Portal:Geography
The Geography Portal

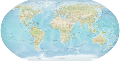
Geography (from Ancient Greek γεωγραφία geōgraphía; combining gê 'Earth' and gráphō 'write') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines."
Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (c. 276 BC – c. 195/194 BC). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." However, the concepts of geography (such as cartography) date back to the earliest attempts to understand the world spatially, with the earliest example of an attempted world map dating to the 9th century BCE in ancient Babylon. The history of geography as a discipline spans cultures and millennia, being independently developed by multiple groups, and cross-pollinated by trade between these groups. The core concepts of geography consistent between all approaches are a focus on space, place, time, and scale.
Today, geography is an extremely broad discipline with multiple approaches and modalities. There have been multiple attempts to organize the discipline, including the four traditions of geography, and into branches. Techniques employed can generally be broken down into quantitative and qualitative approaches, with many studies taking mixed-methods approaches. Common techniques include cartography, remote sensing, interviews, and surveying. (Full article...)
Knowle West is a neighbourhood in the south of Bristol, England, 2 miles (3 km) from the city centre, and mostly in the Filwood ward of Bristol City Council, although a small part of the estate lies within Knowle ward to the east. To the west are Bishopsworth and Hartcliffe, to the north Bedminster and Windmill Hill and to the south Whitchurch Park and Hengrove. In 2008, the population was 11,787.
There is evidence of late Iron Age and Roman settlements in the area. At the time of the Domesday Book, Knowle was a rural area assessed at a taxable value of two geld units. Knowle West remained rural in character until the 1930s, when a council estate was developed to provide homes for people displaced by slum clearance in the centre of the city. (Full article...)
Chat Moss is a large area of peat bog that makes up part of the City of Salford, Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and Trafford in Greater Manchester, England. It also makes up part of Metropolitan Borough of St Helens in Merseyside and Warrington in Cheshire. North of the Manchester Ship Canal and River Mersey, 5 miles (8 km) to the west of Manchester, it occupies an area of about 10.6 square miles (27.5 km).
As it might be recognised today, Chat Moss is thought to be about 7,000 years old, but peat development seems to have begun there with the ending of the last ice age, about 10,000 years ago. The depth of peat ranges from 24 to 30 feet (7 to 9 m). A great deal of reclamation work has been carried out, particularly during the 19th century, but a large-scale network of drainage channels is still required to keep the land from reverting to bog. In 1958 workers extracting peat discovered the severed head of what is believed to be a Romano-British Celt, possibly a sacrificial victim, in the eastern part of the bog near Worsley. (Full article...)

The air-tractor sledge was a converted fixed-wing aircraft taken on the 1911–1914 Australasian Antarctic Expedition, the first plane to be taken to the Antarctic.
Expedition leader Douglas Mawson had planned to use the Vickers R.E.P. Type Monoplane as a reconnaissance and search and rescue tool, and to assist in publicity, but the aircraft crashed heavily during a test flight in Adelaide, only two months before Mawson's scheduled departure date. The plane was nevertheless sent south with the expedition, after having been stripped of its wings and metal sheathing from the fuselage. (Full article...)
Powder House Island (also known as Dynamite Island) is an artificial island on the lower Detroit River in southeast Michigan, directly adjacent to the Canada–United States border. It was constructed in the late 1880s by the Dunbar & Sullivan Company to store explosives during their dredging of the Livingstone Channel, with the purpose of circumventing an 1880 court order forbidding the company to store explosives on nearby Fox Island.
Powder House Island was the location of dynamite storage sheds, as well as a dynamite factory and several ice houses. During this time, it was the site of a series of accidents, including fires in 1895 and 1919 (which both burned the island "to the water's edge"). Twenty short tons (18,000 kg) of the island's dynamite exploded in 1906 after two men "had been shooting with a revolver" near it; while there were no deaths (and only minor injuries to the two men), windows were shattered 3 mi (4.8 km) away and the explosion was clearly audible from 85 mi (137 km) away. (Full article...)
Carabane, also known as Karabane, is an island and a village located in the extreme south-west of Senegal, in the mouth of the Casamance River. This relatively recent geological formation consists of a shoal and alluvium to which soil is added by accumulation in the branches and roots of the mangrove trees which cover most of the island. Along with the rest of Ziguinchor Region, Carabane has a tropical climate, cycling between a dry season and a wet season. The island was once considered an arid location where no useful plants were likely to grow, but it now supports several types of fruit tree, the most common of which are mangos and oranges. Although the nearby Basse Casamance National Park and Kalissaye Avifaunal Reserve have been closed for years because of the Casamance Conflict, Carabane has continued to attract ornithologists interested in its wide variety of birds. Various species of fish are plentiful around the island, but there are very few mammals.
The earliest known inhabitants of the island were the Jola, the ethnic group which is still the most populous on the island. The Portuguese were active in the region from the 16th century onwards; however, they did not linger on "Mosquito Island", the mosquitoes and black flies convincing them to establish their trading post in the town of Ziguinchor instead in 1645. On January 22, 1836, the island was ceded to France by the village leader of Kagnout in return for an annual payment of 196 francs. A series of treaties between the French and the leaders of the local peoples ensued; however, the inhabitants of Carabane did not recognize the authority of the treaties imposed upon them, resulting in lootings and abductions among French rice farmers by the Karoninka people. In 1869, Carabane became autonomous, but it merged with Sédhiou in 1886. Since World War II, the population of the island has gradually declined for a variety of reasons including periods of drought, the Casamance Conflict and, more recently, the sinking of the ferry Joola in 2002. Much of the village's ability to trade and receive tourists was lost until 2014, when MV Aline Sitoe Diatta resumed ferry services to the island. (Full article...)

Dorset (/ˈdɔːrsɪt/ DOR-sit; archaically: Dorsetshire /ˈdɔːrsɪt.ʃɪər, -ʃər/ DOR-sit-sheer, -shər) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north and the north-east, Hampshire to the east, the Isle of Wight across the Solent to the south-east, the English Channel to the south, and Devon to the west. The largest settlement is Bournemouth, and the county town is Dorchester.
The county has an area of 2,653 km (1,024 sq mi) and a population of 772,268. Around half of the population lives in the South East Dorset conurbation, which contains three of the county's largest settlements: Bournemouth (183,491), Poole (151,500), and Christchurch (31,372). The remainder of the county is largely rural, and its principal towns are Weymouth (53,427) and Dorchester (21,366). Dorset contains two unitary authority areas: Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole (BCP) and Dorset. The county did not historically include Bournemouth and Christchurch, which were part of Hampshire. (Full article...)
Manuel Marques de Sousa, Count of Porto Alegre (13 June 1804 – 18 July 1875), nicknamed "the Gloved Centaur", was an army officer, politician and abolitionist of the Empire of Brazil. Born into a wealthy family of military background, Manuel Marques de Sousa joined the Portuguese Army in Brazil in 1817 when he was little more than a child. His military initiation occurred in the conquest of the Banda Oriental (Eastern Bank), which was annexed and became the southernmost Brazilian province of Cisplatina in 1821. For most of the 1820s, he was embroiled in the Brazilian effort to keep Cisplatina as part of its territory: first during the struggle for Brazilian independence and then in the Cisplatine War. It would ultimately prove a futile attempt, as Cisplatina successfully separated from Brazil to become the independent nation of Uruguay in 1828.
A few years later, in 1835 his native province of Rio Grande do Sul was engulfed in a secessionist rebellion, the Ragamuffin War. The conflict lasted for almost ten years, and the Count was leading military engagements for most of that time. He played a decisive role in saving the provincial capital from the Ragamuffin rebels, allowing forces loyal to the legitimate government to secure a key foothold. In 1852, he led a Brazilian division during the Platine War in an invasion of the Argentine Confederation that overthrew its dictator. He was awarded a noble title, eventually raised from baron to viscount and finally to count. (Full article...)
The first ruler to hold the title of Grand Duke was Mindaugas. Traditionally he is considered the founder of the state, the one who united the Baltic tribes and established the Duchy. Some scholars, however, challenge this perception, arguing that an organized state existed before Mindaugas, possibly as early as 1183. After quelling an internal war with his nephews, Mindaugas was baptized in 1251, and was crowned as King of Lithuania in 1253. In 1261, he broke the peace with the Livonian Order, perhaps even renouncing Christianity. His assassination in 1263 by Treniota ended the early Christian kingdom in Lithuania. For another 120 years Lithuania would remain a pagan empire, fighting against the Teutonic and Livonian Orders during the Northern Crusades during their attempts to Christianize the land. (Full article...)
Hebron Church (also historically known as Great Capon Church, Hebron Lutheran Church, and Hebron Evangelical Lutheran Church) is a mid-19th-century Lutheran church in Intermont, Hampshire County, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. Hebron Church was founded in 1786 by German settlers in the Cacapon River Valley, making it the first Lutheran church west of the Shenandoah Valley. The congregation worshiped in a log church, which initially served both Lutheran and Reformed denominations. Its congregation was originally German-speaking; the church's documents and religious services were in German until 1821, when records and sermons transitioned to English.
The church's congregation built the present Greek Revival-style 1+1⁄2-story church building in 1849, when it was renamed Hebron on the Cacapon. The original log church was moved across the road and subsequently used as a sexton's house, Sunday school classroom, and public schoolhouse (attended by future West Virginia governor Herman G. Kump). (Full article...)