Turkic Cuisines
According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia, potentially in Altai-Sayan region, Mongolia or Tuva. Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers; they later became nomadic pastoralists. Early and medieval Turkic groups exhibited a wide range of both East Asian and West-Eurasian physical appearances and genetic origins, in part through long-term contact with neighboring peoples such as Iranic, Mongolic, Tocharian, Uralic and Yeniseian peoples.
Many vastly differing ethnic groups have throughout history become part of the Turkic peoples through language shift, acculturation, conquest, intermixing, adoption, and religious conversion. Nevertheless, Turkic peoples share, to varying degrees, non-linguistic characteristics like cultural traits, ancestry from a common gene pool, and historical experiences. Some of the most notable modern Turkic ethnic groups include the Altai people, Azerbaijanis, Chuvash people, Gagauz people, Kazakhs, Kyrgyz people, Turkmens, Turkish people, Tuvans, Uyghurs, Uzbeks, and Yakuts.
Etymology


The first known mention of the term Turk (Old Turkic: 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰 Türük or 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰜𐰇𐰛 Kök Türük, Chinese: 突厥, Pinyin: Tūjué < Middle Chinese *tɦut-kyat < *dwət-kuɑt, Old Tibetan: drugu) applied to only one Turkic group, namely, the Göktürks, who were also mentioned, as türüg ~ török, in the 6th-century Khüis Tolgoi inscription, most likely not later than 587 AD. A letter by Ishbara Qaghan to Emperor Wen of Sui in 585 described him as "the Great Turk Khan". The Bugut (584 CE) and Orkhon inscriptions (735 CE) use the terms Türküt, Türk and Türük.
During the first century CE, Pomponius Mela refers to the Turcae in the forests north of the Sea of Azov, and Pliny the Elder lists the Tyrcae among the people of the same area. However, English archaeologist Ellis Minns contended that Tyrcae Τῦρκαι is "a false correction" for Iyrcae Ἱύρκαι, a people who dwelt beyond the Thyssagetae, according to Herodotus (Histories, iv. 22), and were likely Ugric ancestors of Magyars. There are references to certain groups in antiquity whose names might have been foreign transcriptions of Tür(ü)k, such as Togarma, Turukha/Turuška, Turukku and so on; but the information gap is so substantial that any connection of these ancient people to the modern Turks is not possible.
The Chinese Book of Zhou (7th century) presents an etymology of the name Turk as derived from 'helmet', explaining that this name comes from the shape of a mountain where they worked in the Altai Mountains. Hungarian scholar András Róna-Tas (1991) pointed to a Khotanese-Saka word, tturakä 'lid', semantically stretchable to 'helmet', as a possible source for this folk etymology, yet Golden thinks this connection requires more data.
It is generally accepted that the name Türk is ultimately derived from the Old-Turkic migration-term 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰 Türük/Törük, which means 'created, born' or 'strong'. Turkologist Peter B. Golden agrees that the term Turk has roots in Old Turkic, yet is not convinced by attempts to link Dili, Dingling, Chile, Tele, and Tiele, which possibly transcribed *tegrek (probably meaning 'cart'), to Tujue, which transliterated to Türküt.
Scholars, including Toru Haneda, Onogawa Hidemi, and Geng Shimin believed that Di, Dili, Dingling, Chile and Tujue all came from the Turkic word Türk, which means 'powerful' and 'strength', and its plural form is Türküt. Even though Gerhard Doerfer supports the proposal that türk means 'strong' in general, Gerard Clauson points out that "the word türk is never used in the generalized sense of 'strong'" and that türk was originally a noun and meant "'the culminating point of maturity' (of a fruit, human being, etc.), but more often used as an [adjective] meaning (of a fruit) 'just fully ripe'; (of a human being) 'in the prime of life, young, and vigorous'". Hakan Aydemir (2022) also contends that Türk originally did not mean "strong, powerful" but "gathered; united, allied, confederated" and was derived from Pre-Proto-Turkic verb *türü "heap up, collect, gather, assemble".
The earliest Turkic-speaking peoples identifiable in Chinese sources are the Yenisei Kyrgyz and Xinli, located in South Siberia. Another example of an early Turkic population would be the Dingling.
In Late Antiquity itself, as well as in and the Middle Ages, the name "Scythians" was used in Greco-Roman and Byzantine literature for various groups of nomadic "barbarians" living on the Pontic-Caspian Steppe who were not related to the actual Scythians. Medieval European chroniclers subsumed various Turkic peoples of the Eurasian steppe as "Scythians". Between 400 CE and the 16th century, Byzantine sources use the name Σκύθαι (Skuthai) in reference to twelve different Turkic peoples.
In the modern Turkish language as used in the Republic of Turkey, a distinction is made between "Turks" and the "Turkic peoples" in loosely speaking: the term Türk corresponds specifically to the "Turkish-speaking" people (in this context, "Turkish-speaking" is considered the same as "Turkic-speaking"), while the term Türki refers generally to the people of modern "Turkic Republics" (Türki Cumhuriyetler or Türk Cumhuriyetleri). However, the proper usage of the term is based on the linguistic classification in order to avoid any political sense. In short, the term Türki can be used for Türk or vice versa.
List of ethnic groups
- Historical Turkic groups
- Az
- Dingling
- Bulgars
- Esegel
- Barsils
- Alat
- Basmyl
- Onogurs
- Saragurs
- Sabirs
- Shatuo
- Ongud (from Shatuo)
- Göktürks
- Oghuz Turks
- Kanglys
- Kabar
- Khazars
- Kipchaks
- Kurykans
- Kumans
- Pechenegs
- Karluks
- Tiele
- Turgesh
- Tukhsi
- Yenisei Kirghiz
- Chigils
- Toquz Oghuz
- Orkhon Uyghurs
- Yagma
- Nushibi
- Duolu
- Kutrigurs
- Utigurs
- Yabaku
- Yueban
- Bulaqs
- Xueyantuo
- Torks
- Chorni Klobuky
- Berendei
- Yemeks
- Karamanlides (partly)
- Naimans (partly)
- Keraites (partly)
- Merkits (partly)
- Uriankhai (partly)
Possible Proto-Turkic ancestry, at least partial, has been posited for Xiongnu, Huns and Pannonian Avars, as well as Tuoba and Rouran, who were of Proto-Mongolic Donghu ancestry. as well as Tatars, Rourans' supposed descendants.
Remarks
- ^ Figure combines population of Turkmen and Uzbeks only. Population estimates of Turkmenistan's minority groups often widely vary. Some sources have cast doubt on the reliability of official government data for minority population figures.
- ^ The Xueyantuo were first known as Xinli 薪犁, later Xue 薛 in the 7th century; the Yenisei Kyrgyz were first known as Gekun (鬲昆) or Jiankun (堅昆), later known as Jiegu (結骨), Hegu (紇骨), Hegusi (紇扢斯), Hejiasi (紇戛斯), Hugu (護骨), Qigu (契骨), Juwu (居勿), and Xiajiasi (黠戛斯), all being transcriptions of Kyrgyz.
- ^ Book of Wei vol. 102. quote: "悅般國 [...] 其風俗言語與高車同" translation: "Yueban nation [...] Their customs and language are the same as the Gaoche['s]"; Gaoche (高車; lit. "High-Carts") was another name of the Turkic-speaking Tiele
- ^ Merkits were always counted as a part of the Mongols within the Mongol Empire, however, some scholars proposed additional Turkic ancestry for Merkits; Christopher P. Atwood – Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire ISBN 978-0-8160-4671-3, Facts on File, Inc. 2004.
- ^ Refers to forest peoples of the North, including the Turkic-speaking Tuvans and Yakuts, and also Mongolic-speaking Altai Uriankhai. The ethnonym Uriankhai is etymologically Mongolic, compare Khalkha uria(n) "war motto" and khai, alternation of khan. Uriankhai people are possibly linked to the Wuluohun tribe of the Shiwei people, who were predominantly Mongolic-speaking.
- ^ Even though Chinese historians routinely ascribed Xiongnu origin to various nomadic peoples, such ascriptions do not necessarily indicate the subjects' exact origins; for examples, Xiongnu ancestry was ascribed to Turkic-speaking Göktürks and Tiele as well as Para-Mongolic-speaking Kumo Xi and Khitan.
Language
Distribution

The Turkic languages constitute a language family of some 30 languages, spoken across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean, to Siberia and Manchuria and through to the Middle East. Some 170 million people have a Turkic language as their native language; an additional 20 million people speak a Turkic language as a second language. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish proper, or Anatolian Turkish, the speakers of which account for about 40% of all Turkic speakers. More than one third of these are ethnic Turks of Turkey, dwelling predominantly in Turkey proper and formerly Ottoman-dominated areas of Southern and Eastern Europe and West Asia; as well as in Western Europe, Australia and the Americas as a result of immigration. The remainder of the Turkic people are concentrated in Central Asia, Russia, the Caucasus, China, and northern Iraq.
The Turkic language family was traditionally considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family. Howeover since the 1950s, a majority of linguists have rejected the proposal, after supposed cognates were found not to be valid, hypothesized sound shifts were not found, and Turkic and Mongolic languages were found to be converging rather than diverging over the centuries. Opponents of the theory proposed that the similarities are due to mutual linguistic influences between the groups concerned.
Alphabet

The Turkic alphabets are sets of related alphabets with letters (formerly known as runes), used for writing mostly Turkic languages. Inscriptions in Turkic alphabets were found in Mongolia. Most of the preserved inscriptions were dated to between 8th and 10th centuries CE.
The earliest positively dated and read Turkic inscriptions date from the 8th century, and the alphabets were generally replaced by the Old Uyghur alphabet in the East and Central Asia, Arabic script in the Middle and Western Asia, Cyrillic in Eastern Europe and in the Balkans, and Latin alphabet in Central Europe. The latest recorded use of Turkic alphabet was recorded in Central Europe's Hungary in 1699 CE.
The Turkic runiform scripts, unlike other typologically close scripts of the world, do not have a uniform palaeography as do, for example, the Gothic runiform scripts, noted for their exceptional uniformity of language and paleography. The Turkic alphabets are divided into four groups, the best known of which is the Orkhon version of the Enisei group. The Orkhon script is the alphabet used by the Göktürks from the 8th century to record the Old Turkic language. It was later used by the Uyghur Empire; a Yenisei variant is known from 9th-century Kyrgyz inscriptions, and it has likely cousins in the Talas Valley of Turkestan and the Old Hungarian script of the 10th century. Irk Bitig is the only known complete manuscript text written in the Old Turkic script.
History
| History of the Turkic peoples pre–14th century |
|---|
 |
Origins
The origins of the Turkic peoples has been a topic of much discussion. Peter Benjamin Golden proposes two locations for the Proto-Turkic Urheimat: the southern Altai-Sayan region, and in Southern Siberia, from Lake Baikal to eastern Mongolia. Other studies suggested an early presence of Turkic peoples in Mongolia, or Tuva.
A possible genealogical link of the Turkic languages to Mongolic and Tungusic languages, specifically a hypothetical homeland in Manchuria, such as proposed in the Transeurasian hypothesis, by Martine Robbeets, has received support but also criticism, with opponents attributing similarities to long-term contact. The proto-Turkic-speakers may be linked to Neolithic East Asian agricultural societies in Northeastern China, which is to be associated with the Xinglongwa culture and the succeeding Hongshan culture, based on varying degrees of specific East Asian genetic substratum among modern Turkic speakers. According to historians, "the Proto-Turkic subsistence strategy included an agricultural component, a tradition that ultimately went back to the origin of millet agriculture in Northeast China". This view is however questioned by other geneticists, who found no evidence for a shared "Neolithic Hongshan ancestry", but in contrary primary Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA) Neolithic ancestry from the Amur region, supporting an origin from Northeast Asia rather than Manchuria.
Around 2,200 BC, the (agricultural) ancestors of the Turkic peoples probably migrated westwards into Mongolia, where they adopted a pastoral lifestyle, in part borrowed from Iranian peoples. Given nomadic peoples such as Xiongnu, Rouran and Xianbei share underlying genetic ancestry "that falls into or close to the northeast Asian gene pool", the proto-Turkic language likely originated in northeastern Asia.
Genetic data found that almost all modern Turkic peoples retained at least some shared ancestry associated with populations in "South Siberia and Mongolia" (SSM), supporting this region as the "Inner Asian Homeland (IAH) of the pioneer carriers of Turkic languages" which subsequently expanded into Central Asia. The main Turkic expansion took place during the 5th–16th centuries, partially overlapping with the Mongol Empire period. Based on single-path IBD tracts, the common Turkic ancestral population lived prior to these migration events, and likely stem from a similar source population as Mongolic peoples further East. Historical data suggests that the Mongol Empire period acted as secondary force of "turkification", as the Mongol conquest "did not involve massive re-settlements of Mongols over the conquered territories. Instead, the Mongol war machine was progressively augmented by various Turkic tribes as they expanded, and in this way Turkic peoples eventually reinforced their expansion over the Eurasian steppe and beyond."

A 2018 autosomal single-nucleotide polymorphism study suggested that the Eurasian Steppe slowly transitioned from Indo European and Iranian-speaking groups with largely western Eurasian ancestry to increasing East Asian ancestry with Turkic and Mongolian groups in the past 4000 years, including extensive Turkic migrations out of Mongolia and slow assimilation of local populations. A 2022 report suggested that Turkic and Mongolic populations in Central Asia formed via admixture events during the Iron Age between "local Indo-Iranian and a South-Siberian or Mongolian group with a high East-Asian ancestry (around 60%)". Modern day Turkmens form an outlier among Central Asian Turkic-speakers with a lower frequency of the Baikal component (c. 22%) and a lack of the Han-like component, being closer to other Indo-Iranian groups. A subsequent study in 2022 also found that the spread of Turkic-speaking populations into Central Asia happened after the spread of Indo-European speakers into the area. Another 2022 study found that all Altaic‐speaking (Turkic, Tungusic, and Mongolic) populations "were a mixture of dominant Siberian Neolithic ancestry and non-negligible YRB ancestry", suggesting their origins were somewhere in Northeast Asia, most likely the Amur river basin. Except Eastern and Southern Mongolic-speakers, all "possessed a high proportion of West Eurasian-related ancestry, in accordance with the linguistically documented language borrowing in Turkic languages".
A 2023 study analyzed the DNA of Empress Ashina (568–578 AD), a Royal Göktürk, whose remains were recovered from a mausoleum in Xianyang, China. The authors determined that Empress Ashina belonged to the North-East Asian mtDNA haplogroup F1d, and that approximately 96-98% of her autosomal ancestry was of Ancient Northeast Asian origin, while roughly 2-4% was of West Eurasian origin, indicating ancient admixture. This study weakened the "western Eurasian origin and multiple origin hypotheses". However, they also noted that "Central Steppe and early Medieval Türk exhibited a high but variable degree of West Eurasian ancestry, indicating there was a genetic substructure of the Türkic empire." The early medieval Türk samples were modelled as having 37.8% West Eurasian ancestry and 62.2% Ancient Northeast Asian ancestry and historic Central Steppe Türk samples were also an admixture of West Eurasian and Ancient Northeast Asian ancestry, while historic Karakhanid, Kipchak and the Turkic Karluk samples had 50.6%-61.1% West Eurasian ancestry and 38.9%–49.4% Iron Age Yellow River farmer ancestry. A 2020 study also found "high genetic heterogeneity and diversity during the Türkic and Uyghur periods" in the early medieval period in Eastern Eurasian Steppe.
Early historical attestation
The earliest separate Turkic peoples, such as the Gekun (鬲昆) and Xinli (薪犁), appeared on the peripheries of the late Xiongnu confederation about 200 BCE (contemporaneous with the Chinese Han dynasty) and later among the Turkic-speaking Tiele as Hegu (紇骨) and Xue (薛).
The Tiele (also known as Gaoche 高車, lit. "High Carts"), may be related to the Xiongnu and the Dingling. According to the Book of Wei, the Tiele people were the remnants of the Chidi (赤狄), the red Di people competing with the Jin in the Spring and Autumn period. Historically they were established after the 6th century BCE.
The Tiele were first mentioned in Chinese literature from the 6th to 8th centuries. Some scholars (Haneda, Onogawa, Geng, etc.) proposed that Tiele, Dili, Dingling, Chile, Tele, & Tujue all transliterated underlying Türk; however, Golden proposed that Dili, Dingling, Chile, Tele, and Tiele transliterated Tegrek while Tujue transliterated Türküt, plural of Türk. The appellation Türük (Old Turkic: 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰) ~ Türk (OT: 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰚) (whence Middle Chinese 突厥 *dwət-kuɑt > *tɦut-kyat > standard Chinese: Tūjué) was initially reserved exclusively for the Göktürks by Chinese, Tibetans, and even the Turkic-speaking Uyghurs. In contrast, medieval Muslim writers, including Turkic speakers like Ottoman historian Mustafa Âlî and explorer Evliya Çelebi as well as Timurid scientist Ulugh Beg, often viewed Inner Asian tribes, "as forming a single entity regardless of their linguistic affiliation" commonly used Turk as a generic name for Inner Asians (whether Turkic- or Mongolic-speaking). Only in modern era do modern historians use Turks to refer to all peoples speaking Turkic languages, differentiated from non-Turkic speakers.
According to some researchers (Duan, Xue, Tang, Lung, Onogawa, etc.) the later Ashina tribe descended from the Tiele confederation. The Tiele however were probably one of many early Turkic groups, ancestral to later Turkic populations. However, according to Lee & Kuang (2017), Chinese histories do not describe the Ashina and the Göktürks as descending from the Dingling or the Tiele confederation.
Xiongnu (3rd c. BCE – 1st c. CE)
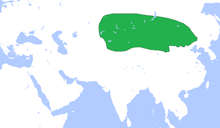
It has even been suggested that the Xiongnu themselves, who were mentioned in Han dynasty records, were Proto-Turkic speakers. The Turks may ultimately have been of Xiongnu descent. Although little is known for certain about the Xiongnu language(s), it seems likely that at least a considerable part of Xiongnu tribes spoke a Turkic language. Some scholars believe they were probably a confederation of various ethnic and linguistic groups. According to a study by Alexander Savelyev and Choongwon Jeong, published in 2020 in the journal Evolutionary Human Sciences by Cambridge University Press, "the predominant part of the Xiongnu population is likely to have spoken Turkic". However, genetic studies found a mixture of western and eastern Eurasian ancestries, suggesting a large genetic diversity within the Xiongnu. The Turkic-related component may be brought by eastern Eurasian genetic substratum.
Using the only extant possibly Xiongnu writings, the rock art of the Yinshan and Helan Mountains, some scholars argue that the older Xiongnu writings are precursors to the earliest known Turkic alphabet, the Orkhon script. Petroglyphs of this region dates from the 9th millennium BCE to the 19th century, and consists mainly of engraved signs (petroglyphs) and few painted images. Excavations done during 1924–1925 in Noin-Ula kurgans located in the Selenga River in the northern Mongolian hills north of Ulaanbaatar produced objects with over 20 carved characters, which were either identical or very similar to the runic letters of the Turkic Orkhon script discovered in the Orkhon Valley.
Steppe expansions
Göktürks – Turkic Khaganate (5th–8th c.)
The earliest certain mentioning of the politonym "Turk" was in the Chinese Book of Zhou. In the 540s AD, this text mentions that the Turks came to China's border seeking silk goods and a trade relationship. A Sogdian diplomat represented China in a series of embassies between the Western Wei dynasty and the Turks in the years 545 and 546.
According to the Book of Sui and the Tongdian, they were "mixed barbarians" (雜胡; záhú) who migrated from Pingliang (now in modern Gansu province, China) to the Rourans seeking inclusion in their confederacy and protection from the prevailing dynasty. Alternatively, according to the Book of Zhou, History of the Northern Dynasties, and New Book of Tang, the Ashina clan was a component of the Xiongnu confederation. Göktürks were also posited as having originated from an obscure Suo state (索國), north of the Xiongnu. The Ashina tribe were famed metalsmiths and were granted land south of the Altai Mountains (金山 Jinshan), which looked like a helmet, from which they were said to have gotten their name 突厥 (Tūjué), the first recorded use of "Turk" as a political name. In the 6th-century, Ashina's power had increased such that they conquered the Tiele on their Rouran overlords' behalf and even overthrew Rourans and established the First Turkic Khaganate.

The original Old Turkic name Kök Türk derives from kök ~ kö:k, "sky, sky-coloured, blue, blue-grey". Unlike its Xiongnu predecessor, the Göktürk Khaganate had its temporary Khagans from the Ashina clan, who were subordinate to a sovereign authority controlled by a council of tribal chiefs. The Khaganate retained elements of its original animistic- shamanistic religion, that later evolved into Tengriism, although it received missionaries of Buddhist monks and practiced a syncretic religion. The Göktürks were the first Turkic people to write Old Turkic in a runic script, the Orkhon script. The Khaganate was also the first state known as "Turk". It eventually collapsed due to a series of dynastic conflicts, but many states and peoples later used the name "Turk".
The Göktürks (First Turkic Kaganate) quickly spread west to the Caspian Sea. Between 581 and 603 the Western Turkic Khaganate in Kazakhstan separated from the Eastern Turkic Khaganate in Mongolia and Manchuria during a civil war. The Han-Chinese successfully overthrew the Eastern Turks in 630 and created a military Protectorate until 682. After that time the Second Turkic Khaganate ruled large parts of the former Göktürk area. After several wars between Turks, Chinese and Tibetans, the weakened Second Turkic Khaganate was replaced by the Uyghur Khaganate in the year 744.
Bulgars, Golden Horde and the Siberian Khanate

The Bulgars established themselves in between the Caspian and Black Seas in the 5th and 6th centuries, followed by their conquerors, the Khazars who converted to Judaism in the 8th or 9th century. After them came the Pechenegs who created a large confederacy, which was subsequently taken over by the Cumans and the Kipchaks. One group of Bulgars settled in the Volga region and mixed with local Volga Finns to become the Volga Bulgars in what is today Tatarstan. These Bulgars were conquered by the Mongols following their westward sweep under Ogedei Khan in the 13th century. Other Bulgars settled in Southeastern Europe in the 7th and 8th centuries, and mixed with the Slavic population, adopting what eventually became the Slavic Bulgarian language. Everywhere, Turkic groups mixed with the local populations to varying degrees.

The Volga Bulgaria became an Islamic state in 922 and influenced the region as it controlled many trade routes. In the 13th century, Mongols invaded Europe and established the Golden Horde in Eastern Europe, western and northern Central Asia, and even western Siberia. The Cuman-Kipchak Confederation and Islamic Volga Bulgaria were absorbed by the Golden Horde in the 13th century; in the 14th century, Islam became the official religion under Uzbeg Khan where the general population (Turks) as well as the aristocracy (Mongols) came to speak the Kipchak language and were collectively known as "Tatars" by Russians and Westerners. This country was also known as the Kipchak Khanate and covered most of what is today Ukraine, as well as the entirety of modern-day southern and eastern Russia (the European section). The Golden Horde disintegrated into several khanates and hordes in the 15th and 16th century including the Crimean Khanate, Khanate of Kazan, and Kazakh Khanate (among others), which were one by one conquered and annexed by the Russian Empire in the 16th through 19th centuries.
In Siberia, the Siberian Khanate was established in the 1490s by fleeing Tatar aristocrats of the disintegrating Golden Horde who established Islam as the official religion in western Siberia over the partly Islamized native Siberian Tatars and indigenous Uralic peoples. It was the northernmost Islamic state in recorded history and it survived up until 1598 when it was conquered by Russia.
Uyghur Khaganate (8th–9th c.)



The Uyghur Khaganate had established itself by the year 744 AD. Through trade relations established with China, its capital city of Ordu Baliq in central Mongolia's Orkhon Valley became a wealthy center of commerce, and a significant portion of the Uyghur population abandoned their nomadic lifestyle for a sedentary one. The Uyghur Khaganate produced extensive literature, and a relatively high number of its inhabitants were literate.
The official state religion of the early Uyghur Khaganate was Manichaeism, which was introduced through the conversion of Bögü Qaghan by the Sogdians after the An Lushan rebellion. The Uyghur Khaganate was tolerant of religious diversity and practiced variety of religions including Buddhism, Christianity, shamanism and Manichaeism.
During the same time period, the Shatuo Turks emerged as power factor in Northern and Central China and were recognized by the Tang Empire as allied power.
In 808, 30,000 Shatuo under Zhuye Jinzhong defected from the Tibetans to Tang China and the Tibetans punished them by killing Zhuye Jinzhong as they were chasing them. The Uyghurs also fought against an alliance of Shatuo and Tibetans at Beshbalik.
The Shatuo Turks under Zhuye Chixin (Li Guochang) served the Tang dynasty in fighting against their fellow Turkic people in the Uyghur Khaganate. In 839, when the Uyghur khaganate (Huigu) general Jueluowu (掘羅勿) rose against the rule of then-reigning Zhangxin Khan, he elicited the help from Zhuye Chixin by giving Zhuye 300 horses, and together, they defeated Zhangxin Khan, who then committed suicide, precipitating the subsequent collapse of the Uyghur Khaganate. In the next few years, when Uyghur Khaganate remnants tried to raid Tang borders, the Shatuo participated extensively in counterattacking the Uyghur Khaganate with other tribes loyal to Tang. In 843, Zhuye Chixin, under the command of the Han Chinese officer Shi Xiong with Tuyuhun, Tangut and Han Chinese troops, participated in a raid against the Uyghur khaganate that led to the slaughter of Uyghur forces at Shahu mountain.

The Shatuo Turks had founded several short-lived sinicized dynasties in northern China during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period starting with Later Tang. The Shatuo chief Zhuye Chixin's family was adopted by the Tang dynasty and given the title prince of Jin and the Tang dynasty imperial surname of Li, which is why the Shatuo of Later Tang claimed to be restoring the Tang dynasty and not founding a new one. The official language of these dynasties was Chinese and they used Chinese titles and names. Some Shaotuo Turk emperors (of the Later Jin, Later Han and Northern Han) also claimed patrilineal Han Chinese ancestry.
After the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907, the Shatuo Turks replaced them and created the Later Tang dynasty in 923. The Shatuo Turks ruled over a large part of northern China, including Beijing. They adopted Chinese names and united Turkic and Chinese traditions. Later Tang fell in 937 but the Shatuo rose to become a powerful faction of northern China. They created two other dynasties, including the Later Jin and Later Han and Northern Han (Later Han and Northern Han were ruled by the same family, with the latter being a rump state of the former). The Shatuo Liu Zhiyuan was a Buddhist and he worshipped the Mengshan Giant Buddha in 945. The Shatuo dynasties were replaced by the Han Chinese Song dynasty. The Shatuo became the Ongud Turks living in Inner Mongolia after the Song dynasty conquered the last Shatuo dynasty of Northern Han. The Ongud assimilated to the Mongols.
The Yenisei Kyrgyz allied with China to destroy the Uyghur Khaganate in the year 840 AD. From the Yenisei River, the Kyrgyz pushed south and eastward in to Xinjiang and the Orkhon Valley in central Mongolia, leaving much of the Uyghur civilization in ruins. Much of the Uyghur population relocated to the southwest of Mongolia, establishing the Ganzhou Uyghur Kingdom in Gansu where their descendants are the modern day Yugurs and Qocho Kingdom in Turpan, Xinjiang.
Central Asia
Kangar union (659–750)

The Kangar Union (Qanghar Odaghu) was a Turkic state in the former territory of the Western Turkic Khaganate (the entire present-day state of Kazakhstan, without Zhetysu). The capital of the Kangar union was located in the Ulytau mountains. Among the Pechenegs, the Kangar formed the elite of the Pecheneg tribes. After being defeated by the Kipchaks, Oghuz Turks, and the Khazars, they migrated west and defeated Magyars, and after forming an alliance with the Bulgars, they defeated the Byzantine Army. The Pecheneg state was established by the 11th century and at its peak carried a population of over 2.5 million, composed of many different ethnic groups.
The elite of the Kangar tribes are believed to have had an Iranian origin, and they likely spoke an Iranian language, while most of the Pecheneg population spoke a Turkic language, with a significant percentage speaking Hunno-Bulgar dialects.
The Yatuks, a tribe within the Kangar state who could not accompany the Kangars as they migrated West, remained in the old lands, where they are known as the Kangly people, who are now part of the Uzbek, Kazakh, and Karakalpak tribes.
Oghuz Yabgu State (766–1055)

The Oguz Yabgu State (Oguz il, meaning "Oguz Land", "Oguz Country")(750–1055) was a Turkic state, founded by Oghuz Turks in 766, located geographically in an area between the coasts of the Caspian and Aral Seas. Oguz tribes occupied a vast territory in Kazakhstan along the Irgiz, Yaik, Emba, and Uil rivers, the Aral Sea area, the Syr Darya valley, the foothills of the Karatau Mountains in Tien-Shan, and the Chui River valley (see map). The Oguz political association developed in the 9th and 10th centuries in the Syr Darya basin.
Salar Oghuz migration
The Salars are descended from Turkmen who migrated from Central Asia and settled in a Tibetan area of Qinghai under Ming Chinese rule. The Salar ethnicity formed and underwent ethnogenesis from a process of male Turkmen migrants from Central Asia marrying Amdo Tibetan women during the early Ming dynasty.
Iranian, Indian, Arabic, and Anatolian expansion
Turkic peoples and related groups migrated west from present-day Northeastern China, Mongolia, Siberia and the Turkestan-region towards the Iranian plateau, South Asia, and Anatolia (modern Turkey) in many waves. The date of the initial expansion remains unknown.
Persia
Ghaznavid dynasty (977–1186)
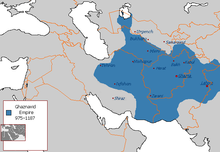
The Ghaznavid dynasty (Persian: غزنویان ġaznaviyān) was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic mamluk origin, at their greatest extent ruling large parts of Iran, Afghanistan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest Indian subcontinent (part of Pakistan) from 977 to 1186. The dynasty was founded by Sabuktigin upon his succession to rule of the region of Ghazna after the death of his father-in-law, Alp Tigin, who was a breakaway ex-general of the Samanid Empire from Balkh, north of the Hindu Kush in Greater Khorasan.
Although the dynasty was of Central Asian Turkic origin, it was thoroughly Persianised in terms of language, culture, literature and habits and hence is regarded by some as a "Persian dynasty".
Seljuk Empire (1037–1194)
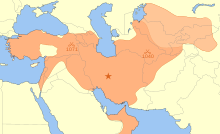
The Seljuk Empire (Persian: آل سلجوق, romanized: Āl-e Saljuq, lit. 'House of Saljuq') or the Great Seljuq Empire was a high medieval Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim empire, originating from the Qiniq branch of Oghuz Turks. At its greatest extent, the Seljuk Empire controlled a vast area stretching from western Anatolia and the Levant to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia to the Persian Gulf in the south.
The Seljuk empire was founded by Tughril Beg (1016–1063) and his brother Chaghri Beg (989–1060) in 1037. From their homelands near the Aral Sea, the Seljuks advanced first into Khorasan and then into mainland Persia, before eventually conquering eastern Anatolia. Here the Seljuks won the battle of Manzikert in 1071 and conquered most of Anatolia from the Byzantine Empire, which became one of the reasons for the First Crusade (1095–1099). From c. 1150–1250, the Seljuk empire declined, and was invaded by the Mongols around 1260. The Mongols divided Anatolia into emirates. Eventually one of these, the Ottoman, would conquer the rest.
Timurid Empire (1370–1507)

The Timurid Empire was a Turko-Mongol empire founded in the late 14th century through military conquests led by Timurlane. The establishment of a cosmopolitan empire was followed by the Timurid Renaissance, a period of local enrichment in mathematics, astronomy, architecture, as well as newfound economic growth. The cultural progress of the Timurid period ended as soon as the empire collapsed in the early 16th century, leaving many intellecuals and artists to turn elsewhere in search of employment.
Central Asian khanates (1501–1920)
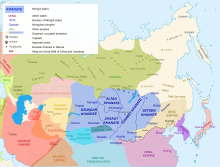
The Bukhara Khanate was an Uzbek state that existed from 1501 to 1785. The khanate was ruled by three dynasties of the Shaybanids, Janids and the Uzbek dynasty of Mangits. In 1785, Shahmurad, formalized the family's dynastic rule (Manghit dynasty), and the khanate became the Emirate of Bukhara (1785–1920). In 1710, the Kokand Khanate (1710–1876) separated from the Bukhara Khanate. In 1511–1920, Khwarazm (Khiva Khanate) was ruled by the Arabshahid dynasty and the Uzbek dynasty of Kungrats.
Afsharid dynasty (1736–1796)
The Afsharid dynasty was named after the Turkic Afshar tribe to which they belonged. The Afshars had migrated from Turkestan to Azerbaijan in the 13th century. The dynasty was founded in 1736 by the military commander Nader Shah who deposed the last member of the Safavid dynasty and proclaimed himself King of Iran. Nader belonged to the Qereqlu branch of the Afshars. During Nader's reign, Iran reached its greatest extent since the Sassanid Empire.
Qajar dynasty (1789–1925)
The Qajar dynasty was created by the Turkic Qajar tribe, ruling over Iran from 1789 to 1925. The Qajar family took full control of Iran in 1794, deposing Lotf 'Ali Khan, the last Shah of the Zand dynasty, and re-asserted Iranian sovereignty over large parts of the Caucasus. In 1796, Mohammad Khan Qajar seized Mashhad with ease, putting an end to the Afsharid dynasty, and Mohammad Khan was formally crowned as Shah after his punitive campaign against Iran's Georgian subjects. In the Caucasus, the Qajar dynasty permanently lost many of Iran's integral areas to the Russians over the course of the 19th century, comprising modern-day Georgia, Dagestan, Azerbaijan and Armenia. The dynasty was founded by Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar and continued until Ahmad Shah Qajar.































![Ghaznavid portrait, Palace of Lashkari Bazar.[274]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/be/Portrait_from_the_Palace_courtroom%2C_Lashkari_Bazar.jpg/92px-Portrait_from_the_Palace_courtroom%2C_Lashkari_Bazar.jpg)












