List Of Leporids
The 64 extant species of Leporidae are contained within 11 genera. One genus, Lepus, contains 32 species that are collectively referred to as hares; the other eight genera are generally referred to as rabbits, with the majority – 19 species – in Sylvilagus, or the cottontail rabbits. Over one hundred extinct Leporidae species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically endangered (1 species) |
| EN | Endangered (9 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (8 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (2 species) |
| LC | Least concern (39 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (5 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (0 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the leporid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†".
Classification
The family Leporidae consists of 64 extant species in 11 genera which are divided into over 200 extant subspecies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species.
- Genus Brachylagus: one species
- Genus Bunolagus: one species
- Genus Caprolagus: one species
- Genus Lepus: thirty-two species
- Genus Nesolagus: two species
- Genus Oryctolagus: one species
- Genus Pentalagus: one species
- Genus Poelagus: one species
- Genus Pronolagus: four species
- Genus Romerolagus: one species
- Genus Sylvilagus: nineteen species
Leporids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis, as supported by both the IUCN and the American Society of Mammalogists.
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pygmy rabbit | B. idahoensis (Merriam, 1891) |
Western America (introduced in red)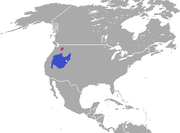
|
Size: 23–30 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and desert Diet: Sagebrush, as well as grass and other plants |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riverine rabbit | B. monticularis (Thomas, 1903) |
Southern South Africa
|
Size: 33–47 cm (13–19 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland Diet: Shrubs as well as grass |
CR
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hispid hare | C. hispidus (Blyth, 1845) |
Himalayas
|
Size: 38–50 cm (15–20 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands Diet: Grass as well as other plants |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abyssinian hare | L. habessinicus Hemprich, Ehrenberg, 1832 Four subspecies
|
Horn of Africa
|
Size: 44–45 cm (17–18 in) long Habitat: Savanna, grassland, and desert Diet: Grass, shrubs, and forbs |
LC
|
| African savanna hare | L. victoriae Heuglin, 1865 |
Sub-Saharan Africa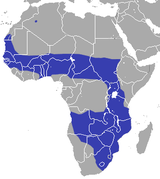
|
Size: 41–58 cm (16–23 in) long Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Variety of plants |
LC
|
| Alaskan hare | L. othus Merriam, 1900 Two subspecies
|
Western Alaska
|
Size: 50–60 cm (20–24 in) long, plus 6–11 cm (2–4 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Dwarf willow, grass, sedges, and other plants |
LC
|
| Antelope jackrabbit | L. alleni Mearns, 1890 Three subspecies
|
Southwestern North America
|
Size: 43–70 cm (17–28 in) long, plus 5–14 cm (2–6 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Grass, velvet mesquite, and cacti |
LC
|
| Arctic hare | L. arcticus Ross, 1819 Four subspecies
|
Arctic North America
|
Size: 56–66 cm (22–26 in) long, plus 4–10 cm (2–4 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Woody plants |
LC
|
| Black jackrabbit | L. insularis Bryant, 1891 |
Tip of Baja California
|
Size: 54–61 cm (21–24 in) long, plus 6–12 cm (2–5 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, caves, desert, and coastal marine Diet: Grass, as well as tree bark |
VU
|
| Black-tailed jackrabbit | L. californicus Gray, 1837 Six subspecies
|
Western and central North America
|
Size: 47–63 cm (19–25 in) long, plus 5–12 cm (2–5 in) tail Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Grass and herbs, as well as twigs and bark |
LC
|
| Broom hare | L. castroviejoi Arribas, 1977 |
Northern Spain
|
Size: 41–59 cm (16–23 in) long Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Grass, herbs, field crops, twigs, buds, and bark |
VU
|
| Burmese hare | L. peguensis Blyth, 1855 Two subspecies
|
Southeastern Asia
|
Size: 40–59 cm (16–23 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Grass, bark and twigs |
LC
|
| Cape hare | L. capensis Linnaeus, 1758 Twelve subspecies
|
Africa and western Asia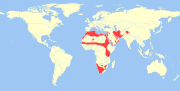
|
Size: 52–60 cm (20–24 in) long Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Grass, shrubs, and herbs |
LC
|
| Chinese hare | L. sinensis Gray, 1832 Three subspecies
|
Southeastern China and Taiwan
|
Size: 36–42 cm (14–17 in) long, plus 17 cm (7 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Leafy plants, green shoots, and twigs |
LC
|
| Corsican hare | L. corsicanus Winton, 1898 |
Southern Italy
|
Size: 55–61 cm (22–24 in) long Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and coastal marine Diet: Grass, as well as mint, sedges, rushes, peas, and flowers |
VU
|
| Desert hare | L. tibetanus Waterhouse, 1841 Five subspecies
|
Northwestern China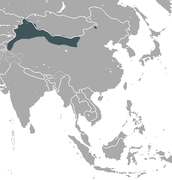
|
Size: 40–76 cm (16–30 in) long Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Variety of plants as well as seeds, berries, roots, and twigs |
LC
|
| Ethiopian hare
|
L. fagani Thomas, 1903 |
Ethiopia
|
Size: 42–50 cm (17–20 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Unknown plants |
LC
|
| Ethiopian highland hare | L. starcki Petter, 1963 |
Central Ethiopia
|
Size: 46–60 cm (18–24 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Grass as well as shrubs |
LC
|
| European hare | L. europaeus Pallas, 1778 Sixteen subspecies
|
Europe, western Asia, northeastern North America, southern South America, eastern Oceana (introduced in light red)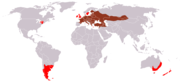
|
Size: 60–75 cm (24–30 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Grass, herbs, field crops, twigs, buds, and bark |
LC
|
| Granada hare | L. granatensis Rosenhauer, 1856 Three subspecies
|
Iberian Peninsula (introduced in pink)
|
Size: 44–48 cm (17–19 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Buds, twigs, bark, and crops |
LC
|
| Hainan hare | L. hainanus Swinhoe, 1870 |
Hainan Island, China
|
Size: 35–40 cm (14–16 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Plants |
EN
|
| Indian hare | L. nigricollis F. Cuvier, 1823 Seven subspecies
|
Indian subcontinent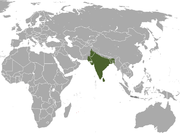
|
Size: 40–70 cm (16–28 in) long Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and desert Diet: Grass and flowering plants |
LC
|
| Japanese hare | L. brachyurus Temminck, 1845 Four subspecies
|
Japan
|
Size: 45–54 cm (18–21 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Grass, buds, seedlings, and shrubs |
LC
|
| Korean hare | L. coreanus Thomas, 1892 |
Korea
|
Size: 45–54 cm (18–21 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Grass, shrubs, and bark |
LC
|
| Manchurian hare | L. mandshuricus Radde, 1861 |
Eastern Asia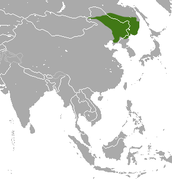
|
Size: 41–54 cm (16–21 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Bark and twigs, as well as shrubs, herbs, and fruit |
LC
|
| Mountain hare | L. timidus Linnaeus, 1758 Fifteen subspecies
|
Europe and northern Asia
|
Size: 50–55 cm (20–22 in) long, plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands Diet: Seeds, berries, roots, twigs, and other plants |
LC
|
| Scrub hare | L. saxatilis F. Cuvier, 1823 Two subspecies
|
Southern Africa
|
Size: 45–65 cm (18–26 in) long Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Grass |
LC
|
| Snowshoe hare | L. americanus Erxleben, 1777 Six subspecies
|
Northern North America
|
Size: 38–51 cm (15–20 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (1.6–2.4 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Grass, forbs, sedges, and ferns |
LC
|
| Tehuantepec jackrabbit | L. flavigularis Wagner, 1844 |
Small region of southern Mexico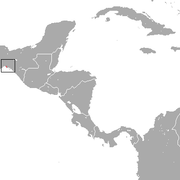
|
Size: 56–61 cm (22–24 in) long Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and coastal marine Diet: Grass, as well as other plants |
EN
|
| Tolai hare | L. tolai Pallas, 1778 Eight subspecies
|
Central and eastern Asia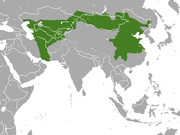
|
Size: 40–59 cm (16–23 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail Habitat: Grassland and rocky areas Diet: Roots, grass, and herbs |
LC
|
| White-sided jackrabbit | L. callotis Wagler, 1830 Two subspecies
|
Southern North America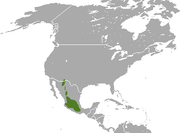
|
Size: 43–60 cm (17–24 in) long, plus 4–10 cm (2–4 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Grass and sedges |
VU
|
| White-tailed jackrabbit | L. townsendii Bachman, 1839 Two subspecies
|
Central and northern North America
|
Size: 53–60 cm (21–24 in) long Habitat: Shrubland and grassland Diet: Grass and forbs, as well as shrubs |
LC
|
| Woolly hare | L. oiostolus Hodgson, 1840 Four subspecies
|
Central Asia
|
Size: 40–50 cm (16–20 in) long, plus 9 cm (4 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Grass and leaves, as well as fruit and crops |
LC
|
| Yarkand hare | L. yarkandensis Günther, 1875 |
Western China
|
Size: 28–43 cm (11–17 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Grass and crops |
NT
|
| Yunnan hare | L. comus Allen, 1927 |
Southern China
|
Size: 28–43 cm (11–17 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail Habitat: Grassland Diet: Forbs and shrubs |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annamite striped rabbit | N. timminsi Averianov, Abramov, Tikhonov, 2000 |
Annamite Range in Southeastern Asia
|
Size: 35–40 cm (14–16 in) long Habitat: Forest Diet: Unknown plants |
EN
|
| Sumatran striped rabbit | N. netscheri (Schlegel, 1880) |
Sumatra
|
Size: 36–42 cm (14–17 in) long, plus 17 cm (7 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Cyrtandra plants |
DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| European rabbit | O. cuniculus (Linnaeus, 1758) Seven subspecies
|
Europe, southern South America, and Oceana (introduced in pink)
|
Size: 38–50 cm (15–20 in) long Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Grass, leaves, buds, bark, and roots |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amami rabbit | P. furnessi (Stone, 1900) |
Southern tip of Japan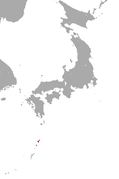
|
Size: 39–53 cm (15–21 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and intertidal marine Diet: Herbs, shrubs, and acorns |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bunyoro rabbit
|
P. marjorita (St. Leger, 1929) |
Central Africa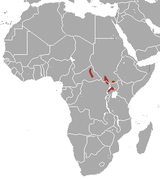
|
Size: 45–50 cm (18–20 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (1.6–2.0 in) tail Habitat: Forest, savanna, and rocky areas Diet: Grass, shrubs, forbs, and tubers |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hewitt's red rock hare | P. saundersiae Hewitt, 1927 |
Southern Africa
|
Size: 38–54 cm (15–21 in) long, plus 5–12 cm (2–5 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas Diet: Grass |
LC
|
| Jameson's red rock hare | P. randensis Jameson, 1907 Three subspecies
|
Southern Africa
|
Size: 42–50 cm (17–20 in) long Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas Diet: Grass |
LC
|
| Natal red rock hare | P. crassicaudatus (Geoffroy, 1832) Two subspecies
|
Southern Africa
|
Size: 46–56 cm (18–22 in) long, plus 3–11 cm (1–4 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas Diet: Grass |
LC
|
| Smith's red rock hare | P. rupestris Smith, 1834 Five subspecies
|
Southern Africa
|
Size: 38–54 cm (15–21 in) long, plus 5–12 cm (2–5 in) tail Habitat: Grassland, rocky areas, and desert Diet: Grass, herbs, and shrubs |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volcano rabbit | R. diazi (Ferrari-Pérez, 1893) |
Southern Mexico
|
Size: 27–32 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail Habitat: Forest and grassland Diet: Grass |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andean tapeti | S. andinus (Thomas, 1897) |
Northern Andes
|
Size: 33–36 cm (13–14 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Grassland Diet: Grass and sedges |
DD
|
| Appalachian cottontail | S. obscurus Chapman, Cramer, Dippenaar, Robinson, 1992 |
Eastern America
|
Size: 32–41 cm (13–16 in) long, plus 2–7 cm (1–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and inland wetlands Diet: Ferns, grass, forbs, shrubs, and conifer needles |
NT
|
| Brush rabbit | S. bachmani (Waterhouse, 1839) Six subspecies
|
Western North America
|
Size: 30–37 cm (12–15 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and desert Diet: Grass, as well as other plants |
LC
|
| Central American tapeti | S. gabbi (Allen, 1877) |
Central America
|
Size: Unknown Habitat: Forest Diet: Unknown plants |
LC
|
| Coastal tapeti
|
S. tapetillus Thomas, 1913 |
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
|
Size: Unknown Habitat: Grassland Diet: Unknown plants |
VU
|
| Common tapeti | S. brasiliensis (Linnaeus, 1758) Seventeen subspecies
|
Northeastern Brazil
|
Size: Unknown Habitat: Forest Diet: Unknown plants |
EN
|
| Davis Mountains cottontail | S. robustus Bailey, 1905 |
Mexico and southern United States
|
Size: Unknown Habitat: Forest Diet: Unknown plants |
VU
|
| Desert cottontail | S. audubonii (Baird, 1858) Seven subspecies
|
Western North America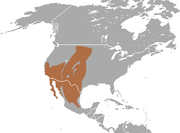
|
Size: 37–40 cm (15–16 in) long, plus 5–6 cm (2.0–2.4 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Forbs, grass, and shrubs |
LC
|
| Dice's cottontail
|
S. dicei Harris Jr., 1932 |
Costa Rica and Panama
|
Size: 34–45 cm (13–18 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Unknown plants |
VU
|
| Eastern cottontail | S. floridanus (Allen, 1890) Seventeen subspecies
|
North America, Central America, and northern South America
|
Size: 39–48 cm (15–19 in) long, plus 2–7 cm (1–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, rocky areas, and desert Diet: Variety of plants |
LC
|
| Marsh rabbit | S. palustris (Bachman, 1837) Three subspecies
|
Eastern America
|
Size: 42–44 cm (17–17 in) long Habitat: Forest, grassland, inland wetlands, and intertidal marine Diet: Berries, rhizomes, bulbs, grass, and other plants |
LC
|
| Mexican cottontail | S. cunicularius (Horsfield, 1848) Two subspecies
|
Southern Mexico
|
Size: 48–52 cm (19–20 in) long, plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Unknown plants |
LC
|
| Mountain cottontail | S. nuttallii (Bachman, 1837) Three subspecies
|
Western North America
|
Size: 28–36 cm (11–14 in) long, plus 3–6 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Sagebrush and grass |
LC
|
| New England cottontail | S. transitionalis (Bangs, 1895) |
New England
|
Size: 39–44 cm (15–17 in) long Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and inland wetlands Diet: Grass, forbs, and twigs |
VU
|
| Omilteme cottontail
|
S. insonus Nelson, 1904 |
Sierra Madre del Sur in Mexico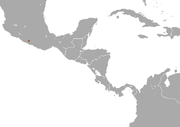
|
Size: 39–44 cm (15–17 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (1.6–2.0 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Unknown plants |
DD
|
| Santa Marta tapeti
|
S. sanctaemartae Hershkovitz, 1950 |
Columbia | Size: Unknown Habitat: Forest, grassland Diet: Unknown plants |
DD
|
| Swamp rabbit | S. aquaticus (Bachman, 1837) Two subspecies
|
Southern America
|
Size: 45–55 cm (18–22 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands Diet: Grass, sedges, shrubs, bark, seedlings, and twigs |
LC
|
| Tres Marias cottontail | S. graysoni (Allen, 1877) |
Southwestern Mexico
|
Size: 21–48 cm (8–19 in) long, plus 1–6 cm (0.4–2.4 in) tail Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland Diet: Wide variety of plants |
EN
|
| Venezuelan lowland rabbit
|
S. varynaensis Durant, Guevara, 2001 |
Venezuela
|
Size: 41–49 cm (16–19 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (0.8–1.2 in) tail Habitat: Forest and savanna Diet: Sida plants |
DD
|
References
- ^ "Fossilworks: Leporidae". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Archived from the original on December 12, 2021. Retrieved December 17, 2021.
- ^ Wilson, Reeder, pp. 194–211
- ^ Rohde, Ashley (2006). "Brachylagus idahoensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Rachlow, J.; Becker, P. A.; Shipley, L. (2016). "Brachylagus idahoensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2963A45176206. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T2963A45176206.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 91
- ^ Collins, K.; Bragg, C.; Birss, C. (2019). "Bunolagus monticularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T3326A45176532. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3326A45176532.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 94
- ^ Aryal, A.; Yadav, B. (2019). "Caprolagus hispidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T3833A45176688. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3833A45176688.en.
- ^ Nickolai, Ashley (2014). "Lepus habessinicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus habessinicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41289A45189637. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41289A45189637.en.
- ^ Riegler, Donald (2013). "Lepus microtis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 5, 2021. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Robinson, T. J.; Relton, C.; Child, M. F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus victoriae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41879A45194215. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41879A45194215.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 204
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus othus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11795A45178124. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11795A45178124.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 160
- ^ Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Lepus alleni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41272A45185265. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41272A45185265.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 166
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus arcticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41274A45185887. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41274A45185887.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 198
- ^ Lorenzo, C.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus insularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11794A45177986. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T11794A45177986.en.
- ^ Mejia, Joseph R. (1999). "Lepus insularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Ballenger, Liz (1999). "Lepus californicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Brown, D. E.; Lorenzo, C.; Álvarez-Castañeda, S. T. (2019). "Lepus californicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41276A45186309. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41276A45186309.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 179
- ^ Ballesteros, F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus castroviejoi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11797A503908. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T11797A503908.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 205
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus peguensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41284A45188632. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41284A45188632.en.
- ^ Begnoche, Dana (2002). "Lepus capensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 5, 2021. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Relton, C. (2019). "Lepus capensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41277A45186750. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41277A45186750.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 96
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus sinensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41286A45189035. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41286A45189035.en.
- ^ Cooper, Thomas (2015). "Lepus corsicanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Randi, E.; Riga, F. (2019). "Lepus corsicanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41305A2952954. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T41305A2952954.en.
- ^ Sullivan, Shaunna (2013). "Lepus tibetanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus tibetanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41307A45193298. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41307A45193298.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 190
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus fagani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11798A45178437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11798A45178437.en.
- ^ Kingdon, p. 310
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus starcki". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41287A45189235. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41287A45189235.en.
- ^ Vu, Alan (2001). "Lepus europaeus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Hacklander, K.; Schai-Braun, S. (2019). "Lepus europaeus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41280A45187424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41280A45187424.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 193
- ^ Soriguer, R.; Carro, F. (2019). "Lepus granatensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41306A2953195. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41306A2953195.en.
- ^ Weaver, Derek (2013). "Lepus granatensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 5, 2021. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 197
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. (2016). "Lepus hainanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11793A45177783. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T11793A45177783.en.
- ^ Lundberg, Annette (2013). "Lepus hainanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 5, 2021. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- ^ Lundrigan, Barbara; Foote, Sarah (2003). "Lepus nigricollis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Nameer, P. O.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus nigricollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41282A45188041. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41282A45188041.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 169
- ^ Yamada, F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus brachyurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41275A45186064. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41275A45186064.en.
- ^ Holmberg, Jennifer (2014). "Lepus brachyurus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 5, 2021. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- ^ Faigle, Stacy (2014). "Lepus coreanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Jo, Y.-S.; Smith, A. T. (2019) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Lepus coreanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41279A161750768. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41279A161750768.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 200
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus mandshuricus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41281A45187882. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41281A45187882.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, et al., p. 289
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 212–213
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus timidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11791A45177198. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11791A45177198.en.
- ^ Kushnereit, Aimee (2004). "Lepus saxatilis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 5, 2021. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- ^ Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Relton, C.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus saxatilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41285A45188827. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41285A45188827.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 163
- ^ Mills, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus americanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41273A45185466. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41273A45185466.en.
- ^ Warlin, Sierra (2013). "Lepus flavigularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Lorenzo, C.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus flavigularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11790A45176906. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T11790A45176906.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, et al., p. 291
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus tolai". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41308A45193447. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41308A45193447.en.
- ^ Dharmani, Aarti (2000). "Lepus callotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Brown, D. E.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus callotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11792A45177499. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T11792A45177499.en.
- ^ Verts, Carraway, p. 142
- ^ Brown, D. E.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus townsendii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41288A45189364. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41288A45189364.en.
- ^ Ng, Jarita (2011). "Lepus oiostolus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus oiostolus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41283A45188432. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41283A45188432.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, et al., p. 292
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Lepus yarkandensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11796A115103994. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T11796A45178274.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 222
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus comus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41278A45187160. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41278A45187160.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, et al., p. 287
- ^ Hoedl, Amanda (2012). "Nesolagus timminsi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Tilker, A.; Timmins, R. J.; Nguyen The Truong, A.; Coudrat, C. N. Z.; Gray, T.; Le Trong Trai, Willcox; D. H. A., Abramov; A. V., Wilkinson; N., Steinmetz; R. (2019). "Nesolagus timminsi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41209A45181925. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41209A45181925.en.
- ^ McCarthy, J.; Holden, J.; Martyr, D.; McCarthy, K. (2019). "Nesolagus netscheri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T14662A45178557. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T14662A45178557.en.
- ^ Tislerics, Ati (2000). "Oryctolagus cuniculus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Villafuerte, R.; Delibes-Mateos, M. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Oryctolagus cuniculus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41291A170619657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41291A170619657.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 105
- ^ Yamada, F. and Smith; A. T. (2016). "Pentalagus furnessi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T16559A45180151. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T16559A45180151.en.
- ^ Portman, Charles (2004). "Poelagus marjorita". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Poelagus marjorita". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41292A45189965. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41292A45189965.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 113
- ^ Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M. (2019). "Pronolagus saundersiae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T136713A45194657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T136713A45194657.en.
- ^ Bartel, Riley (2015). "Pronolagus randensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus randensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41294A45190258. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41294A45190258.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 109
- ^ Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus crassicaudatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41293A45190100. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41293A45190100.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 112
- ^ Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus rupestris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41295A45190415. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41295A45190415.en.
- ^ Sekine, Ryo (2000). "Pronolagus rupestris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on November 8, 2021. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 114–115
- ^ Velázquez, A.; Guerrero, J. A. (2019). "Romerolagus diazi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T19742A45180356. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T19742A45180356.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 127
- ^ Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus andinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T142541491A165117323. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T142541491A165117323.en.
- ^ Kurta, p. 96
- ^ Barry, R.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus obscurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41301A45192437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T41301A45192437.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 123
- ^ Kelly, P. A.; Lorenzo, C.; Alvarez-Castaneda, S. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus bachmani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41302A45192710. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41302A45192710.en.
- ^ Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.
- ^ Ruedas, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus gabbi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T87491157A87491160. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T87491157A87491160.en.
- ^ Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (February 9, 2017). "A Prolegomenon to the Systematics of South American Cottontail Rabbits (Mammalia, Lagomorpha Leporidae: Sylvilagus)". Miscellaneous Publications of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan. 205. ISSN 0076-8405.
- ^ Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus tapetillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T142542759A165117046. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T142542759A165117046.en.
- ^ Ruedas, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus brasiliensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T87491102A45191186. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T87491102A45191186.en.
- ^ Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus robustus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41310A165116781. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41310A165116781.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 120
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Sylvilagus audubonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41297A45190821. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41297A45190821.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 136
- ^ Mora, J. M.; Ruedas, L. and Smith; A. T. (2016). "Sylvilagus dicei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T21209A45180947. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T21209A45180947.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 138
- ^ Nielsen, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus floridanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41299A45191626. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41299A45191626.en.
- ^ Thompson, Leah (2008). "Sylvilagus palustris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ McCleery, R.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus palustris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41303A45192995. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41303A45192995.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 132
- ^ Lorenzo, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus cunicularius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21211A45181292. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T21211A45181292.en.
- ^ Feldhamer, Carlyle, Chapman, p. 104
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Sylvilagus nuttallii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41300A45192243. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41300A45192243.en.
- ^ "Mountain Cottontail – Sylvilagus nuttallii". Montana Field Guide. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Archived from the original on November 8, 2021. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- ^ Berenson, Tessa (2012). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Litvaitis, J.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21212A45181534. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21212A45181534.en.
- ^ Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus insonus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21207A45180771. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21207A45180771.en.
- ^ Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus sanctaemartae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T142642715A165117201. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T142642715A165117201.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 118
- ^ Lanier, H. C.; Nielsen, C. (2019). "Sylvilagus aquaticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41296A45190578. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41296A45190578.en.
- ^ Roszko, Annamarie (2007). "Sylvilagus aquaticus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Viswanathan, Lata (2000). "Sylvilagus graysoni". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on October 23, 2021. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Lorenzo, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus graysoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21206A45180643. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T21206A45180643.en.
- ^ Durant, P.; Guevara, M. A. (March 2001). "A new rabbit species (Sylvilagus, Mammalia: Leporidae) from the lowlands of Venezuela". Revista de Biología Tropical. 49 (1).
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus varynaensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41311A45193972. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41311A45193972.en.
Sources
- Feldhamer, George A.; Thompson, Bruce Carlyle; Chapman, Joseph A. (2003). Wild Mammals of North America. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-7416-1.
- Kingdon, Jonathan (2015). The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (Second ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4729-2531-2.
- Kurta, Allen (1995). Mammals of the Great Lakes Region. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-06497-7.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Johnston, Charlotte H.; Alves, Paolo C.; Hackländer, Klaus, eds. (2018). Lagomorphs: Pikas, Rabbits, and Hares of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-1-4214-2340-1.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan; Hoffmann, Robert S.; Lunde, Darrin; MacKinnon, John; Wilson, Don E.; Wozencraft, W. Chris, eds. (2010). A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-3411-2.
- Verts, B. J.; Carraway, Leslie N. (1998). Land Mammals of Oregon. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21199-5.
- Hoffmann, Robert S.; Smith, Andrew T. (2005). Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
























































