled trials". Asian Journal of Andrology. 15 (4): 471–82. doi:10.1038/aja.2012.173. PMC 3739225. PMID 23728585.
- ^ Su CX, Yan LJ, Lewith G, Liu JP (December 2013). "Chinese herbal medicine for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials". Clinical Otolaryngology. 38 (6): 455–73. doi:10.1111/coa.12198. PMID 24209508. S2CID 35688209.
- ^ Gu S, Yang AW, Xue CC, Li CG, Pang C, Zhang W, Williams HC (September 2013). Gu S (ed.). "Chinese herbal medicine for atopic eczema". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 9 (9): CD008642. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008642.pub2. PMC 10639001. PMID 24018636. Archived from the original on 1 August 2020. Retrieved 30 August 2017.
- ^ Leonti M, Casu L (2013). "Traditional medicines and globalization: current and future perspectives in ethnopharmacology". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 4: 92. doi:10.3389/fphar.2013.00092. PMC 3722488. PMID 23898296.
- ^ Liu X, Zhang M, He L, Li Y (October 2012). Li Y (ed.). "Chinese herbs combined with Western medicine for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10 (10): CD004882. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004882.pub3. PMC 6993561. PMID 23076910.
- ^ Suo T, Gu X, Andersson R, Ma H, Zhang W, Deng W, et al. (May 2012). Qin X (ed.). "Oral traditional Chinese medication for adhesive small bowel obstruction". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 5 (5): CD008836. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008836.pub2. PMID 22592734.
- ^ Luo H, Han M, Liu JP (March 2011). "[Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome]". Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao = Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine. 9 (3): 257–74. doi:10.3736/jcim20110306. PMID 21419078.
- ^ Liu, Zhao Lan; Liu, Jian Ping; Zhang, Anthony Lin; Wu, Qiong; Ruan, Yao; Lewith, George; Visconte, Denise (5 July 2011). Cochrane Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Group (ed.). "Chinese herbal medicines for hypercholesterolemia". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD008305. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008305.pub2. PMC 3402023. PMID 21735427.
- ^ Brophy, Sinead; Davies, Helen; Mannan, Sopna; Brunt, Huw; Williams, Rhys (7 September 2011). "Interventions for latent autoimmune diabetes (LADA) in adults". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2011 (9): CD006165. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006165.pub3. ISSN 1465-1858. PMC 6486159. PMID 21901702.
- ^ Cao H, Liu J, Lewith GT (April 2010). "Traditional Chinese Medicine for treatment of fibromyalgia: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials". Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 16 (4): 397–409. doi:10.1089/acm.2009.0599. PMC 3110829. PMID 20423209.
- ^ Zhu X, Proctor M, Bensoussan A, Wu E, Smith CA (April 2008). Zhu X (ed.). "Chinese herbal medicine for primary dysmenorrhoea". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD005288. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005288.pub3. PMID 18425916.
- ^ Gautam, Subhash C.; Gao, Xiaohua; Dulchavsky, Scott (2007). "Immunomodulation by Curcumin". The Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Curcumin in Health and Disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 595. pp. 321–341. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_14. ISBN 978-0-387-46400-8. PMID 17569218.
- ^ Liu JP, Manheimer E, Yang M (July 2005). Liu JP (ed.). "Herbal medicines for treating HIV infection and AIDS". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (3): CD003937. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003937.pub2. PMC 8759069. PMID 16034917.
- ^ Zhuo Q, Yuan Z, Chen H, Wu T (May 2010). "Traditional Chinese herbal products for stable angina". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (5): CD004468. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd004468.pub2. PMC 6718232. PMID 20464731.
- ^ Gan T, Liu YD, Wang Y, Yang J (October 2010). "Traditional Chinese Medicine herbs for stopping bleeding from haemorrhoids". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD006791. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006791.pub2. PMID 20927750.
- ^ Miller LH, Su X (September 2011). "Artemisinin: discovery from the Chinese herbal garden". Cell. 146 (6): 855–8. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.024. PMC 3414217. PMID 21907397.
- ^ "Lasker Award Rekindles Debate Over Artemisinin's Discovery | Science/AAAS". News.sciencemag.org. 29 September 2011. Archived from the original on 4 January 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2014.
- ^ Fairhurst RM, Nayyar GM, Breman JG, Hallett R, Vennerstrom JL, Duong S, et al. (August 2012). "Artemisinin-resistant malaria: research challenges, opportunities, and public health implications". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 87 (2): 231–241. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0025. PMC 3414557. PMID 22855752.
- ^ Chrubasik C, Jacobson RL (July 2010). "The development of artemisinin resistance in malaria: reasons and solutions". Phytotherapy Research. 24 (7): 1104–6. doi:10.1002/ptr.3133. PMID 20578122. S2CID 37901416.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2015". NobelPrize.org. Archived from the original on 22 April 2020. Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- ^ Rao Y, Li R, Zhang D (June 2013). "A drug from poison: how the therapeutic effect of arsenic trioxide on acute promyelocytic leukemia was discovered". Science China Life Sciences. 56 (6): 495–502. doi:10.1007/s11427-013-4487-z. PMID 23645104.
- ^ Bian Z, Chen S, Cheng C, Wang J, Xiao H, Qin H (2012). "Developing new drugs from annals of Chinese medicine". Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2: 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2011.12.007.
- ^ Yang G, Wang Y, Tian J, Liu JP (2013). Scherer RW (ed.). "Huperzine A for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials". PLOS ONE. 8 (9): e74916. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...874916Y. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074916. PMC 3781107. PMID 24086396.
- ^ Levy WO, Kalidas K, Miller NS (26 February 2010). Principles of Addictions and the Law: Applications in Forensic, Mental Health, and Medical Practice. Academic Press. pp. 307–08. ISBN 978-0-12-496736-6.
- ^ Lock (1984). East Asian Medicine in Urban Japan: Varieties of Medical Experience. University of California Press; Reprint edition. ISBN 978-0-520-05231-4.
- ^ "Galena, Acupuncture Today". Archived from the original on 12 March 2011. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ^ Bensky D (2004). Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica (3 ed.). Seattle: Eastland Press Inc. p. 1042. ISBN 978-0-939616-4-28.
- ^ Ko RJ, Greenwald MS, Loscutoff SM, Au AM, Appel BR, Kreutzer RA, et al. (January 1996). "Lethal ingestion of Chinese herbal tea containing ch'an su". The Western Journal of Medicine. 164 (1): 71–5. PMC 1303306. PMID 8779214.
- ^ Byard RW (January 2010). "A review of the potential forensic significance of traditional herbal medicines" (PDF). Journal of Forensic Sciences. 55 (1): 89–92. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.627.5612. doi:10.1111/j.1556-4029.2009.01252.x. PMID 20412155. S2CID 205768581. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
- ^ Efferth T, Kaina B (December 2011). "Toxicities by herbal medicines with emphasis to traditional Chinese medicine". Current Drug Metabolism. 12 (10): 989–96. doi:10.2174/138920011798062328. PMID 21892916.
- ^ Yuan X, Chapman RL, Wu Z (2011). "Analytical methods for heavy metals in herbal medicines". Phytochemical Analysis. 22 (3): 189–98. Bibcode:2011PChAn..22..189Y. doi:10.1002/pca.1287. PMID 21341339.
- ^ Ernst E (August 2002). "Adulteration of Chinese herbal medicines with synthetic drugs: a systematic review". Journal of Internal Medicine (Systematic Review). 252 (2): 107–13. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2796.2002.00999.x. PMID 12190885. S2CID 29077682.

- ^ "Centipede, Acupuncture Today". Acupuncturetoday.com. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ Namba T, Ma YH, Inagaki K (December 1988). "Insect-derived crude drugs in the Chinese Song dynasty". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 24 (2–3): 247–85. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(88)90157-2. PMID 3075674.
- ^ Wang XP, Yang RM (2003). "Movement disorders possibly induced by traditional chinese herbs". European Neurology. 50 (3): 153–9. doi:10.1159/000073056. PMID 14530621. S2CID 43878555.
- ^ Genuis SJ, Schwalfenberg G, Siy AK, Rodushkin I (2012). "Toxic element contamination of natural health products and pharmaceutical preparations". PLOS ONE. 7 (11): e49676. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...749676G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049676. PMC 3504157. PMID 23185404.
- ^ Wong, H.C. George (November 2004). "Mercury and Chinese herbal medicine | British Columbia Medical Journal". BCMJ. 46 (9): 442. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022.
- ^ Huang CF, Hsu CJ, Liu SH, Lin-Shiau SY (2012). "Exposure to low dose of cinnabar (a naturally occurring mercuric sulfide (HgS)) caused neurotoxicological effects in offspring mice". Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology. 2012: 254582. doi:10.1155/2012/254582. PMC 3408718. PMID 22888198.
- ^ Encyclopedic Reference of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xinrong Yang, p. 8, [2] Archived 2 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gill SK, Rieder MJ (2008). "Toxicity of a traditional Chinese medicine, Ganoderma lucidum, in children with cancer". The Canadian Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 15 (2): e275-85. PMID 18603664.
- ^ Abolaji AO, Eteng MU, Ebong PE, Brisibe EA, Dar A, Kabir N, Choudhary MI (May 2013). "A safety assessment of the antimalarial herb Artemisia annua during pregnancy in Wistar rats". Phytotherapy Research. 27 (5): 647–54. doi:10.1002/ptr.4760. PMID 22736625. S2CID 22650085.
- ^ Zhao P, Wang C, Liu W, Chen G, Liu X, Wang X, et al. (2013). Avila MA (ed.). "Causes and outcomes of acute liver failure in China". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e80991. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880991Z. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080991. PMC 3838343. PMID 24278360.
- ^ Wassenaar, T.M.; Zou, Y. (May 2020). "2019_nCoV/SARS-CoV-2: rapid classification of betacoronaviruses and identification of Traditional Chinese Medicine as potential origin of zoonotic coronaviruses". Letters in Applied Microbiology. 70 (5): 342–348. doi:10.1111/lam.13285. PMC 7165814. PMID 32060933.
- ^ Li, Wendong; Shi, Zhengli; Yu, Meng; Ren, Wuze; Smith, Craig; Epstein, Jonathan H.; Wang, Hanzhong; Crameri, Gary; Hu, Zhihong; Zhang, Huajun; Zhang, Jianhong; McEachern, Jennifer; Field, Hume; Daszak, Peter; Eaton, Bryan T.; Zhang, Shuyi; Wang, Lin-Fa (28 October 2005). "Bats Are Natural Reservoirs of SARS-Like Coronaviruses". Science. 310 (5748): 676–679. Bibcode:2005Sci...310..676L. doi:10.1126/science.1118391. PMID 16195424. S2CID 2971923. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ^ "Acupuncture – Consensus Development Conference Statement". National Institutes of Health. 5 November 1997. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ^ Novak PD, Dorland NW, Dorland WA (1995). Dorland's Pocket Medical Dictionary (25th ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. ISBN 978-0-7216-5738-7. OCLC 33123537.
- ^ "CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21". FDA US Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Archived from the original on 27 March 2019. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ^ "Moxibustion, Acupuncture Today". Acupuncturetoday.com. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ "Moxibustion". American Cancer Society. 8 March 2011. Archived from the original on 9 August 2013. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
- ^ Robertson V, Ward A, Low J, Reed A (2006). Electrotherapy explained: principles and practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-0-7506-8843-7.
- ^ Andrews (2013a), pp. 237–238.
- ^ Colquhoun D, Novella SP (June 2013). "Acupuncture is theatrical placebo" (PDF). Anesthesia and Analgesia. 116 (6): 1360–3. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e31828f2d5e. PMID 23709076. S2CID 207135491. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- ^ U.S. National Institute of Health (11 May 2006). "Complementary and Alternative Medicine: Questions and Answers About Acupuncture". National Cancer Institute. Archived from the original on 4 March 2018. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ^ Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Maschino AC, Lewith G, MacPherson H, Foster NE, et al. (October 2012). "Acupuncture for chronic pain: individual patient data meta-analysis". Archives of Internal Medicine. 172 (19): 1444–53. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3654. PMC 3658605. PMID 22965186.
- ^ Jha A (10 September 2012). "Acupuncture useful, but overall of little benefit, study shows". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 4 January 2017. Retrieved 18 December 2016.
- ^ Colquhoun, David (17 September 2012). "Re: Risks of acupuncture range from stray needles to pneumothorax, finds study". BMJ. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 10 January 2022. Reply to: Kmietowicz, Z. (7 September 2012). "Risks of acupuncture range from stray needles to pneumothorax, finds study". BMJ. 345 (sep07 2): e6060. doi:10.1136/bmj.e6060. PMID 22960463. S2CID 32788662.
- ^ Lee MS, Ernst E (March 2011). "Acupuncture for pain: an overview of Cochrane reviews". Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 17 (3): 187–9. doi:10.1007/s11655-011-0665-7. PMID 21359919. S2CID 21513259.
- ^ Rubinstein SM, van Middelkoop M, Kuijpers T, Ostelo R, Verhagen AP, de Boer MR, et al. (August 2010). "A systematic review on the effectiveness of complementary and alternative medicine for chronic non-specific low-back pain". European Spine Journal. 19 (8): 1213–28. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1356-3. PMC 2989199. PMID 20229280.
- ^ Singh S, Ernst EE (2008). "The Truth about Acupuncture". Trick or treatment: The undeniable facts about alternative medicine. W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 103–06. ISBN 978-0-393-06661-6.
"These initial conclusions have generally been disappointing for acupuncturists: They provide no convincing evidence that real acupuncture is significantly more effective than placebo." (p. 104)
- ^ Madsen MV, Gøtzsche PC, Hróbjartsson A (January 2009). "Acupuncture treatment for pain: systematic review of randomised clinical trials with acupuncture, placebo acupuncture, and no acupuncture groups". BMJ. 338: a3115. doi:10.1136/bmj.a3115. PMC 2769056. PMID 19174438.
- ^ Xu S, Wang L, Cooper E, Zhang M, Manheimer E, Berman B, et al. (2013). "Adverse events of acupuncture: a systematic review of case reports". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013: 581203. doi:10.1155/2013/581203. PMC 3616356. PMID 23573135.
- ^ Ernst E, Lee MS, Choi TY (April 2011). "Acupuncture: does it alleviate pain and are there serious risks? A review of reviews". Pain. 152 (4): 755–764. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.004. PMID 21440191. S2CID 20205666.
- ^ Ernst E (2019). Alternative Medicine – A Critical Assessment of 150 Modalities. Springer. pp. 203–204. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-12601-8. ISBN 978-3-030-12600-1. S2CID 34148480.
- ^ Holland A (2000). Voices of Qi: An Introductory Guide to Traditional Chinese Medicine. North Atlantic Books. ISBN 978-1-55643-326-9.
- ^ Silva LM, Schalock M, Ayres R, Bunse C, Budden S (2009). "Qigong massage treatment for sensory and self-regulation problems in young children with autism: a randomized controlled trial" (PDF). The American Journal of Occupational Therapy. 63 (4): 423–32. doi:10.5014/ajot.63.4.423. PMID 19708471.
- ^ Silva LM, Schalock M, Gabrielsen K (2011). "Early intervention for autism with a parent-delivered Qigong massage program: a randomized controlled trial" (PDF). The American Journal of Occupational Therapy. 65 (5): 550–9. doi:10.5014/ajot.2011.000661. PMID 22026323.
- ^ Chen N (2003). Breathing Spaces. Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231128056.
- ^ "What is Cupping? Here's What You Need to Know". 8 August 2016. Archived from the original on 23 January 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2018.
- ^ "GuaSha Treatment of Disease". Tcmwell.com. Archived from the original on 2 July 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ "Chinese Medicine Board of Australia – Registration". Chinese Medicine Board of Australia. Archived from the original on 24 October 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- ^ "CTCMA". College of Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioners and Acupuncturists of British Columbia. Archived from the original on 14 October 2012. Retrieved 25 May 2013.
- ^ "Traditional Chinese Medicine Act, 2006". S.O. 2006, c. 27. 24 July 2014. Archived from the original on 23 May 2010. Retrieved 4 June 2014.
- ^ State Council of the People's Republic of China (20 July 1986). 国务院关于成立国家中医管理局的通知(国发〔1986〕79号) [State Countil notification on establishing the NATCM (SC [1986] 79)]. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China (25 June 1998). 国务院办公厅关于印发国家中医药管理局职能配置内设机构和人员编制规定的通知(国办发〔1998〕95号) [State Office notification on provisions for nstitutions and staffing of the NATCM (SO [1998] 95)]. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ "China passes first law on traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)". WebMD China. 28 December 2016. Archived from the original on 28 August 2018. Retrieved 28 August 2018.
- ^ "香港执业中医的概况". 央视国际. 24 August 2004. Archived from the original on 6 June 2021. Retrieved 1 June 2021.
- ^ The Chinese Medicine Council of Hong Kong Archived 11 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine Hong Kong Registered the Chinese Medicine Practitioner licensure requirements
- ^ "3 Institutions offering Chinese Medicine Courses In Hongkong". Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ^ "澳门的高等中医药教育". 世界中医药教育. 19 April 2013. Archived from the original on 6 June 2021. Retrieved 1 June 2021.
- ^ "Lei n.º 11/2021" (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 8 January 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2022 – via Imprensa Oficial.
- ^ "Special Report – Traditional Chinese Medicine – Breathing a new life". 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 24 February 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2022 – via Macau Business.
- ^ "KEPUTUSAN MENTERI KESEHATAN REPUBLIK INDONESIA" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 January 2022.
- ^ Cheta Nilawaty dan Rini Kustiati. 13 August 2012. TEMPO, Belum Ada Aturan Soal Klinik Pengobatan Cina Archived 19 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine. (in Indonesian)
- ^ "・あん摩マツサージ指圧師、はり師、きゆう師等に関する法律(◆昭和22年12月20日法律第217号)". www.mhlw.go.jp (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 14 August 2023. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "MEDICAL SERVICE ACT | KOREAN LAW INFORMATION CENTER | LAW SEARCH". www.law.go.kr. Archived from the original on 28 January 2023. Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- ^ "Traditional and Complementary Medicine (T&CM) Act [What Should You Know?]" (PDF). Traditional and Complementary Medicine Division. Ministry of Health, Malaysia. 2015. p. 10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2019. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- ^ CAM Regulation admin (31 December 2012). "Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the Netherlands". Norway's National Research Center in Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Archived from the original on 30 March 2020. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Nederlandse Vereniging voor Traditionele Chinese Geneeskunde (ZHONG) - Dutch Association of Chinese Traditional Medicine". European Traditional Chinese Medicine Association (ETCMA). 2020. Archived from the original on 30 March 2020. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Acupunctuur (2020)". Zorgwijzer (in Dutch). 2020. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Home". Acupuncture NZ. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ "NZASA - Home". nzasa.org. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ "Accident Compensation Act 2001 No 49 (as at 01 August 2020), Public Act Contents – New Zealand Legislation". www.legislation.govt.nz. Archived from the original on 25 October 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ "Registration Requirements for the Registration of TCM Physicians". Archived from the original on 30 July 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ^ "NTU to offer its own Chinese Medicine degree accredited by Health Ministry's TCM board". CNA. Archived from the original on 27 December 2023. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ^ "中醫學系畢業之中醫師自即日起得執行醫事檢驗、普通放射檢查及靜止狀態心電圖等權限。" (in Chinese (Taiwan)). National Union of Chinese Medical Doctors' Association, R.O.C. 27 December 2017. Archived from the original on 23 February 2024. Retrieved 23 February 2024.
- ^ "Physicians Act - Article Content - Laws & Regulations Database of The Republic of China (Taiwan)". law.moj.gov.tw. Archived from the original on 27 January 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ "Origin and the Past History". www.nricm.edu.tw. Archived from the original on 27 January 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ "A Consumer's Guide to Acupuncture and Asian Medicine - Acupuncture Board". Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 8 July 2012. California Acupuncture Board.
Sources
- Andrews, Bridie (2013a). "The Republic of China". In Hinrichs, T. J.; Barnes, Linda L. (eds.). Chinese Medicine and Healing: An Illustrated History. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674047372. Archived from the original on 21 November 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- ———— (2013b). The Making of Modern Chinese Medicine. Vancouver, BC: UBC Press. ISBN 978-0774824323.
- Aung SK, Chen WP (2007). Clinical introduction to medical acupuncture. Thieme Mecial Publishers. ISBN 978-1-58890-221-4.
- Borowy, Iris, ed. (2009). Uneasy Encounters: The Politics of Medicine and Health in China, 1900-1937. Frankfurt am Maim; New York, NY: Peter Lang. ISBN 9783631578032. Archived from the original on 19 March 2022. Retrieved 11 July 2021.
- Hinrichs, T. J. (2005). "Healing and Medicine in China". In Jones, Lindsay (ed.). Healing and Medicine. Vol. 6. Detroit, MI: Macmillan Reference USA. pp. 3859–3864.
- Hinrichs, T. J.; Barnes, Linda L., eds. (2013). Chinese Medicine and Healing: An Illustrated History. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674047372. Archived from the original on 21 November 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- Johnson, Ian (2021). "Chinese Medicine in the Covid Wards". New York Review of Books. 68 (17). Archived from the original on 9 March 2022. Review of Liu Lihong Classical Chinese Medicine (below). Also free online at China File Chinese Medicine in Covid Wards Archived 15 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine.
- Lei, Sean Xianglin (2014). Neither Donkey nor Horse: Medicine in the Struggle over China's Modernity. Chicago: University of Chicago. ISBN 9780226169880.
- Novella S (25 January 2012). "What Is Traditional Chinese Medicine?". Science-Based Medicine. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 14 April 2014.
- Singh S, Ernst E (2008). Trick or Treatment: Alternative Medicine on Trial. London: Bantam. ISBN 978-0593061299.
- Sivin, Nathan (1988). "Science and Medicine in Imperial China—the State of the Field". The Journal of Asian Studies. 47 (1): 41–90. doi:10.2307/2056359. JSTOR 2056359. PMID 11617269. S2CID 26443679.
- Taylor, Kim (2005). Chinese Medicine in Early Communist China, 1945-63 A Medicine of Revolution. London, England; New York, NY: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 041534512X.
- Unschuld, Paul U. (1985). Medicine in China: A History of Ideas. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520266131.
- —— (1988). "[Review] Liu Yanchi. The Essential Book of Traditional Chinese Medicine, trans. Fang Tingyu and Chen Laidi, vol. 1, "Theory", ed. Kathleen Vian and Peter Eckman". Bulletin of the History of Medicine. 62 (4): 647–649. JSTOR 44443097.
- Watt, John R. (2014). Saving Lives in Wartime China: How Medical Reformers Built Modern Healthcare Systems Amid War and Epidemics, 1928-1945. Boston;Leiden: Brill. ISBN 9789004256453.
- Wiseman N, Ellis A (1996). Fundamentals of Chinese medicine. Paradigm Publications. ISBN 978-0-912111-44-5. Archived from the original on 13 April 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2020.
- Xu, Juncai; Xia, Zhijie (2019). "Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) – Does Its Contemporary Business Booming and Globalization Really Reconfirm Its Medical Efficacy & Safety?". Medicine in Drug Discovery. 1: 100003. doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2019.100003. S2CID 198835183.
Further reading
- WHO traditional medicine strategy: 2014-2023. World Health Organization. 2013. hdl:10665/92455. ISBN 9789241506090. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- Baran GR, Kiana MF, Samuel SP (2014). "Chapter 2: Science, Pseudoscience, and Not Science: How Do They Differ?". Healthcare and Biomedical Technology in the 21st Century. Springer. pp. 19–57. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8541-4_2. ISBN 978-1-4614-8540-7.
- Barnes, Linda L. (2005). Needles, Herbs, Gods, and Ghosts: China, Healing, and the West to 1848. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674018729. Shows early use of Chinese medicine not always perceived as "Chinese."
- Baum, Emily (2020). "Medicine and Public Health in Twentieth-Century China: Histories of Modernization and Change". History Compass. 18 (7). doi:10.1111/hic3.12616. S2CID 225622823.
- Liu, Lihong (2019). Classical Chinese Medicine. Translated by Weiss, Gabriel; Henry Buchtel; Sabine Wilms. Shatin, NT Hong Kong: Chinese University of Hong Kong Press; distributed by Columbia University Press. ISBN 9789882370579.
- Lloyd, G. E. R.; Sivin, Nathan (2002). The Way and the Word: Science and Medicine in Early China and Greece. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300092970.
- Lo, Vivienne; Stanley-Baker, Michael, eds. (2022), Routledge Handbook of Chinese Medicine, New York: Routledge, ISBN 9780415830645 Online Open Access. 51 articles on history of Chinese medicine; called "impressive and essential" for latest scholarship and trustworthy bibliographic sources. "(Review) H-Sci-Med-Tech, July 2023.
- McGrew, Roderick. Encyclopedia of Medical History (1985), brief history on pp. 56–59
- Needham J (2000). Sivin N (ed.). Part VI: Medicine. Science and Civilisation in China. Vol. 6, Biology and Biological Technology. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-63262-1. OCLC 163502797.
- Palmer, James (13 June 2013), "Do Some Harm", Aeon
- Raphals, Lisa (Winter 2020), "Chinese Philosophy and Chinese Medicine", in Zalta, Edward N. (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University
- Shelton, Tamara Venit (2019). Herbs and Roots: A History of Chinese Doctors in the American Medical Marketplace. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 9780300249408.
- Unschuld, Paul (1986). Nan-Ching: The Classic of Difficult Issues. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520053724.
- —— (1986a). Medicine in China: A History of Pharmaceutics. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520050259.
- —— (2000). Medicine in China: Historical Artifacts and Images. Munich: Prestel. ISBN 9783791321493.
- —— (2018). Traditional Chinese Medicine: Heritage and Adaptation [Traditionelle chinesische Medizin (2013)]. Translated by Bridie J. Andrews. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231175005.
External links
- Medicinal Plant Images Database—School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University (in Chinese)
- Chinese Medicine Specimen Database—School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University (in Chinese)
- Literary Review Compilation on Traditional Chinese Medicine, PDF, 133 pages; compiled by the Association Québécoise des Thérapeutes Naturels (AQTN)

