Finistere Department
History
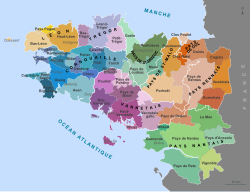
The present department consists of the historical region of Léon and parts of Cornouaille and Trégor, both parts of pre-revolutionary Brittany.
The name Finistère derives from the Latin Finis Terræ, meaning end of the earth. In England, a similar area is called Land's End. The Breton name for Finistère, Penn ar Bed, translates as "Head/End of the World" and is similar to the Cornish name for Land's End, Pedn-an-Wlas (Head/End of the country), and also Penfro (English: Pembroke) in Wales (pen = end, bro = country). Finistère is not to be confused with Fisterra in Galicia, Spain, which shares the same etymology.
Geography
The largest population centre in Finistère is Brest. Other large towns in the department include Quimper (the capital), Concarneau, Morlaix, Carhaix, Quimperlé and Douarnenez. Finistère includes the island of Ushant (Eusa in Breton, Ouessant in French).
Finistère is the westernmost department of Metropolitan France and can also claim to be the "most coastal" department in Metropolitan France. Of its 277 communes, 117 are located on the coast. Its total coastline of approximately 1,250 km (776.71 mi) accounts for almost a quarter of the entire Brittany coast-line.

The abers, rugged fjord-like inlets on the north coast, are a notable feature of the landscape.
The westernmost point of continental France, known as the Pointe de Corsen, extends from the northwestern tip of Finistère. About 40 kilometres to the south (as the crow flies) is the slightly less westerly, but rugged and isolated, headland of Pointe du Raz.
Principal towns
The most populous commune is Brest; the prefecture Quimper is the second-most populous. As of 2019, there are 5 communes with more than 15,000 inhabitants:
| Commune | Population (2019) |
|---|---|
| Brest | 139,926 |
| Quimper | 63,283 |
| Concarneau | 19,816 |
| Landerneau | 15,918 |
| Guipavas | 15,050 |
Demographics
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| source: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Economy
Agriculture, fisheries, food processing and various related industries occupy an important place in Finistère's economy.
The military presence in Finistère (Île Longue nuclear submarine base and the Naval Air base of Lanvéoc-Poulmic), as well as military-related industries, such as the Brest headquarters of DCNS, employ a significant number of the département's population.
The port of Roscoff links Brittany by ferry with Ireland and Great Britain.
Politics
Current National Assembly Representatives
Culture
Finistère is the area where Breton survives most strongly as a spoken language. Breton-speaking schools are called Diwan, Divyezh and Dihun.
The Festival de Cornouaille, which takes place in Quimper, is a celebration of Breton music and traditions. One of the highlights of summer in Finistère is the "Festival des Vieilles Charrues" held in Carhaix-Plouguer. Major international stars attract tens of thousands of spectators.
The painter Raymond Wintz (1884–1956) featured many locations around Finistère.
Roland Doré was a sculptor who executed many of the calvaries in Finistère.
Tourism
-
Granite rocks in Ouessant
-
Pontusval lighthouse near Brignogan-Plages
-
Pointe du Chateau, Plougrescant
See also
- Cantons of the Finistère department
- Communes of the Finistère department
- Arrondissements of the Finistère department
- Ys
- Calvary at Saint-Herbot near Plonévez-du-Faou and the Chapelle Saint-Herbot.
- Notre Dame de Roscudon Church
References
- ^ "Répertoire national des élus: les conseillers départementaux". data.gouv.fr, Plateforme ouverte des données publiques françaises (in French). 4 May 2022.
- ^ "Populations de référence 2022" (in French). The National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies. 19 December 2024.
- ^ Populations légales 2019: 29 Finistère, INSEE
- ^ "Historique du Finistère". Le SPLAF.
- ^ "Évolution et structure de la population en 2016". INSEE.
- ^ "Assemblée nationale ~ les députés, le vote de la loi, le Parlement français". Archived from the original on 2006-03-18. Retrieved 2018-12-13.
- ^ "Vieilles Charrues Festival" Archived 2011-02-03 at the Wayback Machine, official website
External links
- (in French) Departmental Council website
- (in French) Prefecture website
- (in French) Finistère Tourisme, agence de développement touristique du Finistère







