Portal:Geography
The Geography Portal

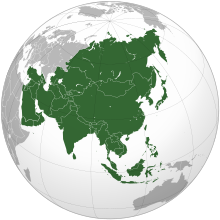
Geography (from Ancient Greek γεωγραφία geōgraphía; combining gê 'Earth' and gráphō 'write') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines."
Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (c. 276 BC – c. 195/194 BC). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." However, the concepts of geography (such as cartography) date back to the earliest attempts to understand the world spatially, with the earliest example of an attempted world map dating to the 9th century BCE in ancient Babylon. The history of geography as a discipline spans cultures and millennia, being independently developed by multiple groups, and cross-pollinated by trade between these groups. The core concepts of geography consistent between all approaches are a focus on space, place, time, and scale.
Today, geography is an extremely broad discipline with multiple approaches and modalities. There have been multiple attempts to organize the discipline, including the four traditions of geography, and into branches. Techniques employed can generally be broken down into quantitative and qualitative approaches, with many studies taking mixed-methods approaches. Common techniques include cartography, remote sensing, interviews, and surveying. (Full article...)
Arlington is a city in northern Snohomish County, Washington, United States, part of the Seattle metropolitan area. The city lies on the Stillaguamish River in the western foothills of the Cascade Range, adjacent to the city of Marysville. It is approximately 10 miles (16 km) north of Everett, the county seat, and 40 miles (64 km) north of Seattle, the state's largest city. As of the 2020 U.S. census, Arlington had a population of 19,868; its estimated population is 20,075 as of 2021.
The city lies in the traditional territory of the Stillaguamish people, an indigenous Coast Salish group. Arlington was established in the 1880s by settlers and the area was platted as two towns, Arlington and Haller City. Haller City was absorbed by the larger Arlington, which was incorporated as a city in 1903. During the Great Depression of the 1930s, the Arlington area was the site of major projects undertaken for employment under the direction of federal relief agencies, including construction of a municipal airport that would serve as a naval air station during World War II. Arlington began suburbanizing in the 1980s, growing by more than 450 percent by 2000 and annexing the unincorporated area of Smokey Point to the southwest. (Full article...)
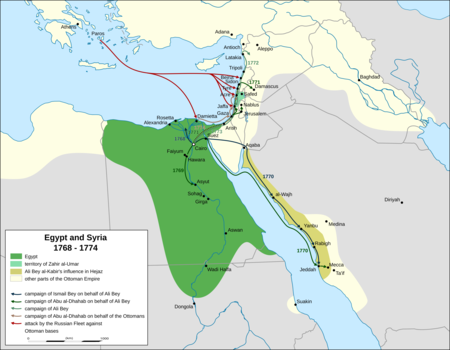
Beirut was twice occupied during the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 by squadrons of the Imperial Russian Navy's Mediterranean Fleet, first in June 1772 and second from October 1773 to early 1774, as part of its Levant campaign. Russia's main objective in this campaign was to assist local forces led by Egypt's autonomous ruler, Ali Bey al-Kabir, who was in open rebellion against the Ottoman Empire.
Russia, led by Catherine the Great, was pressing the Ottomans in Europe. Ali took advantage of the Empire's preoccupation with Russia to declare Egypt's independence; in 1771 he sent an army led by Muhammad Bey Abu al-Dhahab to occupy Ottoman territory in the Levant. Abu al-Dhahab unexpectedly returned to challenge Ali for control of Egypt. Ali requested Russian military assistance against both his rival and the Ottomans. When this aid, in the form of a small Russian squadron, arrived in the region, Ali had already fled Egypt and taken refuge in Acre, the power base of his ally, Zahir al-Umar. After helping repel an Ottoman offensive on Sidon, the Russian squadron sailed for Beirut. They bombarded the town in June 1772 and occupied it from June 23 to 28. (Full article...)
Boston (US: /ˈbɔːstən/ ) is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It has an area of 48.4 sq mi (125 km) and a population of 675,647 as of the 2020 census, making it the third-largest city in the Northeast after New York City and Philadelphia. The larger Greater Boston metropolitan statistical area, which includes and surrounds the city, has a population of 4,919,179 as of 2023, making it the largest in New England and eleventh-largest in the country.
Boston was founded on the Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by Puritan settlers. The city was named after Boston, Lincolnshire, England. During the American Revolution, Boston was home to several events that proved central to the revolution and subsequent Revolutionary War, including the Boston Massacre (1770), the Boston Tea Party (1773), Paul Revere's Midnight Ride (1775), the Battle of Bunker Hill (1775), and the Siege of Boston (1775–1776). Following American independence from Great Britain, the city continued to play an important role as a port, manufacturing hub, and center for education and culture. The city also expanded significantly beyond the original peninsula by filling in land and annexing neighboring towns. Boston's many firsts include the United States' first public park (Boston Common, 1634), the first public school (Boston Latin School, 1635), and the first subway system (Tremont Street subway, 1897). (Full article...)
Hudson Volcano (Spanish: Volcán Hudson, Cerro Hudson, or Monte Hudson) is the most active volcano in the southern part of the Southern Volcanic Zone of the Andes Mountains in Chile, having erupted most recently in 2011. It was formed by the subduction of the oceanic Nazca Plate under the continental South American Plate. South of Hudson is a smaller volcano, followed by a long gap without active volcanoes, then the Austral Volcanic Zone. Hudson has the form of a 10-kilometre-wide (6-mile) caldera filled with ice; the Huemules Glacier emerges from the northwestern side of the caldera. The volcano has erupted rocks ranging from basalt to rhyolite, but large parts of the caldera are formed by non-volcanic rocks.
The volcano erupted numerous times in the late Pleistocene and Holocene, forming widespread tephra deposits both in the proximity of Hudson and in the wider region.
Four large eruptions took place in 17,300–17,440 BP ("H0 eruption"), 7,750 BP ("H1 eruption"), 4,200 BP ("H2 eruption") and in 1991 AD ("H3 eruption"); the second is among the most intense volcanic eruptions in South America during the Holocene. A smaller eruption occurred in 1971. The 7,750 BP and 1991 eruptions had a substantial impact on the human population of Patagonia and (for the 7,750 BP eruption) Tierra del Fuego: The 7,750 BP eruption devastated the local ecosystem and may have caused substantial shifts in human settlement and lifestyle. During the 1991 eruption, volcanic ash covered a large area in Chile and neighbouring Argentina, causing high mortality in farm animals, aggravating an existing economic crisis, and reaching as far as Antarctica. (Full article...)
Carabane, also known as Karabane, is an island and a village located in the extreme south-west of Senegal, in the mouth of the Casamance River. This relatively recent geological formation consists of a shoal and alluvium to which soil is added by accumulation in the branches and roots of the mangrove trees which cover most of the island. Along with the rest of Ziguinchor Region, Carabane has a tropical climate, cycling between a dry season and a wet season. The island was once considered an arid location where no useful plants were likely to grow, but it now supports several types of fruit tree, the most common of which are mangos and oranges. Although the nearby Basse Casamance National Park and Kalissaye Avifaunal Reserve have been closed for years because of the Casamance Conflict, Carabane has continued to attract ornithologists interested in its wide variety of birds. Various species of fish are plentiful around the island, but there are very few mammals.
The earliest known inhabitants of the island were the Jola, the ethnic group which is still the most populous on the island. The Portuguese were active in the region from the 16th century onwards; however, they did not linger on "Mosquito Island", the mosquitoes and black flies convincing them to establish their trading post in the town of Ziguinchor instead in 1645. On January 22, 1836, the island was ceded to France by the village leader of Kagnout in return for an annual payment of 196 francs. A series of treaties between the French and the leaders of the local peoples ensued; however, the inhabitants of Carabane did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them, resulting in lootings and abductions among French rice farmers by the Karoninka people. In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Since World War II, the population of the island has gradually declined for a variety of reasons including periods of drought, the Casamance Conflict and, more recently, the sinking of the ferry Joola in 2002. Much of the village's ability to trade and receive tourists was lost until 2014, when MV Aline Sitoe Diatta resumed ferry services to the island. (Full article...)

Dorset (/ˈdɔːrsɪt/ DOR-sit; archaically: Dorsetshire /ˈdɔːrsɪt.ʃɪər, -ʃər/ DOR-sit-sheer, -shər) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north and the north-east, Hampshire to the east, the Isle of Wight across the Solent to the south-east, the English Channel to the south, and Devon to the west. The largest settlement is Bournemouth, and the county town is Dorchester.
The county has an area of 2,653 km (1,024 sq mi) and a population of 772,268. Around half of the population lives in the South East Dorset conurbation, which contains three of the county's largest settlements: Bournemouth (183,491), Poole (151,500), and Christchurch (31,372). The remainder of the county is largely rural, and its principal towns are Weymouth (53,427) and Dorchester (21,366). Dorset contains two unitary authority areas: Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole (BCP) and Dorset. The county did not historically include Bournemouth and Christchurch, which were part of Hampshire. (Full article...)

There are 24 named waterfalls in Ricketts Glen State Park in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania along Kitchen Creek as it flows in three steep, narrow valleys, or glens. They range in height from 9 feet (2.7 m) to the 94-foot (29 m) Ganoga Falls. Ricketts Glen State Park is named for R. Bruce Ricketts, a colonel in the American Civil War who owned over 80,000 acres (32,000 hectares) in the area in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, but spared the old-growth forests in the glens from clearcutting. The park, which opened in 1944, is administered by the Bureau of State Parks of the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources (DCNR). Nearly all of the waterfalls are visible from the Falls Trail, which Ricketts had built from 1889 to 1893 and which the state park rebuilt in the 1940s and late 1990s. The Falls Trail has been called "the most magnificent hike in the state" and one of "the top hikes in the East". (Full article...)

Macedonia (/ˌmæsɪˈdoʊniə/ MASS-ih-DOH-nee-ə; Greek: Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (/ˈmæsɪdɒn/ MASS-ih-don), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the southwest, Illyria to the northwest, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.
Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king Philip II (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the sarissa pike, Philip II defeated the old powers of Athens and Thebes in the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC. Philip II's son Alexander the Great, leading a federation of Greek states, accomplished his father's objective of commanding the whole of Greece when he destroyed Thebes after the city revolted. During Alexander's subsequent campaign of conquest, he overthrew the Achaemenid Empire and conquered territory that stretched as far as the Indus River. For a brief period, his Macedonian Empire was the most powerful in the world – the definitive Hellenistic state, inaugurating the transition to a new period of Ancient Greek civilization. Greek arts and literature flourished in the new conquered lands and advances in philosophy, engineering, and science spread across the empire and beyond. Of particular importance were the contributions of Aristotle, tutor to Alexander, whose writings became a keystone of Western philosophy. (Full article...)

The drift of the Antarctic exploration vessel SY Aurora was an ordeal which lasted 312 days, affecting the Ross Sea party of Sir Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1914–1917. It began when the ship broke loose from its anchorage in McMurdo Sound in May 1915, during a gale. Caught in heavy pack ice and unable to manoeuvre, Aurora, with eighteen men aboard, was carried into the open waters of the Ross Sea and Southern Ocean, leaving ten men stranded ashore with meagre provisions.
Aurora, a 40-year-old former Arctic whaler registered as a steam yacht, had brought the Ross Sea party to Cape Evans in McMurdo Sound in January 1915, to establish its base there in support of Shackleton's proposed transcontinental crossing. When Aurora's captain Aeneas Mackintosh took charge of activities ashore, first officer Joseph Stenhouse assumed command of the ship. Stenhouse's inexperience may have contributed to the choice of an inappropriate winter's berth, although his options were restricted by the instructions of his superiors. After the ship was blown away it suffered severe damage in the ice, including the destruction of its rudder and the loss of its anchors; on several occasions its situation was such that Stenhouse considered abandonment. Efforts to make wireless contact with Cape Evans and, later, with stations in New Zealand and Australia, were unavailing; the drift extended through the southern winter and spring to reach a position north of the Antarctic Circle. In February 1916 the ice broke up, and a month later the ship was free. It was subsequently able to reach New Zealand for repairs and resupply, before returning to Antarctica to rescue the seven surviving members of the shore party. (Full article...)
Wormshill (/wɜːrmzˈhɪl/ wurmz-HIL), historically Wormsell, is a small village and civil parish within the Borough of Maidstone, Kent, England. The parish is approximately 7 miles (11 km) south of the Swale and 8 mi (13 km) east of Maidstone. The village of Frinsted lies 0.6 mi (1 km) to the east and Bicknor 1+1⁄2 mi (2.4 km) to the north-west; while Hollingbourne is 3 mi (5 km) to the south-west. The village lies on an exposed high point of the North Downs, within the Kent Downs Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
Archaeological and toponymic evidence of Wormshill's existence predates its appearance in the Domesday Book of 1086. The village contains a number of heritage-listed buildings, which include a Norman church, a public house and one of the oldest surviving post office buildings in the United Kingdom. The fields and woodland surrounding Wormshill have changed little in the past 500 years, and the village itself remains rural with a low population density compared to the national average. The population of 200 is a mixture of agricultural workers employed by local farms, and professional residents who commute to nearby towns. (Full article...)
Little Butte Creek is a 17-mile-long (27 km) tributary of the Rogue River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Its drainage basin consists of approximately 354 square miles (917 km) of Jackson County and another 19 square miles (49 km) of Klamath County. Its two forks, the North Fork and the South Fork, both begin high in the Cascade Range near Mount McLoughlin and Brown Mountain. They both flow generally west until they meet near Lake Creek. The main stem continues west, flowing through the communities of Brownsboro, Eagle Point, and White City, before finally emptying into the Rogue River about 3 miles (5 km) southwest of Eagle Point.
Little Butte Creek's watershed was originally settled by the Takelma, and possibly the Shasta tribes of Native Americans. In the Rogue River Wars of the 1850s, most of the Native Americans were either killed or forced onto Indian reservations. Early settlers named Little Butte Creek and nearby Big Butte Creek after their proximity to Mount McLoughlin, which was known as Snowy Butte. In the late 19th century, the watershed was primarily used for agriculture and lumber production. The city of Eagle Point was incorporated in 1911, and remains the only incorporated town within the watershed's boundaries. (Full article...)